
Brain's blood supply
Brain’s blood supply
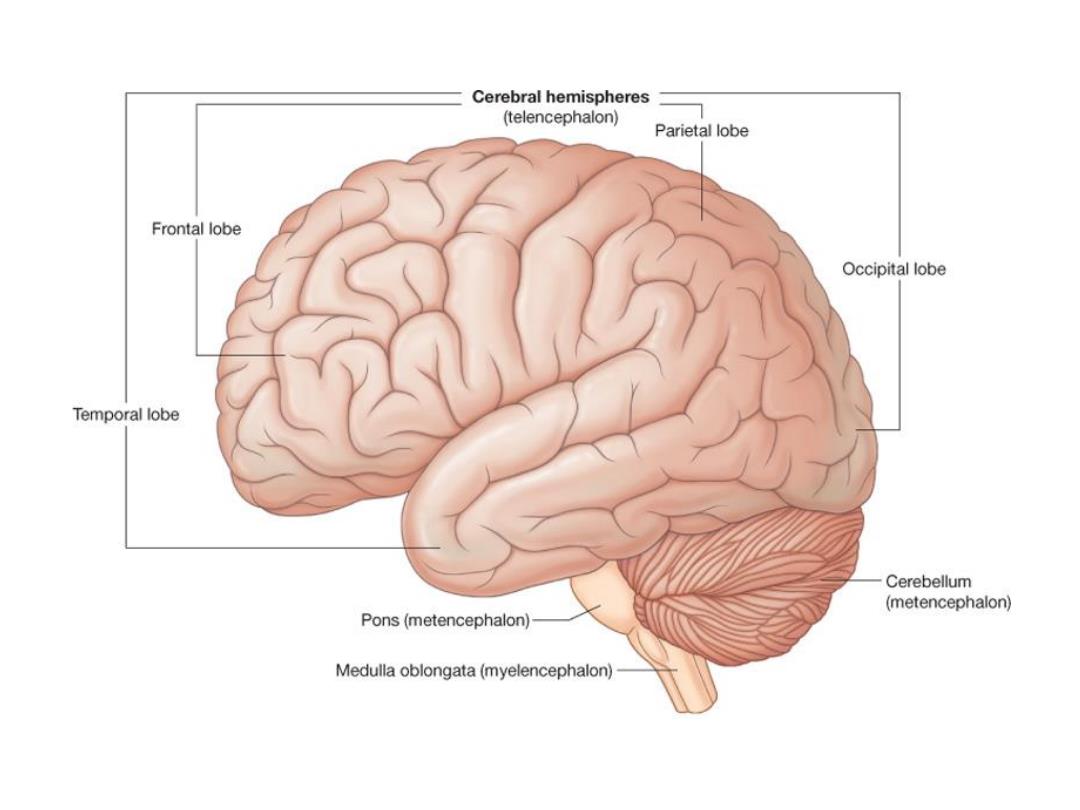
Cerebral hemispheres (telencephalon) Parietal lobe Frontal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Cerebellum (metencephalon) Pons(metencephalon) Medulla oblongata(myelencephalon)
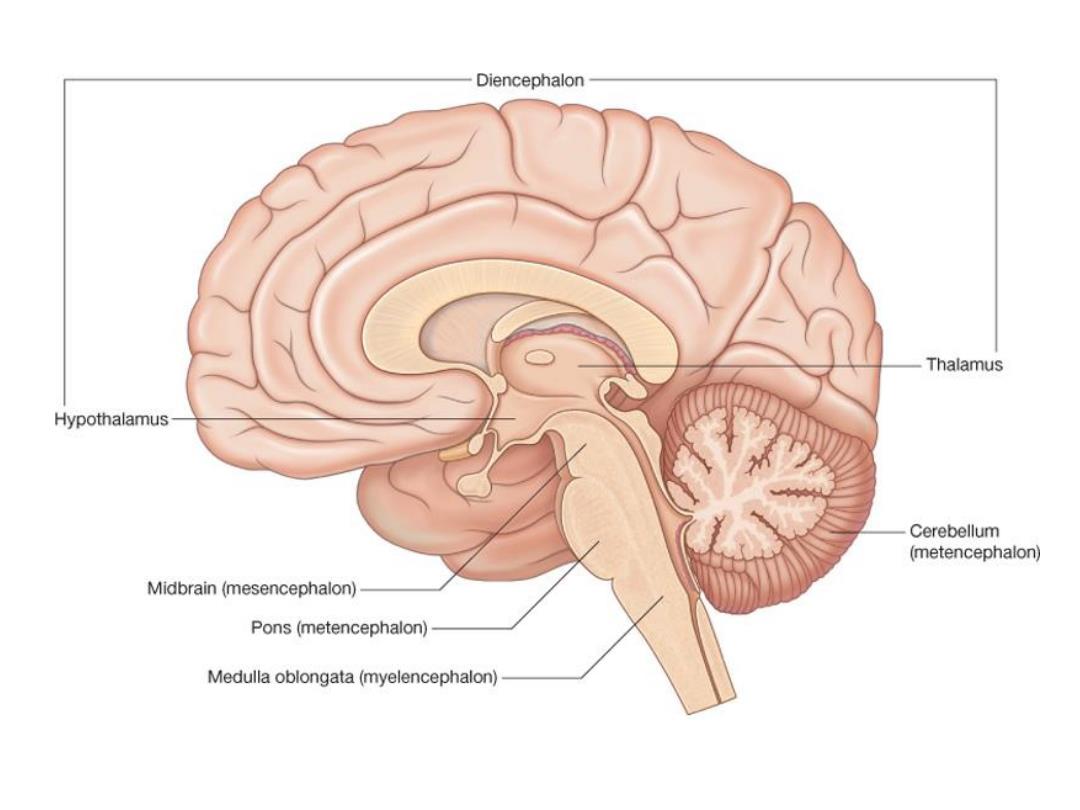
Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebellum (metencephalon) Midbrain(mesencephalon) Pons(metencephalon) Medulla oblongata(myelencephalon)
Brain’s blood supply

Anterior communicating Cerebral arterial circle Anterior cerebral Posterior Middle cerebral communicating Ophthalmic The brain receives its Posterior cerebral Basilar arterial supply from two Right internal carotid -Left internal pairs of vessels: carotid 1.vertebral artery 2.internal carotid artery Right common carotid Left vertebral Right vertebral Right subclavian Left subclavian Brachiocephalic Left common carotid Aortic arch
