IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN ▣802.11b ▣802.11a o 2.4-5 GHz unlicensed o 5-6 GHz range radio spectrum o up to 54 Mbps o up to 11 Mbps 口802.11g o direct sequence spread spectrum(DSSS)in o 2.4-5 GHz range physical layer o up to 54 Mbps ·all hosts use same ▣All use CSMA/CA for chipping code multiple access o widely deployed,using All have base-station base stations and ad-hoc network versions 6:Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-16
6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-16 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN 802.11b 2.4-5 GHz unlicensed radio spectrum up to 11 Mbps direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) in physical layer • all hosts use same chipping code widely deployed, using base stations 802.11a 5-6 GHz range up to 54 Mbps 802.11g 2.4-5 GHz range up to 54 Mbps All use CSMA/CA for multiple access All have base-station and ad-hoc network versions
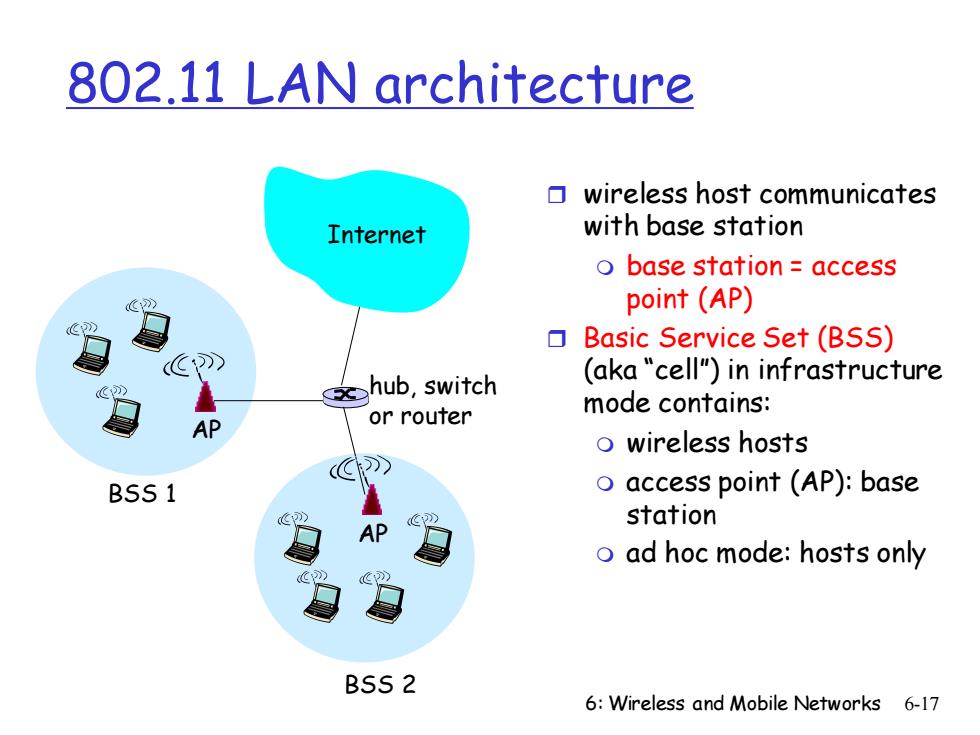
802.11 LAN architecture wireless host communicates Internet with base station o base station access point(AP) Basic Service Set(BSS) 文hub,switch (aka "cell")in infrastructure mode contains: AP or router o wireless hosts BSS1 o access point (AP):base station o ad hoc mode:hosts only BSS2 6:Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-17
6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-17 802.11 LAN architecture wireless host communicates with base station base station = access point (AP) Basic Service Set (BSS) (aka “cell”) in infrastructure mode contains: wireless hosts access point (AP): base station ad hoc mode: hosts only BSS 1 BSS 2 Internet hub, switch or router AP AP
802.11:Channels,association 802.11b:2.4GHz-2.485GHz spectrum divided into 11 channels at different frequencies o AP admin chooses frequency for AP o interference possible:channel can be same as that chosen by neighboring AP! host:must associate with an AP o scans channels,listening for beacon frames containing AP's name(SSID)and MAC address o selects AP to associate with o may perform authentication [Chapter 8] o will typically run DHCP to get IP address in AP's subnet 6:Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-18
