
Syllabus of Thermodynamics and Statistic Physics) 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Thermodynamics and Statistical 课程代码 PHYS3127 Physics 课程性质 Degree course 授课对象 Physics (International Class) 学分 3 Credits 学时 72 Classes 主讲教师Tianhui Zhang 修订日期 Sep.2021 指定教材 S.J.Blundell and K.K.Blundell,(Concepts in thermal physics),Oxfor University Press,2006. 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: The objective of this course is to provide third-or fourth year physics students with a solid introduction to the classical and statistical theories of thermodynamics.In this course.students are supposed to achieve a full knowledge about the theoretical frame ork of the classic th nodynamies,and how the phenomenon can (二)课程目标: Objective 1:Understand the macroscopic properties of thermal systems.Have a full knowledge about the general principles and the relations between state functions and state variables Objective 2:Develop a clear understanding and firm grasp of the basic principles of statistical physics.Develop some necessary skills to work with probability theory. Objective 3:Have a full and clear picture about the historic development of thermodynamics.Develop an intuitive feel out the vay to explore an d find out the underlying principles of phenomenon.Be able to think and solve scientific problems independently. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系 1
1 Syllabus of 《Thermodynamics and Statistic Physics》 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics 课程代码 PHYS3127 课程性质 Degree course 授课对象 Physics (International Class) 学 分 3 Credits 学 时 72 Classes 主讲教师 Tianhui Zhang 修订日期 Sep. 2021 指定教材 S. J. Blundell and K. K. Blundell,《Concepts in thermal physics》,Oxford University Press,2006. 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: The objective of this course is to provide third-or fourth year physics students with a solid introduction to the classical and statistical theories of thermodynamics. In this course, students are supposed to achieve a full knowledge about the theoretical framework of the classic thermodynamics, and how the macroscopic phenomenon can be understood with the microscopic properties of the components. (二)课程目标: Objective 1: Understand the macroscopic properties of thermal systems. Have a full knowledge about the general principles and the relations between state functions and state variables Objective 2:Develop a clear understanding and firm grasp of the basic principles of statistical physics. Develop some necessary skills to work with probability theory. Objective 3:Have a full and clear picture about the historic development of thermodynamics. Develop an intuitive feel about the way to explore and find out the underlying principles of phenomenon. Be able to think and solve scientific problems independently. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系
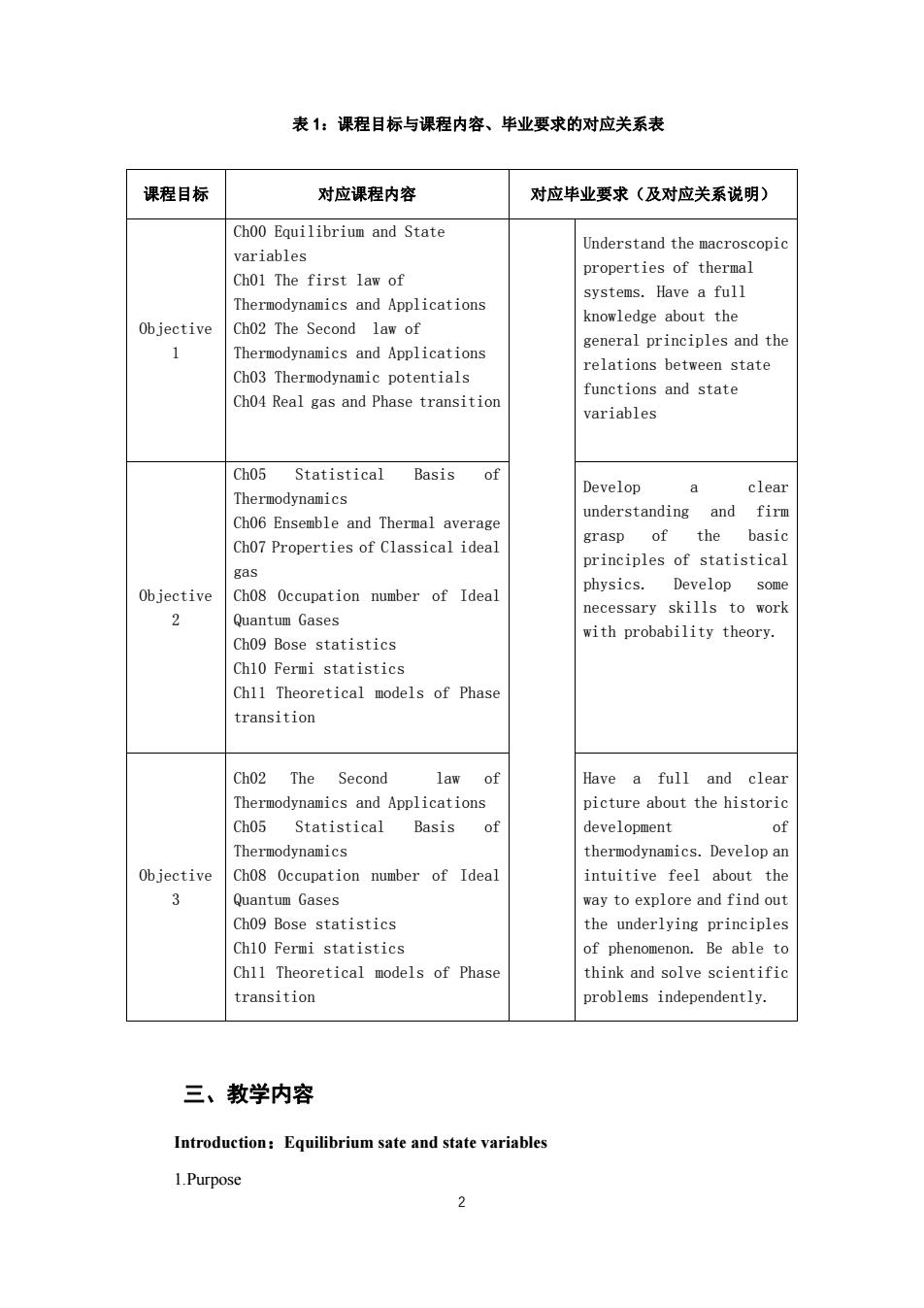
表1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求(及对应关系说明) Ch00 Equilibrium and State Understand the macroscopic variables properties of thermal Chol The first law of systems.Have a full Thermodynamics and Applications Objective Ch02 The Second law knowledge about the general principles and the Thermodynamics and Applications Ch03 Thermodynamic potentials relations between state functions and state Ch04 Real gas and Phase transition variables Ch05 Statistical Basis Develop clear Thermodynamics Ch06 Ensemble and Thermal average understanding and firm grasp of the basic Cho7 Properties of classical ideal principles of statistical Objective physics. 