Nabothian cysts Normal cervix on the cervix Cervical polyps A0A则 Sagittal view As viewed through a speculum ADAM

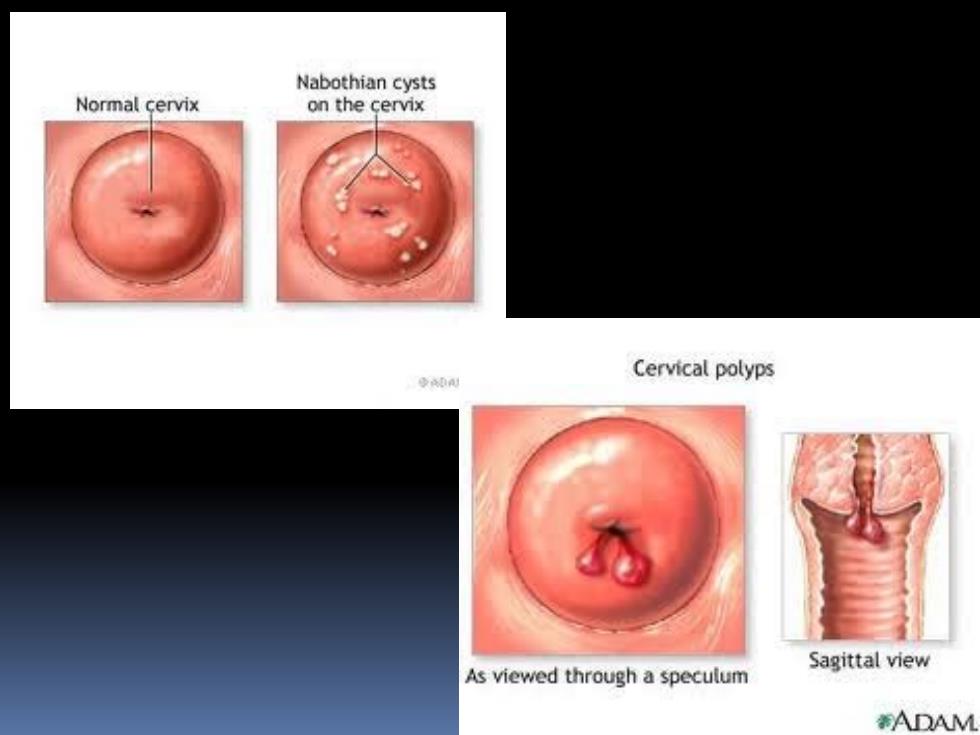
Clinical Features There is increase in amount of mucus secretion and discharge (leukorrhes) Cervix appear reddish,or congestive Its surface may be granular
Clinical Features There is increase in amount of mucus secretion and discharge (leukorrhes) Cervix appear reddish, or congestive Its surface may be granular

Il.Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cervical Carcinoma Cervical carcinoma,despite dramatic improvements in early diagnosis and treatment,continues to be one of the major causes of cancer-related deaths in women,particularly in the developing world But the widespread use of Papanicolaou (cytologic) screening of women has dramatically lowered the incidence of invasive tumors By contrast,the incidence of precursor cervical intraepithelial neoplasia(CIN)has increased
II. Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cervical Carcinoma Cervical carcinoma, despite dramatic improvements in early diagnosis and treatment, continues to be one of the major causes of cancer-related deaths in women, particularly in the developing world But the widespread use of Papanicolaou (cytologic) screening of women has dramatically lowered the incidence of invasive tumors By contrast, the incidence of precursor cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) has increased

Pathogenesis Trauma injury and chronic inflammation will predispose to regeneration of cervical epithelium,may lead to the development of carcinoma -Chemical carcinogen such as smegma of the partner may be carcinogenic Virus infection HPV -16,18,31,33 is believed to be closely related to development of carcinoma."high risk"(inactivation of P53, RB and activation of Cyclin E)
Pathogenesis Trauma injury and chronic inflammation will predispose to regeneration of cervical epithelium, may lead to the development of carcinoma Chemical carcinogen such as smegma of the partner may be carcinogenic Virus infection HPV -16, 18, 31, 33 is believed to be closely related to development of carcinoma. “high risk” (inactivation of P53, RB and activation of Cyclin E)

Prominent risk factors for the development of CIN and invasive carcinoma are as follows Early age at first intercourse Multiple sexual partners A male partner with multiple previous sexual partners Persistent infection by "high-risk"papillomaviruses
Prominent risk factors for the development of CIN and invasive carcinoma are as follows Early age at first intercourse Multiple sexual partners A male partner with multiple previous sexual partners Persistent infection by "high-risk" papillomaviruses