The brain receives its arterial supply from two pairs of vessels: 1. vertebral artery 2. internal carotid artery
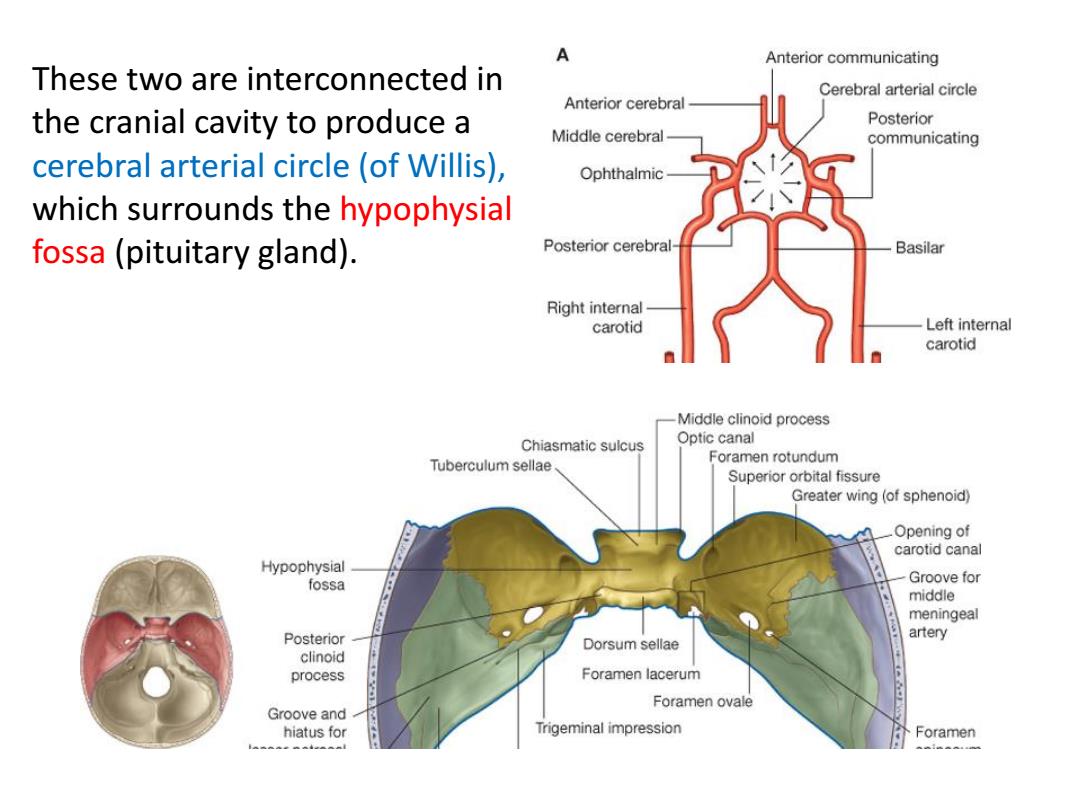
Anterior communicating These two are interconnected in Cerebral arterial circle Anterior cerebral the cranial cavity to produce a Posterior Middle cerebral communicating cerebral arterial circle (of Willis), Ophthalmic which surrounds the hypophysial fossa(pituitary gland). Posterior cerebral Basilar Right internal carotid Left internal carotid Middle clinoid process Chiasmatic sulcus Optic canal Tuberculum sellae Foramen rotundum Superior orbital fissure Greater wing (of sphenoid) .Opening of carotid canal Hypophysial Groove for tossa middle meningeal Posterior artery Dorsum sellae clinoid process Foramen lacerum Groove and Foramen ovale hiatus for Trigeminal impression Foramen
These two are interconnected in the cranial cavity to produce a cerebral arterial circle (of Willis), which surrounds the hypophysial fossa (pituitary gland)