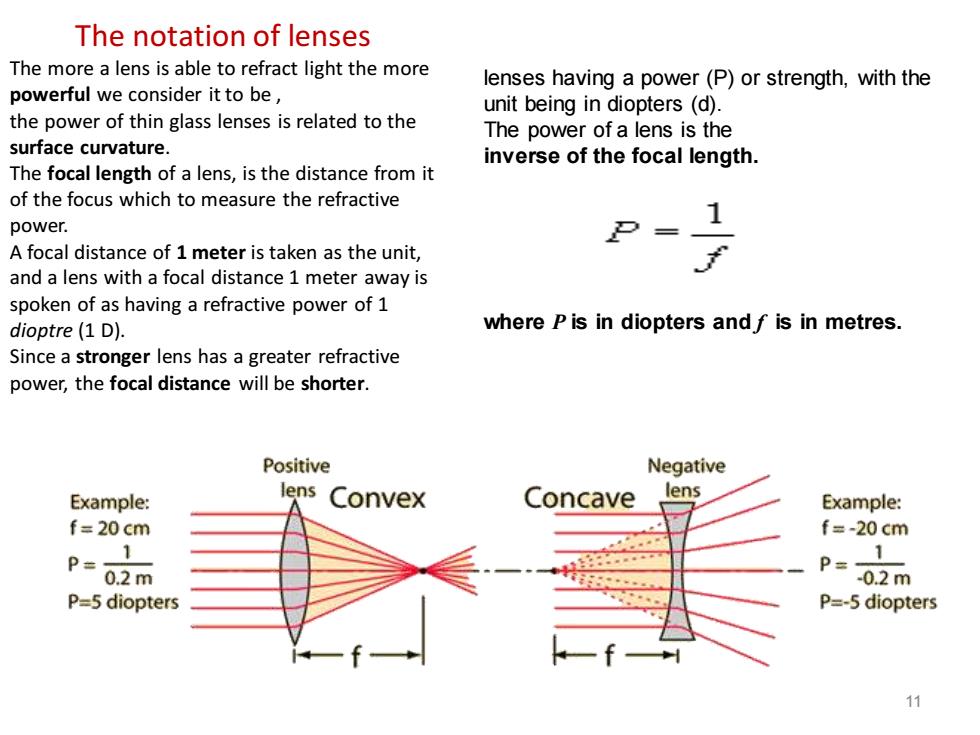
The notation of lenses The more a lens is able to refract light the more lenses having a power(P)or strength,with the powerful we consider it to be, unit being in diopters (d). the power of thin glass lenses is related to the The power of a lens is the surface curvature. inverse of the focal length The focal length of a lens,is the distance from it of the focus which to measure the refractive power. A focal distance of 1 meter is taken as the unit, and a lens with a focal distance 1 meter away is spoken of as having a refractive power of 1 dioptre(1 D). where P is in diopters and f is in metres. Since a stronger lens has a greater refractive power,the focal distance will be shorter. Positive Negative Example: lens Convex Concave lens Example: f=20cm f=-20 cm 1 P=02m 1 P=02m P=5 diopters P=-5 diopters 11
The notation of lenses The more a lens is able to refract light the more powerful we consider it to be , the power of thin glass lenses is related to the surface curvature. The focal length of a lens, is the distance from it of the focus which to measure the refractive power. A focal distance of 1 meter is taken as the unit, and a lens with a focal distance 1 meter away is spoken of as having a refractive power of 1 dioptre (1 D). Since a stronger lens has a greater refractive power, the focal distance will be shorter. 11 lenses having a power (P) or strength, with the unit being in diopters (d). The power of a lens is the inverse of the focal length. .......... where P is in diopters and f is in metres
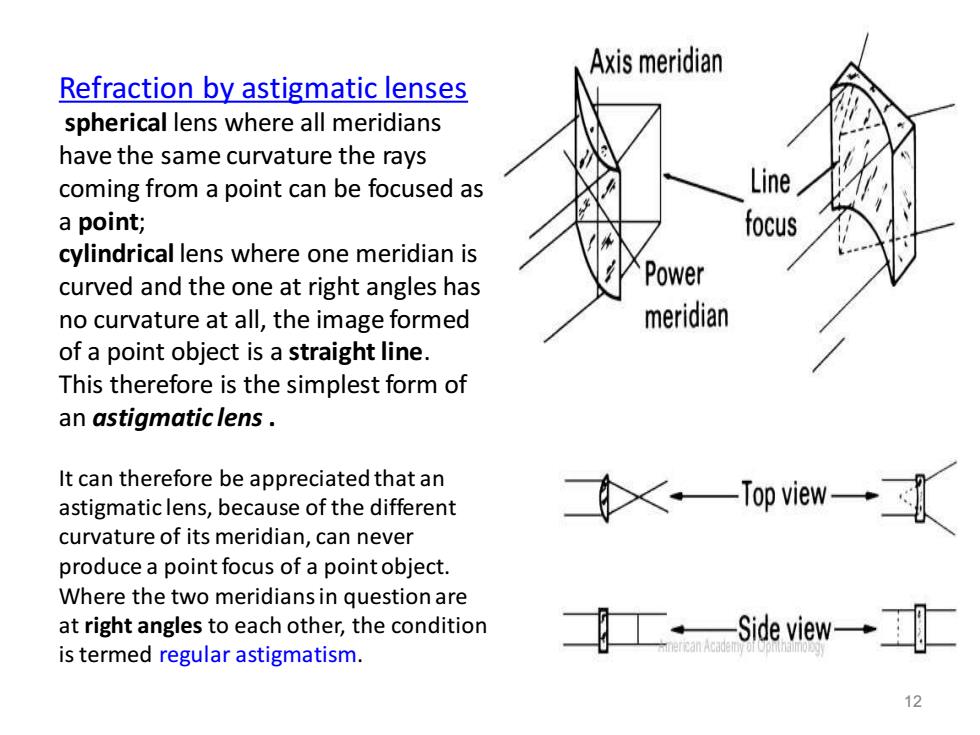
Axis meridian Refraction by astigmatic lenses spherical lens where all meridians have the same curvature the rays coming from a point can be focused as Line a point; focus cylindrical lens where one meridian is curved and the one at right angles has Power no curvature at all,the image formed meridian of a point object is a straight line. This therefore is the simplest form of an astigmatic lens. It can therefore be appreciated that an astigmaticlens,because of the different curvature of its meridian,can never produce a point focus of a pointobject. Where the two meridians in question are at right angles to each other,the condition 工·-Side view-→ ercan Acad is termed regular astigmatism. 12
