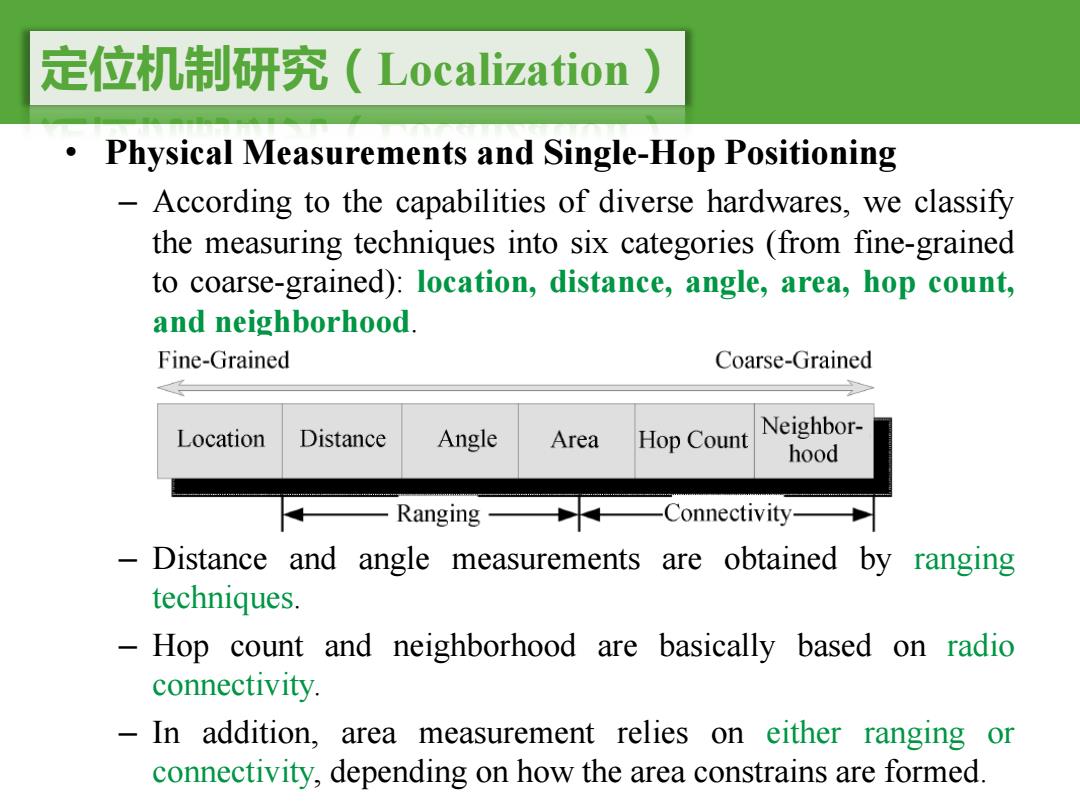
定位机制研究(Localization .Physical Measurements and Single-Hop Positioning According to the capabilities of diverse hardwares,we classify the measuring techniques into six categories (from fine-grained to coarse-grained):location,distance,angle,area,hop count, and neighborhood. Fine-Grained Coarse-Grained Location Distance Angle Area Hop Count Neighbor- hood Ranging Connectivity- Distance and angle measurements a are obtained by ranging techniques. Hop count and neighborhood are basically based on radio connectivity. -In addition, area measurement relies on either ranging or connectivity,depending on how the area constrains are formed
定位机制研究(Localization) • Physical Measurements and Single-Hop Positioning – According to the capabilities of diverse hardwares, we classify the measuring techniques into six categories (from fine-grained to coarse-grained): location, distance, angle, area, hop count, and neighborhood. – Distance and angle measurements are obtained by ranging techniques. – Hop count and neighborhood are basically based on radio connectivity. – In addition, area measurement relies on either ranging or connectivity, depending on how the area constrains are formed
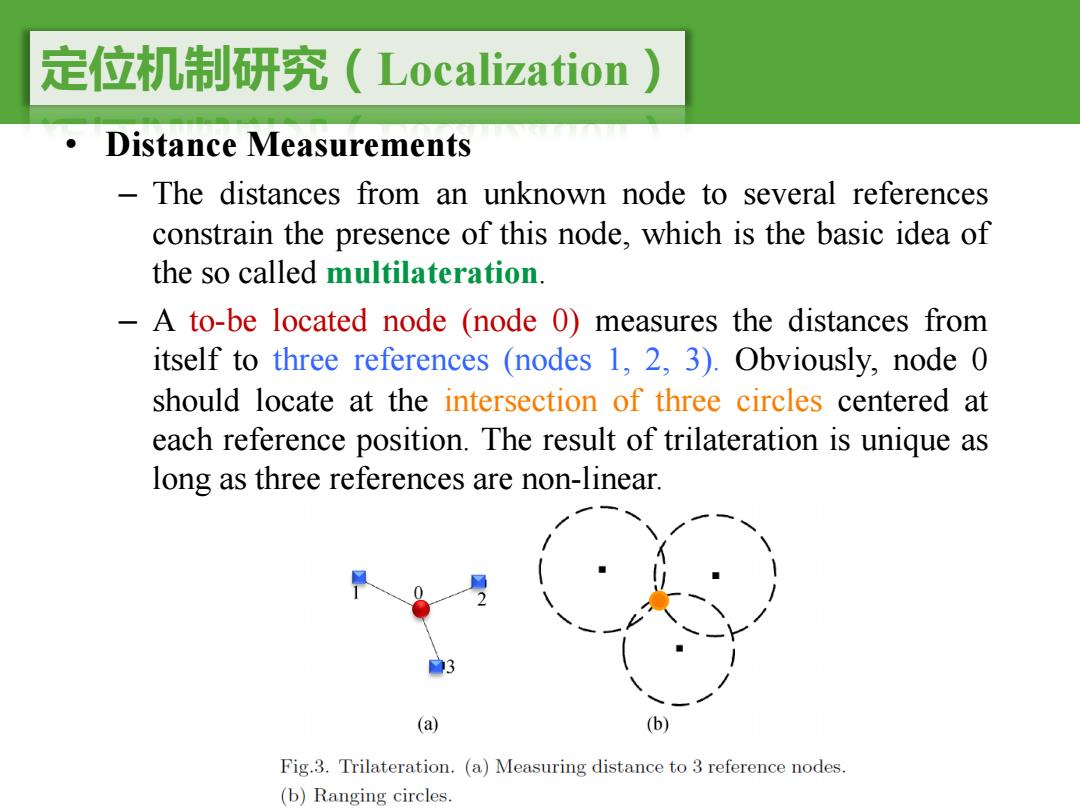