2 Quantum Gases necessary skills to work with probability theory. Ch09 Bose statistics Ch10 Fermi statistics Ch11 Theoretical models of Phas transition Ch02 The Second law of Have a full and clear Thermodynamics and applications picture about the historic Cho5 Basis of developmen o odynamics thermodynamics.Develop ar Objective Ch08 Occupation number of Ideal intuitive feel about the 3 I Quantum Gases way to explore and find out Ch09 Bose statistics the underlving principles Ch10 Fermi statistics of phenomenon.Be able to Chl1 Theoretical models of Phase think and solve scientifi transition problems independently. 三、教学内容 Introduction:Equilibrium sate and state variables 1.Purpose 2
2 表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 三、教学内容 Introduction:Equilibrium sate and state variables 1.Purpose 课程目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求(及对应关系说明) Objective 1 Ch00 Equilibrium and State variables Ch01 The first law of Thermodynamics and Applications Ch02 The Second law of Thermodynamics and Applications Ch03 Thermodynamic potentials Ch04 Real gas and Phase transition Understand the macroscopic properties of thermal systems. Have a full knowledge about the general principles and the relations between state functions and state variables Objective 2 Ch05 Statistical Basis of Thermodynamics Ch06 Ensemble and Thermal average Ch07 Properties of Classical ideal gas Ch08 Occupation number of Ideal Quantum Gases Ch09 Bose statistics Ch10 Fermi statistics Ch11 Theoretical models of Phase transition Develop a clear understanding and firm grasp of the basic principles of statistical physics. Develop some necessary skills to work with probability theory. Objective 3 Ch02 The Second law of Thermodynamics and Applications Ch05 Statistical Basis of Thermodynamics Ch08 Occupation number of Ideal Quantum Gases Ch09 Bose statistics Ch10 Fermi statistics Ch11 Theoretical models of Phase transition Have a full and clear picture about the historic development of thermodynamics. Develop an intuitive feel about the way to explore and find out the underlying principles of phenomenon. Be able to think and solve scientific problems independently

Understand the basic concepts of thermodynamics 2.Key points Equilibrium state;Reversible process 3.Content Equilibrium state:State variables,Work 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment Chapter 1 The Frist law and Applications 1.Purpose Understand the First law and solve simple problems with it 2.Key points: Mathematical forms of the first law and the limitation for different forms. 3.Content 3.1 The first law Internal energy;heat and work. 3.2 Isothermal process of ideal gas Ideal gas,isothermal expansion of ideal gas 3.3 Adiabatic process of ideal gas Adiabatic equation of ideal gas 4.Teachingmethod Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment Chapter 2 The second law and entropy 1.Purpose Understand properties of Carnot cycle:Develop a full picture of the definition of the
3 Understand the basic concepts of thermodynamics 2.Key points: Equilibrium state; Reversible process 3.Content Equilibrium state;State variables; Work 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 1 The Frist law and Applications 1.Purpose Understand the First law and solve simple problems with it. 2.Key points: Mathematical forms of the first law and the limitation for different forms. 3.Content 3.1 The first law Internal energy; heat and work. 3.2 Isothermal process of ideal gas Ideal gas; isothermal expansion of ideal gas 3.3 Adiabatic process of ideal gas Adiabatic equation of ideal gas 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 2 The second law and entropy 1.Purpose Understand properties of Carnot cycle; Develop a full picture of the definition of the

efficiency of engine:Understand the different statements of the second law. 2.Key points Statement of the second law,entropy 3.Content 3.1 Carnot cycle Work and heat in each step of Camnot cycle 3.2 The second law Statements of the second law 3.3 Reversible engine: Efficiency of reversible engines 3.4 Entropy: Definition of entropy 3.5 Application of the second law: The change of entropy in reversible processes.the entropy of dieal gas 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter3 Thermodynamic potentials 1.Purpose Understand the definitions and their roles of thermodynamic potentials 2.Key points: Enthalpy;Free energy:Maxwell relations 3.Content 3.1 Thermodynamically potentials: Internal energy.entropy.Free energ 3.2 Maxwell relations: Derive the Maxwell relations 4.Teaching method
4 efficiency of engine; Understand the different statements of the second law. 2.Key points: Statement of the second law; entropy 3.Content 3.1 Carnot cycle Work and heat in each step of Carnot cycle 3.2 The second law Statements of the second law 3.3 Reversible engine; Efficiency of reversible engines 3.4 Entropy; Definition of entropy; 3.5 Application of the second law; The change of entropy in reversible processes; the entropy of dieal gas 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 3 Thermodynamic potentials 1.Purpose Understand the definitions and their roles of thermodynamic potentials 2.Key points: Enthalpy; Free energy; Maxwell relations 3.Content 3.1 Thermodynamically potentials: Internal energy; entropy; Free energy 3.2 Maxwell relations; Derive the Maxwell relations。 4.Teaching method

Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 4 Real gas and phase transition 1.Purpose Understand the limitations of ideal gas model:develop a deep understanding of phase transitions 2Key points Gibbs's phase rule;Maxwell construction 3.Content 3.1 van der Waals'equation of state: Effect of Attraction on pressure 3.2 Phase diagram of real gas: Maxwell construction of phase diagram;types of phase transitions: 3.3 Clausius-Clapeyron Equation Boundaries between phases 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 5 Statistical Basis of Thermodynamics 1.Purpose Develop a deep understanding of the kinetic theory of macroscopic systems.Establish a bridge between classic thermodynamics and statistic theory 2.Key points Microscopic state,Statistical explanation of entropy 3.Content 3.1 Microscopic state:
5 Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 4 Real gas and phase transition 1.Purpose Understand the limitations of ideal gas model; develop a deep understanding of phase transitions 2.Key points: Gibbs's phase rule; Maxwell construction 3.Content 3.1 van der Waals' equation of state: Effect of Attraction on pressure 3.2 Phase diagram of real gas; Maxwell construction of phase diagram; types of phase transitions; 3.3 Clausius–Clapeyron Equation Boundaries between phases 4.Teaching method Talk and discussion 5.Evaluation Assignment. Chapter 5 Statistical Basis of Thermodynamics 1.Purpose Develop a deep understanding of the kinetic theory of macroscopic systems; Establish a bridge between classic thermodynamics and statistic theory. 2.Key points: Microscopic state; Statistical explanation of entropy 3.Content 3.1 Microscopic state: