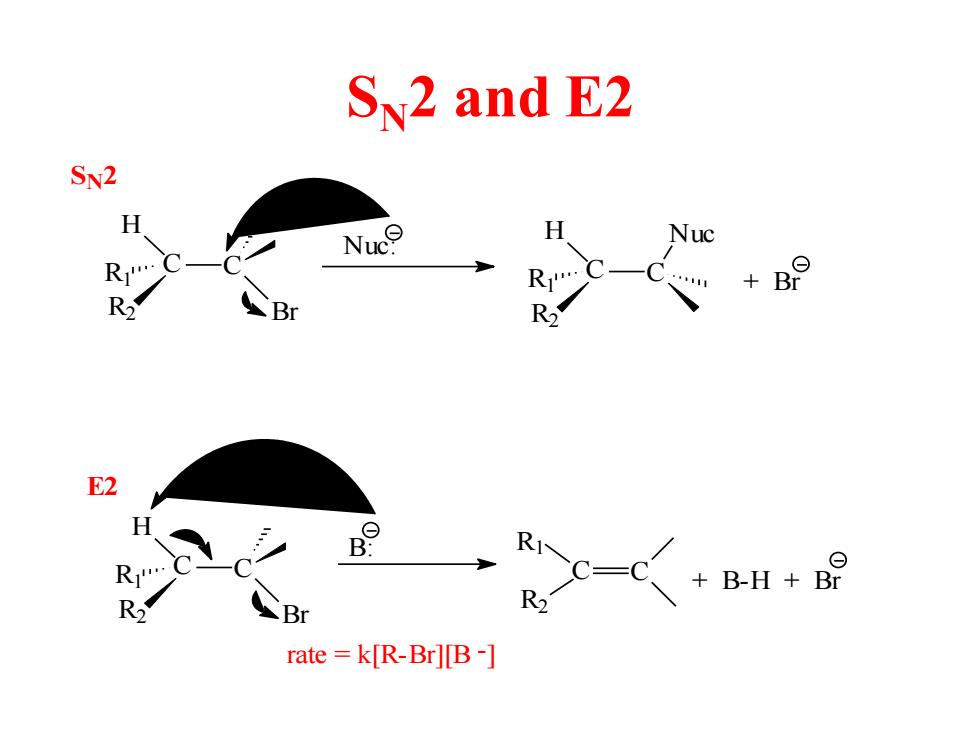
SN2 and E2 SN2 H Nuc H Nuc R R Br R Br R E2 RI B-H Br R R Br rate =k[R-Br][B-]
SN2 and E2 C C Br H R2 R1 R1 R2 H C Nuc C Nuc: + Br R1 R2 H C Br C C C R2 B: R1 + B-H + Br rate = k[R-Br][B -] SN2 E2
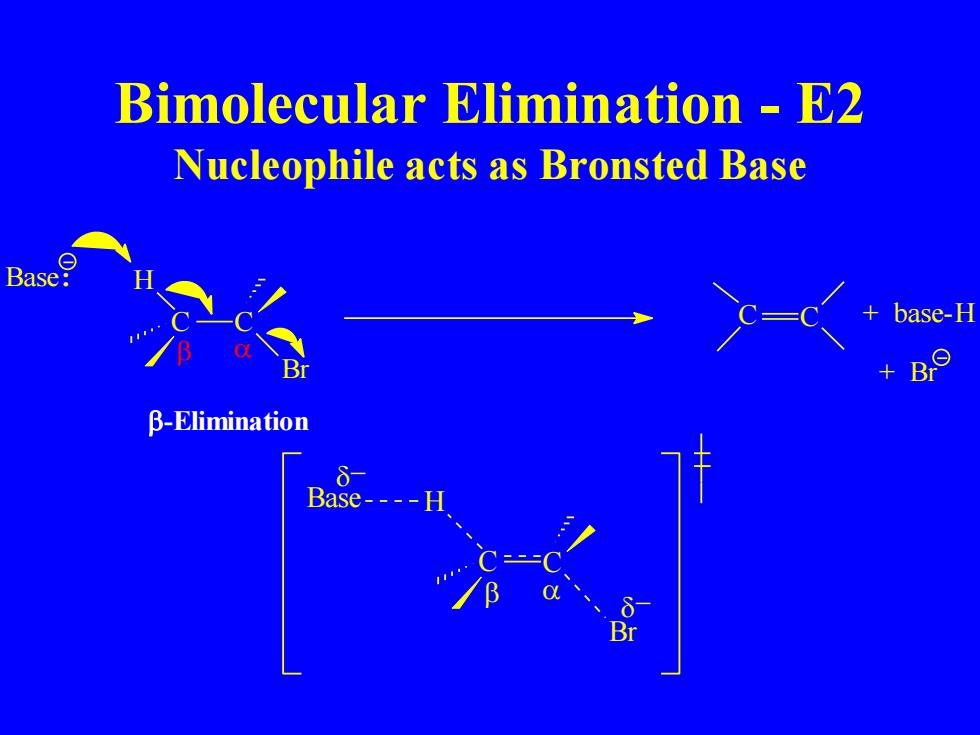
Bimolecular Elimination E2 Nucleophile acts as Bronsted Base Base: base-H B-Elimination Base---- Br
Bimolecular Elimination - E2 Nucleophile acts as Bronsted Base C C Br Base: H -Elimination C C + base-H + Br − − C C Br Base H
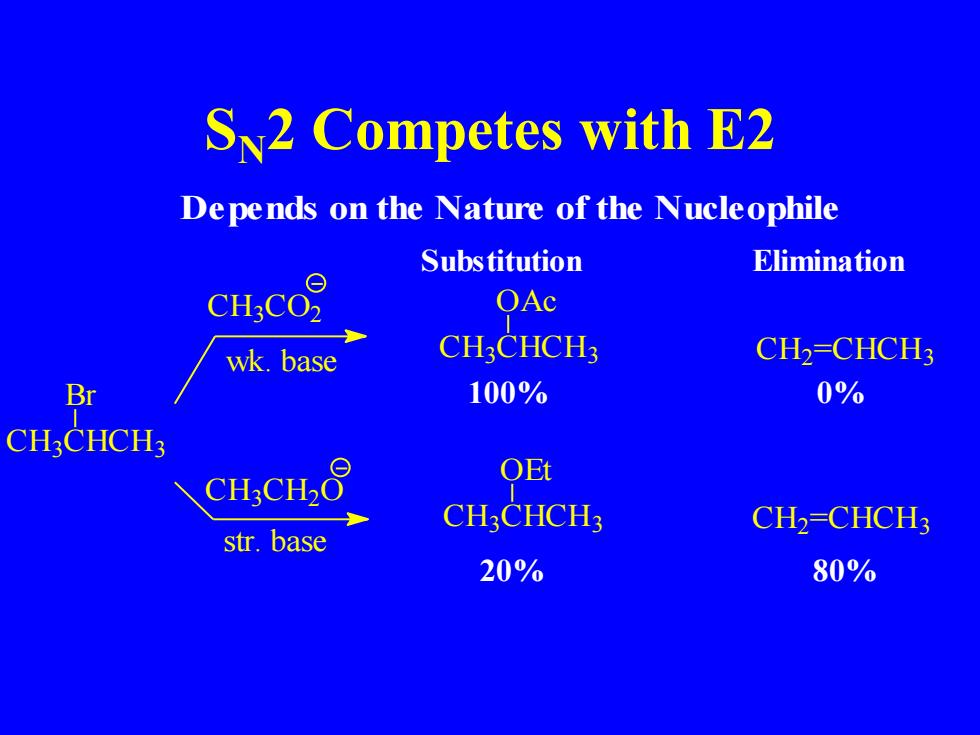
Sv2 Competes with E2 Depends on the Nature of the Nucleophile Substitution Elimination CH:CO2 OAc wk.base CH:CHCH3 CH2=CHCH3 Br 100% 0% CHCHCH3 CH3CH2O QEt CH:CHCH3 CH2=CHCH3 str.base 20% 80%
SN2 Competes with E2 C H3 CHCH3 Br C H3 C O2 wk. base C H3 C H2 O Substitution Elimination OAc C H3 CHCH3 OEt C H3 CHCH3 str. base C H2 =CHCH3 C H2 =CHCH3 100% 0% 20% 80% Depends on the Nature of the Nucleophile
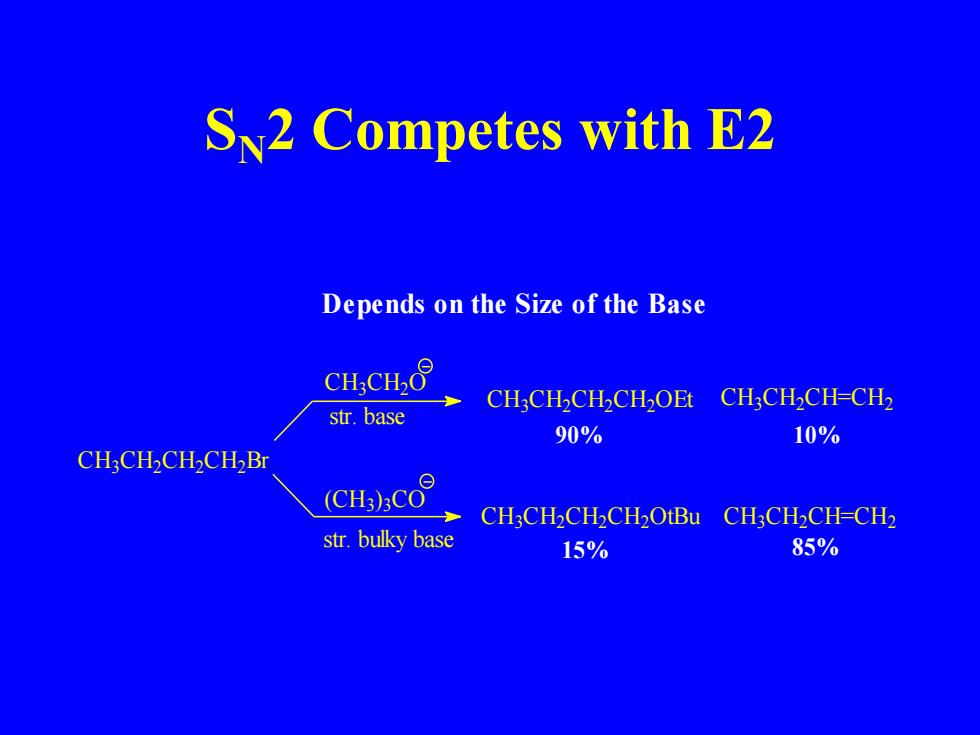
S2 Competes with E2 Depends on the Size of the Base CH:CH2O CH;CH2CH2CH2OEt CH3CH2CH-CH2 str.base 90% 10% CH:CH2CH2CH2Br (CH:)CO CH3CH2CH2CH2OtBu CH3CH2CH-CH2 str.bulky base 15% 85%
SN2 Competes with E2 15% 90% 10% C H3C H2C H2C H2Br C H3C H2O (CH3)3C O str. bulky base str. base C H3C H2CH=CH2 C H3C H2CH=CH2 C H3C H2C H2C H2OEt C H3C H2C H2C H2OtBu 85% Depends on the Size of the Base
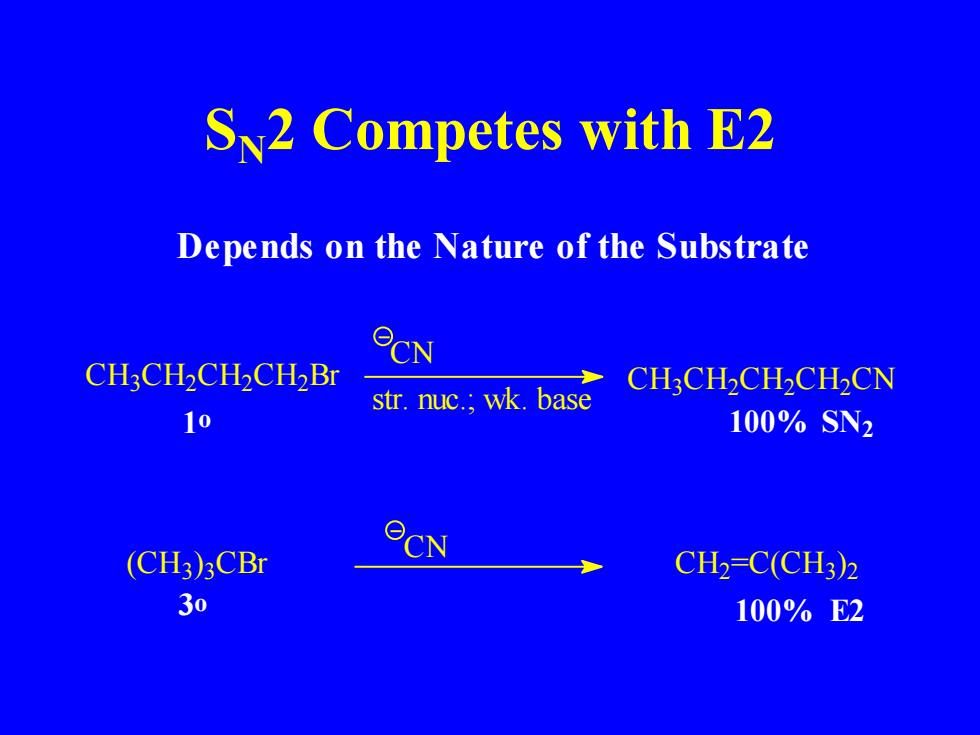
S2 Competes with E2 Depends on the Nature of the Substrate CH3CH2CH2CH2Br CN CH3CH2CH2CH2CN str.nuc.;wk.base 10 100%SN2 CN (CH3)3CBr CH2=C(CH3)2 30 100%E2
SN2 Competes with E2 C H3 C H2 C H2 C H2 Br C N C H3 C H2 C H2 C H2 C N 1o 100% (CH3) 3 CBr C N C H2 =C(CH3) 2 100% E2 SN2 3o str. nuc.; wk. base Depends on the Nature of the Substrate