定位机制研究(Localization Distance Measurements The distances from an unknown node to several references constrain the presence of this node,which is the basic idea of the so called multilateration. -A to-be located node (node 0)measures the distances from itself to three references (nodes 1,2,3).Obviously,node 0 should locate at the intersection of three circles centered at each reference position.The result of trilateration is unique as long as three references are non-linear. (a) (b) Fig.3.Trilateration.(a)Measuring distance to 3 reference nodes. (b)Ranging circles
定位机制研究(Localization) • Distance Measurements – The distances from an unknown node to several references constrain the presence of this node, which is the basic idea of the so called multilateration. – A to-be located node (node 0) measures the distances from itself to three references (nodes 1, 2, 3). Obviously, node 0 should locate at the intersection of three circles centered at each reference position. The result of trilateration is unique as long as three references are non-linear
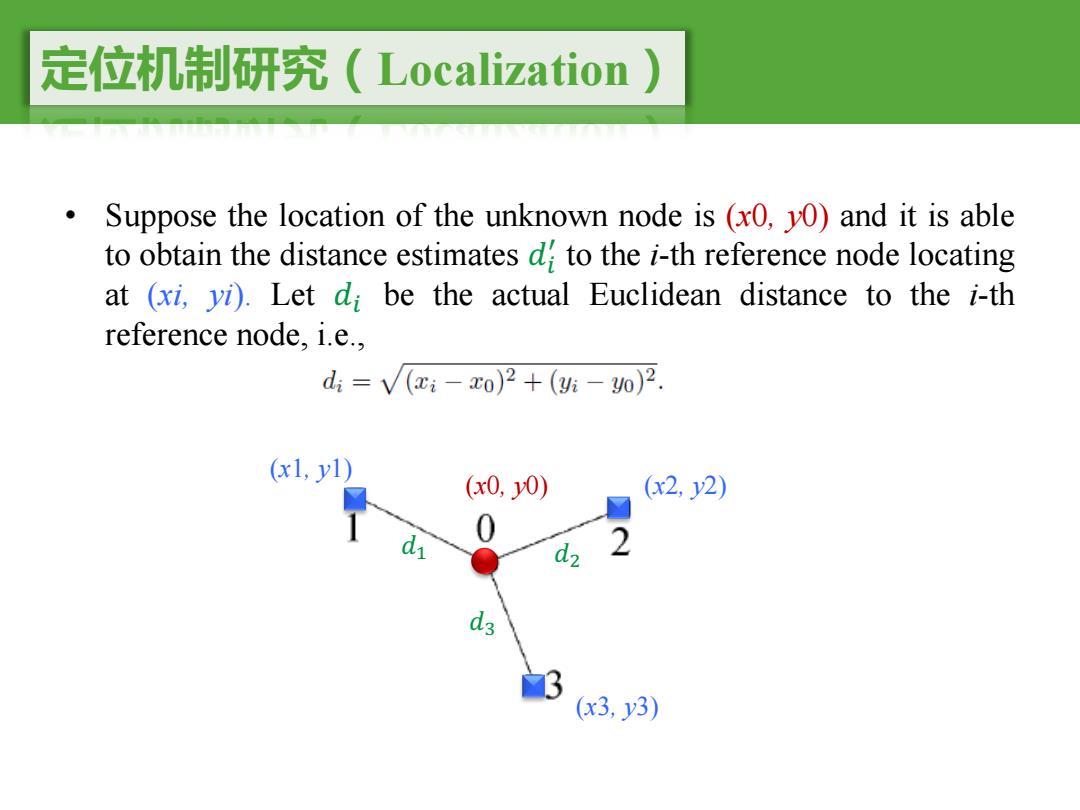
定位机制研究(Localization) Suppose the location of the unknown node is (x0,y0)and it is able to obtain the distance estimates d to the i-th reference node locating at (xi,vi).Let di be the actual Euclidean distance to the i-th reference node,i.e., d:=√(c-x0)2+(-o)2. (x1,y1) (x0,0) (x2,y2) 0 d d2 2 (x3,y3)
