
cMSc5706TopicsinTheoreticalcoMputerScience wek1法Qat如me0mpig Instructor:Shengyu Zhang 1
Instructor: Shengyu Zhang 1

Roadmap Intro to math model of quantum mechanics Review of quantum algorithms The power of quantum computers. 。Quantum games
Roadmap • Intro to math model of quantum mechanics • Review of quantum algorithms • The power of quantum computers. • Quantum games
Postulate 1:States State space:Every isolated physical system corresponds to a unit vector in a complex vector space. -Unit vector:2-norm is 1. Such states are called pure states. ·Ve use a weird“ket"notation'〉to denote such a state
Postulate 1: States • State space: Every isolated physical system corresponds to a unit vector in a complex vector space. – Unit vector: ℓ2 -norm is 1. • Such states are called pure states. • We use a weird “ket” notation ⋅ to denote such a state
Ket notation ·Mathematically,〉is a column vector. ·And(is a row vector. ·yΦ)is the inner product between the vectorsΦ)andlψ). ·〈ylMlψ〉is just the quadratic formψrMp
Ket notation • Mathematically, ⋅ is a column vector. • And ⋅ is a row vector. • 𝜓 𝜙 is the inner product between the vectors 𝜙 and 𝜓 . • 𝜓 𝑀 𝜓 is just the quadratic form 𝜓 𝑇𝑀𝜓
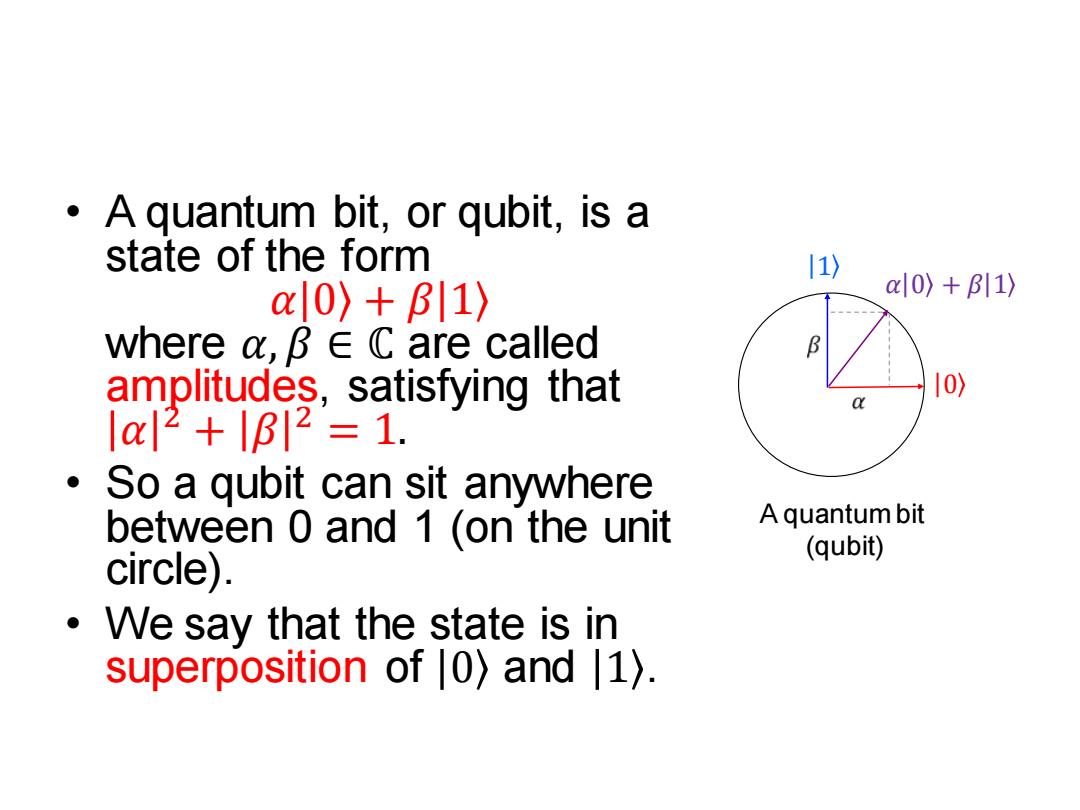
A quantum bit,or qubit,is a state of the form 11) 0〉+B11〉 a0)+B11)》 where a,B∈C are called amplitudes,satisfying that 10)》 |2+lB12=1. 。 So a qubit can sit anywhere between 0 and 1 (on the unit A quantum bit (qubit) circle). We say that the state is in superposition of |0)and 1)
• A quantum bit, or qubit, is a state of the form 𝛼 0 + 𝛽 1 where 𝛼, 𝛽 ∈ ℂ are called amplitudes, satisfying that 𝛼 2 + 𝛽 2 = 1. • So a qubit can sit anywhere between 0 and 1 (on the unit circle). • We say that the state is in superposition of 0 and 1 . A quantum bit (qubit) 𝛼 0 + 𝛽 1 0 1