
Mutagens While the spontaneous rate of mutation is very low,there are a variety of chemical,physical, or biological agents that can increase the mutation rate,and are therefore said to induce mutations.These agents are referred to as mutagens
While the spontaneous rate of mutation is very low, there are a variety of chemical, physical, or biological agents that can increase the mutation rate, and are therefore said to induce mutations. These agents are referred to as mutagens. Mutagens
8.2 Genetic recombination Genetic recombination is the process by which genetic elements contained in two separate genomes are brought together in one unit. This mechanism may enable the organism to carry out some new functions and result in adaptation to changing environments. Genetic recombination usually involves much larger changes.Entire genes,sets of genes,or even whole chromosomes,are transferred between organisms
Genetic recombination is the process by which genetic elements contained in two separate genomes are brought together in one unit. This mechanism may enable the organism to carry out some new functions and result in adaptation to changing environments. Genetic recombination usually involves much larger changes. Entire genes, sets of genes, or even whole chromosomes, are transferred between organisms. 8.2 Genetic recombination

A number of prokaryotes have been found to be naturally transformable certain species of G+and G Bacteria some species of Archaea However,even within transformable genera,only certain strains or species are transformable
A number of prokaryotes have been found to be naturally transformable • certain species of G+ and G- Bacteria • some species of Archaea However, even within transformable genera, only certain strains or species are transformable
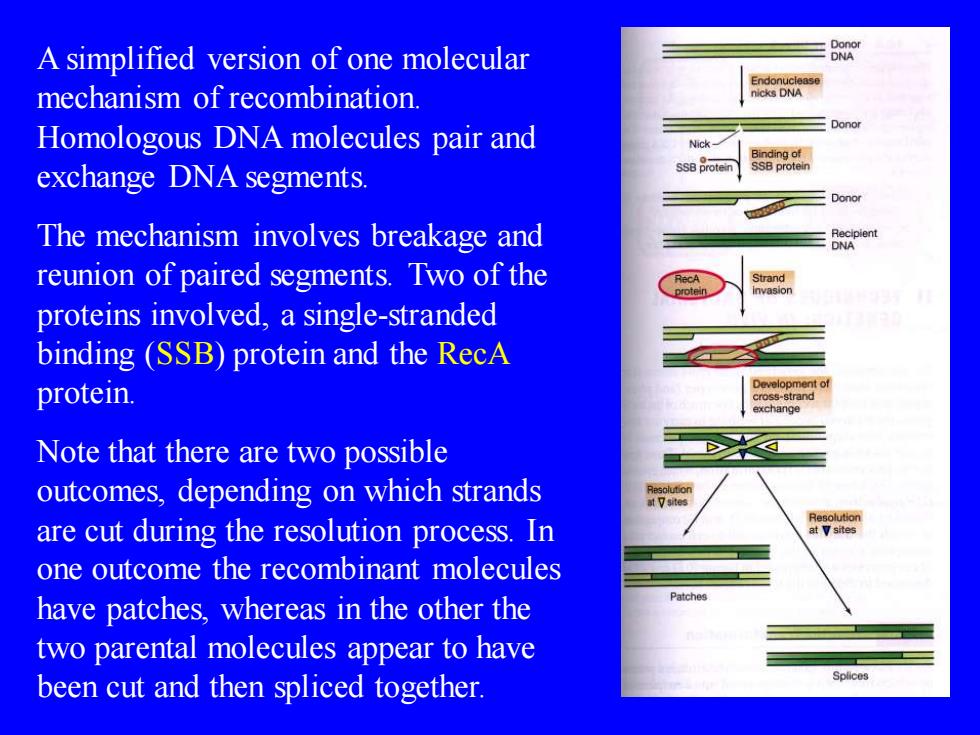
A simplified version of one molecular NA Endonuclease mechanism of recombination. nicks DNA Homologous DNA molecules pair and Nick- Binding of exchange DNA segments. SSB protein SSB protein -Donor The mechanism involves breakage and reunion of paired segments.Two of the RecA proteins involved,a single-stranded binding (SSB)protein and the RecA protein. Note that there are two possible outcomes,depending on which strands are cut during the resolution process.In one outcome the recombinant molecules Patche have patches,whereas in the other the two parental molecules appear to have been cut and then spliced together. Splices
A simplified version of one molecular mechanism of recombination. Homologous DNA molecules pair and exchange DNA segments. The mechanism involves breakage and reunion of paired segments. Two of the proteins involved, a single-stranded binding (SSB) protein and the RecA protein. Note that there are two possible outcomes, depending on which strands are cut during the resolution process. In one outcome the recombinant molecules have patches, whereas in the other the two parental molecules appear to have been cut and then spliced together

Detection of Recombination Recombinants must be phenotypically different from the parents. selectable characteristics For instance,the recipient may not be able to grow on a particular medium,and genetic recombinants are selected that can. selectable and nonselectable markers such as drug resistance,nutritional requirements. and so on
Recombinants must be phenotypically different from the parents. Detection of Recombination ❖ selectable characteristics For instance, the recipient may not be able to grow on a particular medium, and genetic recombinants are selected that can. ❖ selectable and nonselectable markers such as drug resistance, nutritional requirements, and so on