6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-18 802.11: Channels, association 802.11b: 2.4GHz-2.485GHz spectrum divided into 11 channels at different frequencies AP admin chooses frequency for AP interference possible: channel can be same as that chosen by neighboring AP! host: must associate with an AP scans channels, listening for beacon frames containing AP’s name (SSID) and MAC address selects AP to associate with may perform authentication [Chapter 8] will typically run DHCP to get IP address in AP’s subnet
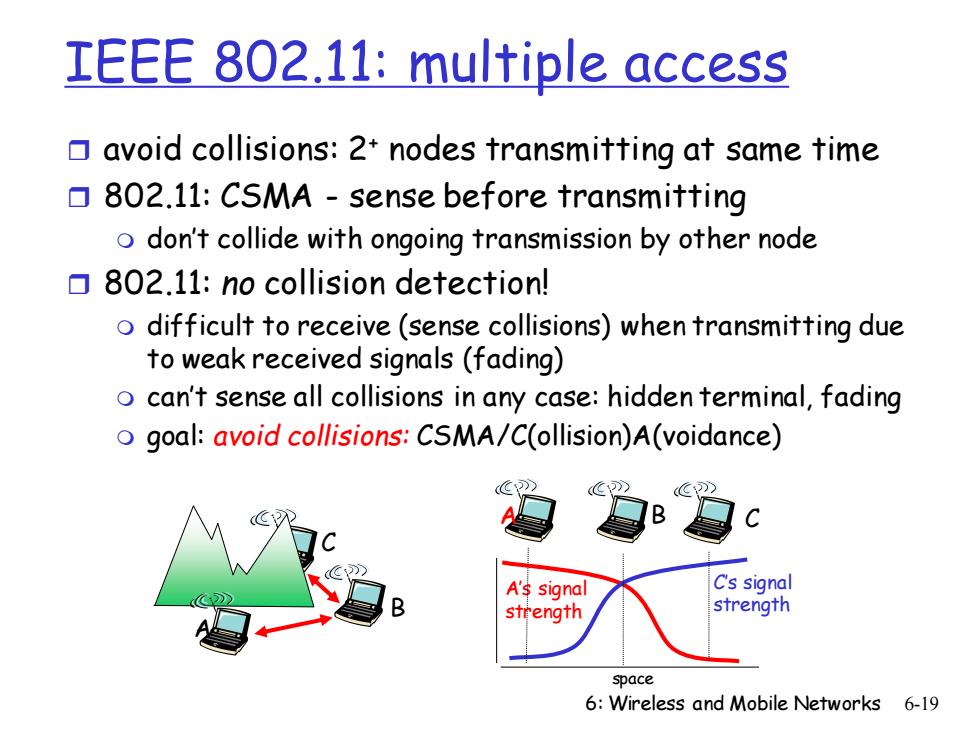
IEEE 802.11:multiple access avoid collisions:2*nodes transmitting at same time 802.11:CSMA-sense before transmitting o don't collide with ongoing transmission by other node 口802.11:no collision detection! o difficult to receive(sense collisions)when transmitting due to weak received signals (fading) o can't sense all collisions in any case:hidden terminal,fading o goal:avoid collisions:CSMA/C(ollision)A(voidance) A's signal C's signal strength strength space 6:Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-19
6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-19 IEEE 802.11: multiple access avoid collisions: 2+ nodes transmitting at same time 802.11: CSMA - sense before transmitting don’t collide with ongoing transmission by other node 802.11: no collision detection! difficult to receive (sense collisions) when transmitting due to weak received signals (fading) can’t sense all collisions in any case: hidden terminal, fading goal: avoid collisions: CSMA/C(ollision)A(voidance) A B C A B C A’s signal strength space C’s signal strength
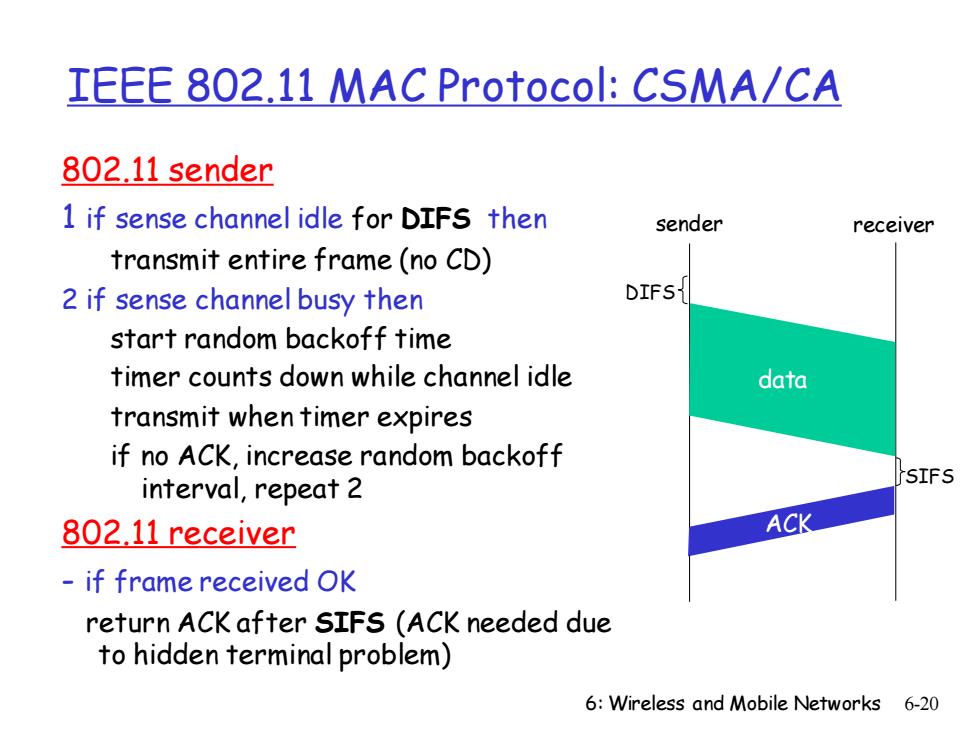
IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol:CSMA/CA 802.11 sender 1 if sense channel idle for DIFS then sender receiver transmit entire frame(no CD) 2 if sense channel busy then DIFS start random backoff time timer counts down while channel idle data transmit when timer expires if no ACK,increase random backoff interval,repeat 2 SIFS 802.11 receiver ACK if frame received OK return ACK after SIFS (ACK needed due to hidden terminal problem) 6:Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-20
6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6-20 IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol: CSMA/CA 802.11 sender 1 if sense channel idle for DIFS then transmit entire frame (no CD) 2 if sense channel busy then start random backoff time timer counts down while channel idle transmit when timer expires if no ACK, increase random backoff interval, repeat 2 802.11 receiver - if frame received OK return ACK after SIFS (ACK needed due to hidden terminal problem) sender receiver DIFS data SIFS ACK