定位机制研究(Localization) • Suppose the location of the unknown node is (x0, y0) and it is able to obtain the distance estimates �" # to the i-th reference node locating at (xi, yi). Let �" be the actual Euclidean distance to the i-th reference node, i.e., (x0, y0) (x1, y1) (x3, y3) (x2, y2) �$ �% �&
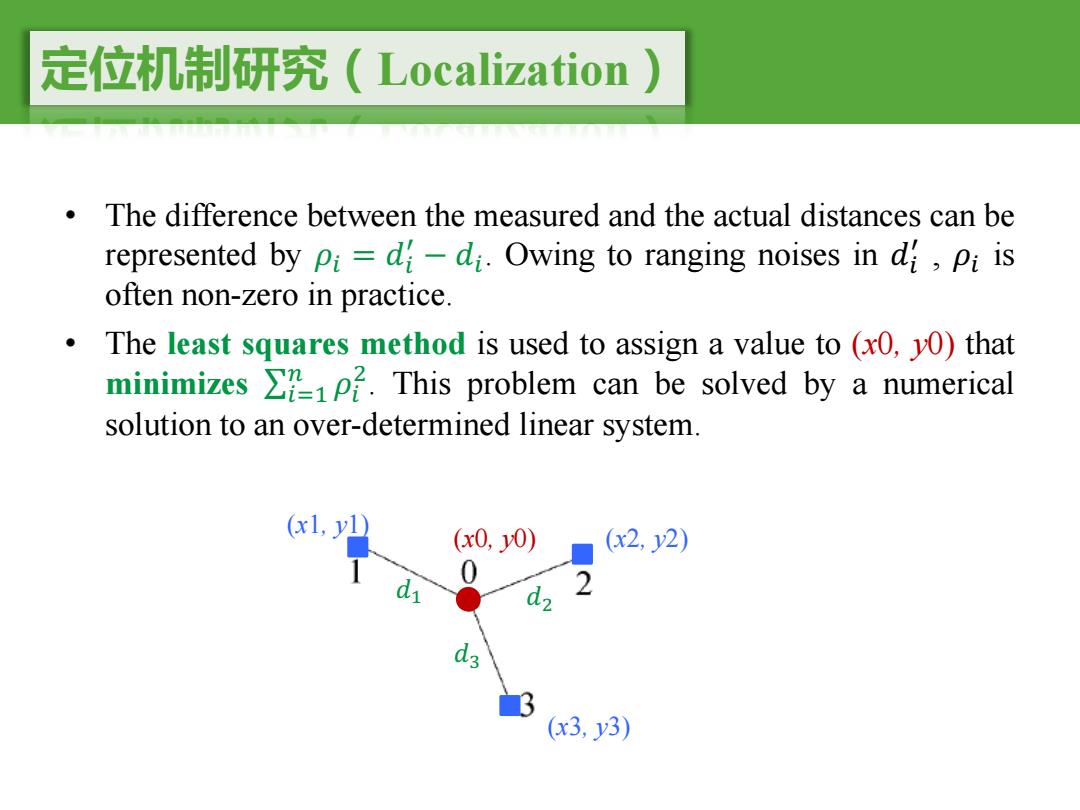
定位机制研究(Localization) The difference between the measured and the actual distances can be represented by pi=d-di.Owing to ranging noises in d,pi is often non-zero in practice. The least squares method is used to assign a value to (xO,yO)that minimizes >21P2.This problem can be solved by a numerical solution to an over-determined linear system. (x0,y0) (x2,y2) 0 d2 2 d3 (x3,y3)
定位机制研究(Localization) • The difference between the measured and the actual distances can be represented by �" = �" # − �". Owing to ranging noises in �" # , �" is often non-zero in practice. • The least squares method is used to assign a value to (x0, y0) that minimizes ∑"+$ , �" %. This problem can be solved by a numerical solution to an over-determined linear system. (x0, y0) (x1, y1) (x3, y3) (x2, y2) �$ �% �&

定位机制研究(Localization So far,for distance-based positioning,the only thing omitted is how to measure distances in the physical world.Many ranging techniques are proposed and developed;among them,the radio signal strength based and time based ranging are two of the most widely used ones in existing designs. (a)Radio Signal Strength Based Distance Measurement Radio Signal Strength(RSS)based ranging techniques are based on the fact that the strength of radio signal diminishes during propagation. -In theory,radio signal strengths diminish with distance according to a power law.A generally employed model for wireless radio propagation is as follows:
定位机制研究(Localization) • So far, for distance-based positioning, the only thing omitted is how to measure distances in the physical world. Many ranging techniques are proposed and developed; among them, the radio signal strength based and time based ranging are two of the most widely used ones in existing designs. • (a) Radio Signal Strength Based Distance Measurement – Radio Signal Strength (RSS) based ranging techniques are based on the fact that the strength of radio signal diminishes during propagation. – In theory, radio signal strengths diminish with distance according to a power law. A generally employed model for wireless radio propagation is as follows: