
Digitizing conventional films Conventional radiographic images can be converted into digital information by a "digitizer",and therefore electronically stored Such a conversion also allows some numerical post-processing Such a technique cannot be considered as a"digital radiologytechnique. IAEA 20:Digital Radiology 11
IAEA 20: Digital Radiology 11 Digitizing conventional films Conventional radiographic images can be converted into digital information by a “digitizer”, and therefore electronically stored Such a conversion also allows some numerical post-processing Such a technique cannot be considered as a “ digital radiology” technique

IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Part 20:Digital Radiology Topic 2:Basic concepts IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency
IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency Part 20: Digital Radiology Topic 2: Basic concepts IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
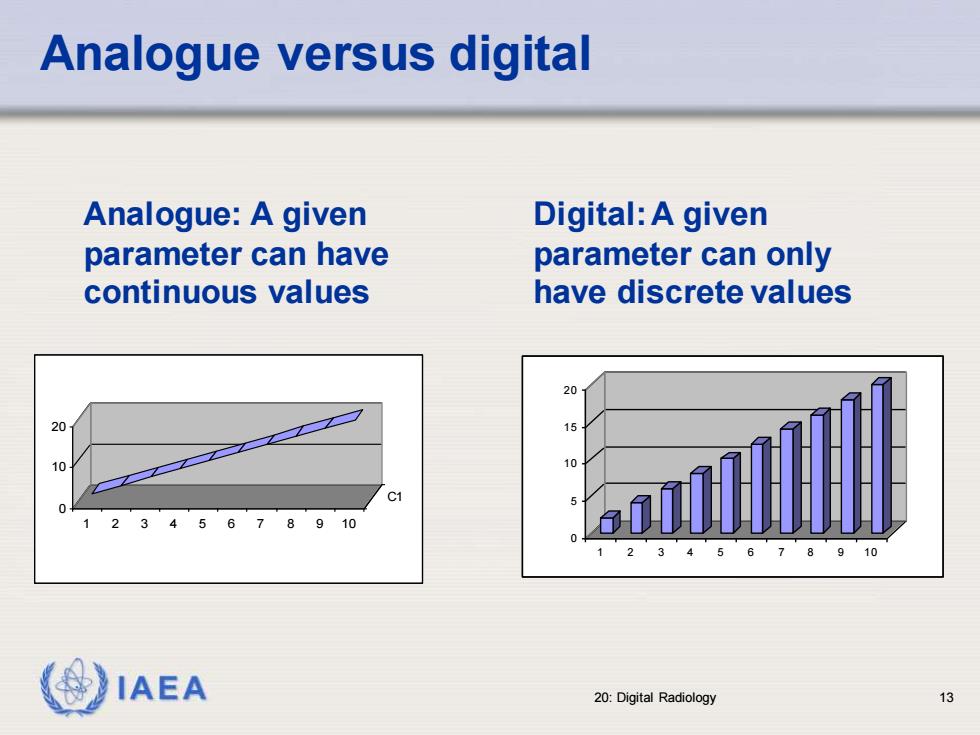
Analogue versus digital Analogue:A given Digital:A given parameter can have parameter can only continuous values have discrete values 20 10 10 IAEA 20:Digital Radiology 13
IAEA 20: Digital Radiology 13 Analogue versus digital 0 5 1 0 1 5 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 Digital: A given parameter can only have discrete values Analogue: A given parameter can have continuous values 0 10 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 C1

What is digital radiology? In conventional radiographic images,spatial position and blackening are analogue values Digital radiology uses a matrix to represent an image G了 A matrix is a square or rectangular area divided into rows and columns.The smallest element of a matrix is called "pixel" Each pixel of the matrix is used to store the individual grey levels of an image,which are represented by positive integer numbers The location of each pixel in a matrix is encoded by its row and column number(x,y) IAEA 20:Digital Radiology 14
IAEA 20: Digital Radiology 14 What is digital radiology? In conventional radiographic images, spatial position and blackening are analogue values Digital radiology uses a matrix to represent an image A matrix is a square or rectangular area divided into rows and columns. The smallest element of a matrix is called ”pixel” Each pixel of the matrix is used to store the individual grey levels of an image, which are represented by positive integer numbers The location of each pixel in a matrix is encoded by its row and column number (x,y)
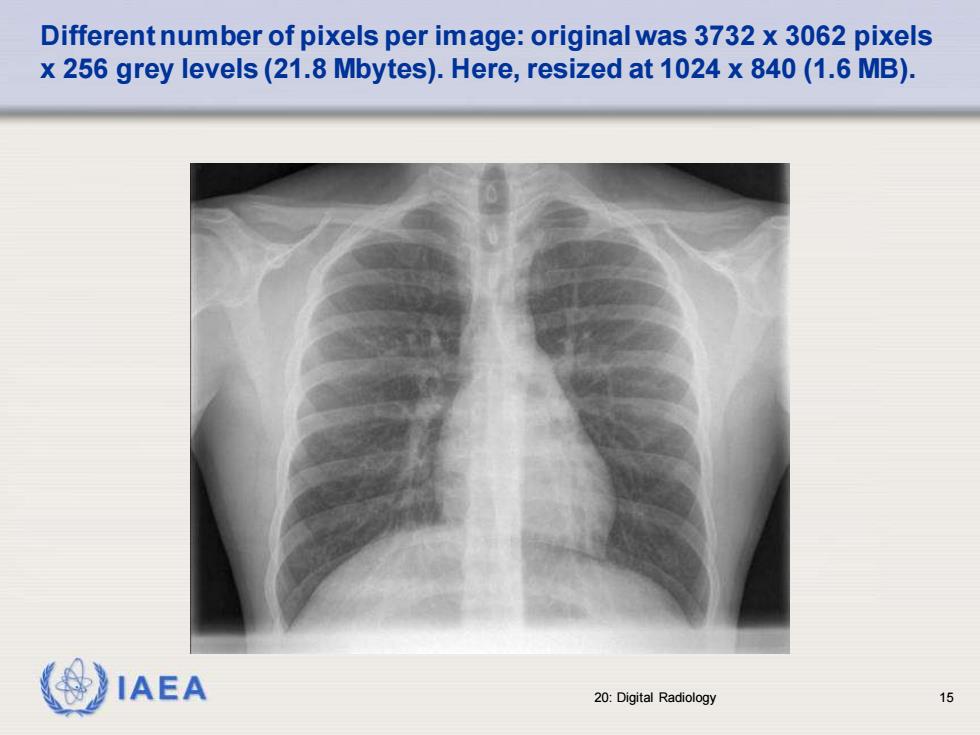
Differentnumber of pixels per image:original was 3732 x 3062 pixels x 256 grey levels(21.8 Mbytes).Here,resized at 1024 x 840(1.6 MB). IAEA 20:Digital Radiology 15
IAEA 20: Digital Radiology 15 Different number of pixels per image: original was 3732 x 3062 pixels x 256 grey levels (21.8 Mbytes). Here, resized at 1024 x 840 (1.6 MB)