
Processes
Processes

Outline contemporary computer systems allow multiple programs to be loaded into memory and executed concurrently A system therefore consists of a collection of processes (a program in execution):operating system processes executing system code and user processes executing user code. ·Process Concept ·Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication Examples of IPC Systems Communication in Client-Server Systems*
Outline • contemporary computer systems allow multiple programs to be loaded into memory and executed concurrently • A system therefore consists of a collection of processes (a program in execution): operating system processes executing system code and user processes executing user code. • Process Concept • Process Scheduling • Operations on Processes • Interprocess Communication • Examples of IPC Systems • Communication in Client-Server Systems*

Process Concept A process is an instance of a program in execution. Batch systems work in terms of "jobs".Many modern process concepts are still expressed in terms of jobs,(e.g.job scheduling ) and the two terms are often used interchangeably
Process Concept • A process is an instance of a program in execution. • Batch systems work in terms of "jobs". Many modern process concepts are still expressed in terms of jobs, ( e.g. job scheduling ), and the two terms are often used interchangeably
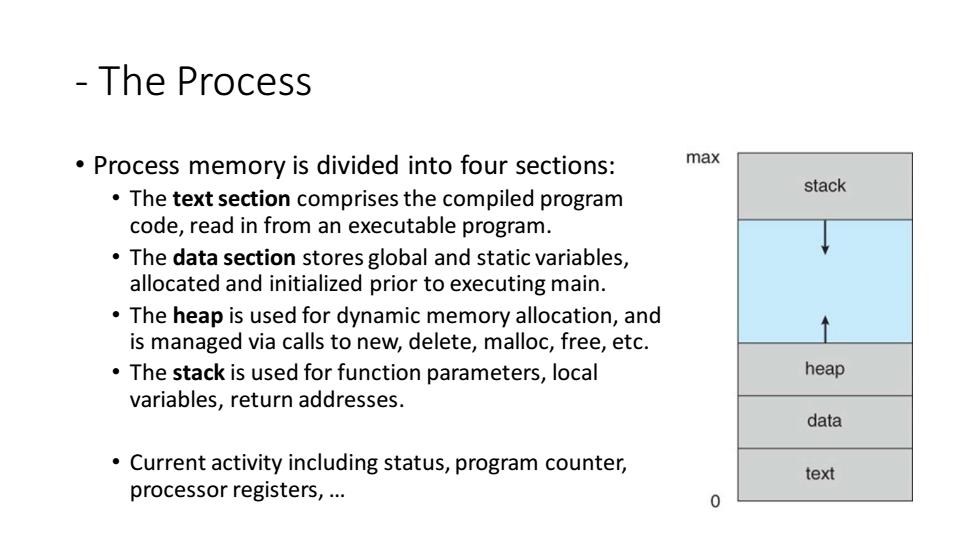
The Process Process memory is divided into four sections: max stack The text section comprises the compiled program code,read in from an executable program. The data section stores global and static variables, allocated and initialized prior to executing main. The heap is used for dynamic memory allocation,and is managed via calls to new,delete,malloc,free,etc. The stack is used for function parameters,local heap variables,return addresses. data Current activity including status,program counter, text processor registers,... 0
- The Process • Process memory is divided into four sections: • The text section comprises the compiled program code, read in from an executable program. • The data section stores global and static variables, allocated and initialized prior to executing main. • The heap is used for dynamic memory allocation, and is managed via calls to new, delete, malloc, free, etc. • The stack is used for function parameters, local variables, return addresses. • Current activity including status, program counter, processor registers, …

When processes are swapped out of CPU and later restored, additional information must also be stored and restored.Key among them are the program counter and the value of all program registers
• When processes are swapped out of CPU and later restored, additional information must also be stored and restored. Key among them are the program counter and the value of all program registers