
The result that a competitive equilibrium is economically efficient is often described as the first theorem of Welfare economics-If everyone trades in the competitive marketplace, all mutually beneficial trades will be completed and the resulting equilibrium allocation of resources will be economically efficient. ▣MRS'rc=PcPr=MRSKFC Note:MRS of clothing for food
The result that a competitive equilibrium is economically efficient is often described as the first theorem of Welfare economics-If everyone trades in the competitive marketplace, all mutually beneficial trades will be completed and the resulting equilibrium allocation of resources will be economically efficient. MRSJ FC= PC/PF = MRSK FC Note: MRS of clothing for food
Utility O1 ●L H G Ox James's Utility Utility Possibilities Frontier
Utility Possibilities Frontier

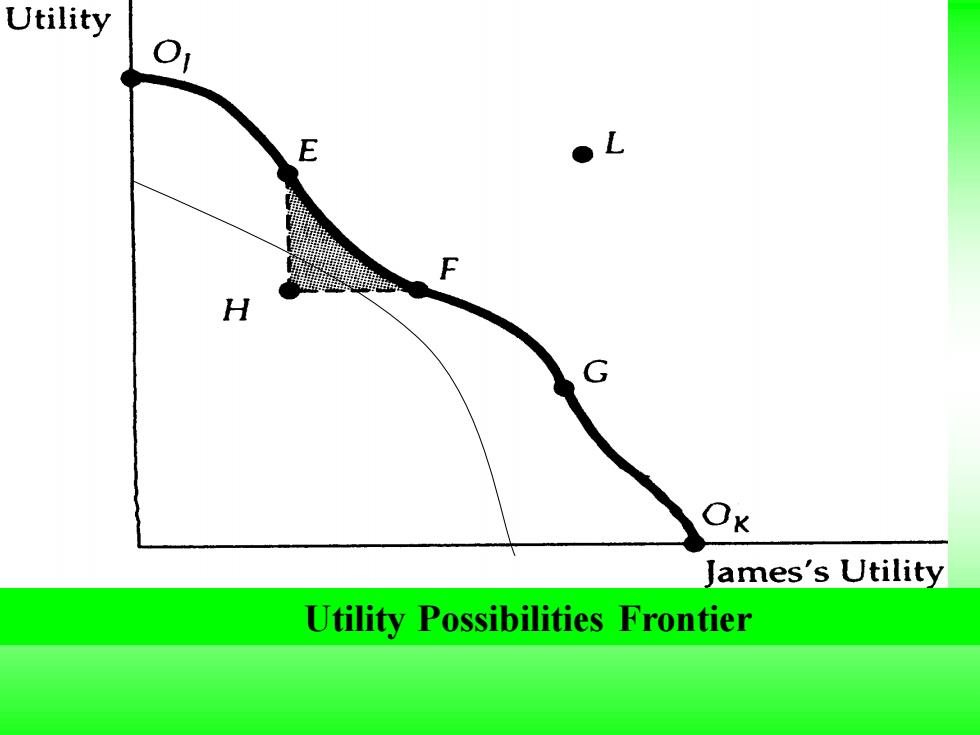
The utility possibilities frontier shows the levels of satisfaction that each of two people achieve when they have traded to an efficient outcome on the contract curve. Points E,F,and G correspond to points on the contract curve and are efficient.Point H is inefficient because any trade within the shaded area will make one or both people better off
The utility possibilities frontier shows the levels of satisfaction that each of two people achieve when they have traded to an efficient outcome on the contract curve. Points E, F, and G correspond to points on the contract curve and are efficient. Point H is inefficient because any trade within the shaded area will make one or both people better off

Utility possibilities frontier-Curve showing all efficient allocations of resources measured in terms of the utility levels of two individuals. Social welfare function-Weights applied to each individual's utility in determining what is socially desirable. The second theorem of Welfare economics-if individual preferences are convex,then every efficient allocation (every point on the contract)is a competitive equilibrium for some initial allocation of goods
Utility possibilities frontier - Curve showing all efficient allocations of resources measured in terms of the utility levels of two individuals. Social welfare function -Weights applied to each individual’s utility in determining what is socially desirable. The second theorem of Welfare economics—if individual preferences are convex, then every efficient allocation (every point on the contract) is a competitive equilibrium for some initial allocation of goods