
Operating-System Structures
Operating-System Structures

Outline Operating System Services User Operating System Interface ·System Calls ·Types of System Calls ·System Programs Operating System Design and Implementation Operating System Structure Operating System Debugging Operating System Generation ·System Boot
Outline • Operating System Services • User Operating System Interface • System Calls • Types of System Calls • System Programs • Operating System Design and Implementation • Operating System Structure • Operating System Debugging • Operating System Generation • System Boot
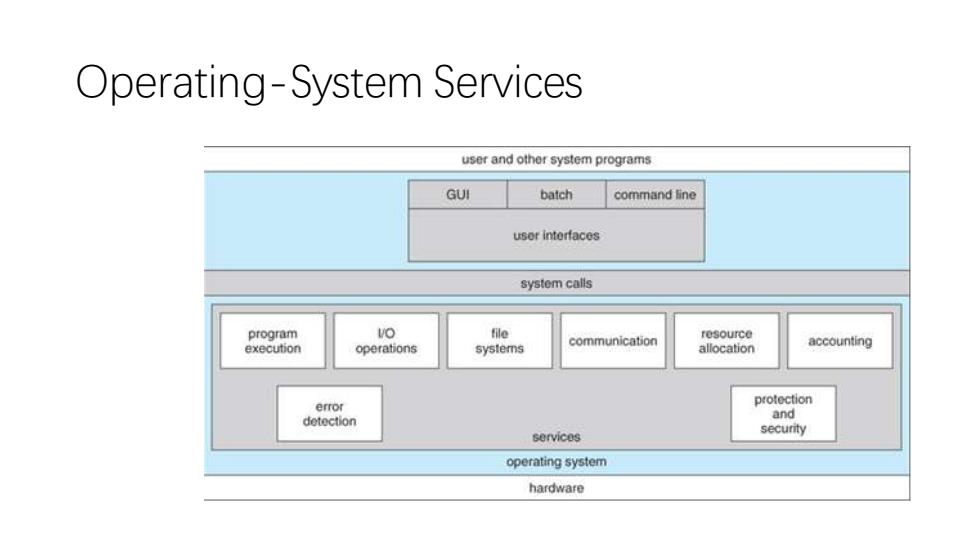
Operating-System Services user and other system programs GUI batch command line usor interfaces system calls program VO file resource communication execution operations systems allocation accounting error protection detection and secunty services operating system hardware
Operating-System Services

User Interfaces -Means by which users can issue commands to the system. a command-line interface e.g.sh,csh,ksh,tcsh,etc.) a GUl interface e.g.Windows,X-Windows,KDE,Gnome,etc. or a batch command systems.The latter are generally older systems using punch cards of job-control language,JCL,but may still be used today for specialty systems designed for a single purpose
• User Interfaces - Means by which users can issue commands to the system. • a command-line interface ( e.g. sh, csh, ksh, tcsh, etc. ), • a GUI interface ( e.g. Windows, X-Windows, KDE, Gnome, etc. ) • or a batch command systems. The latter are generally older systems using punch cards of job-control language, JCL, but may still be used today for specialty systems designed for a single purpose

Program Execution-The OS must be able to load a program into RAM,run the program,and terminate the program,either normally or abnormally.(process lifecycle) 1/O Operations -The OS is responsible for transferring data to and from 1/O devices,including keyboards,terminals,printers,and storage devices. File-System Manipulation -In addition to raw data storage,the OS is also responsible for maintaining directory and subdirectory structures,mapping file names to specific blocks of data storage, and providing tools for navigating and utilizing the file system
• Program Execution - The OS must be able to load a program into RAM, run the program, and terminate the program, either normally or abnormally.(process lifecycle) • I/O Operations - The OS is responsible for transferring data to and from I/O devices, including keyboards, terminals, printers, and storage devices. • File-System Manipulation - In addition to raw data storage, the OS is also responsible for maintaining directory and subdirectory structures, mapping file names to specific blocks of data storage, and providing tools for navigating and utilizing the file system