Refraction by astigmatic lenses spherical lens where all meridians have the same curvature the rays coming from a point can be focused as a point; cylindrical lens where one meridian is curved and the one at right angles has no curvature at all, the image formed of a point object is a straight line . This therefore is the simplest form of an astigmatic lens . It can therefore be appreciated that an astigmatic lens, because of the different curvature of its meridian, can never produce a point focus of a point object. Where the two meridians in question are at right angles to each other, the condition is termed regular astigmatism . 12
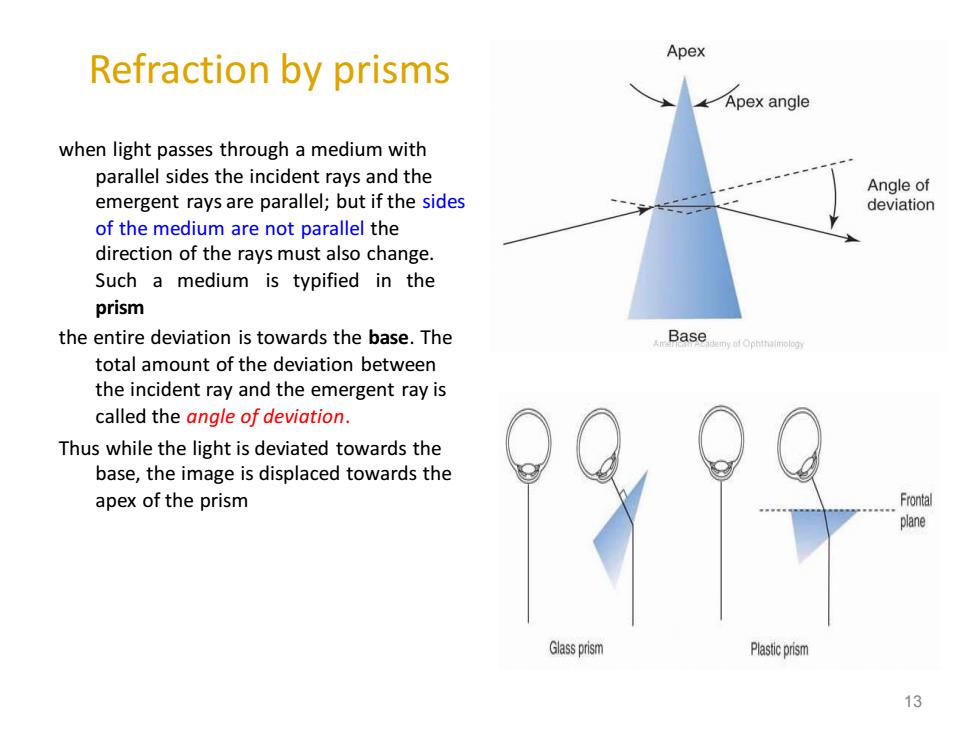
Apex Refraction by prisms Apex angle when light passes through a medium with parallel sides the incident rays and the Angle of emergent rays are parallel;but if the sides deviation of the medium are not parallel the direction of the rays must also change. Such a medium is typified in the prism the entire deviation is towards the base.The my af Ophitaimology total amount of the deviation between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation. Thus while the light is deviated towards the base,the image is displaced towards the apex of the prism plane Glass prism Plasticprism 13
Refraction by prisms when light passes through a medium with parallel sides the incident rays and the emergent rays are parallel; but if the sides of the medium are not parallel the direction of the rays must also change. Such a medium is typified in the prism the entire deviation is towards the base. The total amount of the deviation between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation. Thus while the light is deviated towards the base, the image is displaced towards the apex of the prism 13

Example of use of prism
Example of use of prism 14
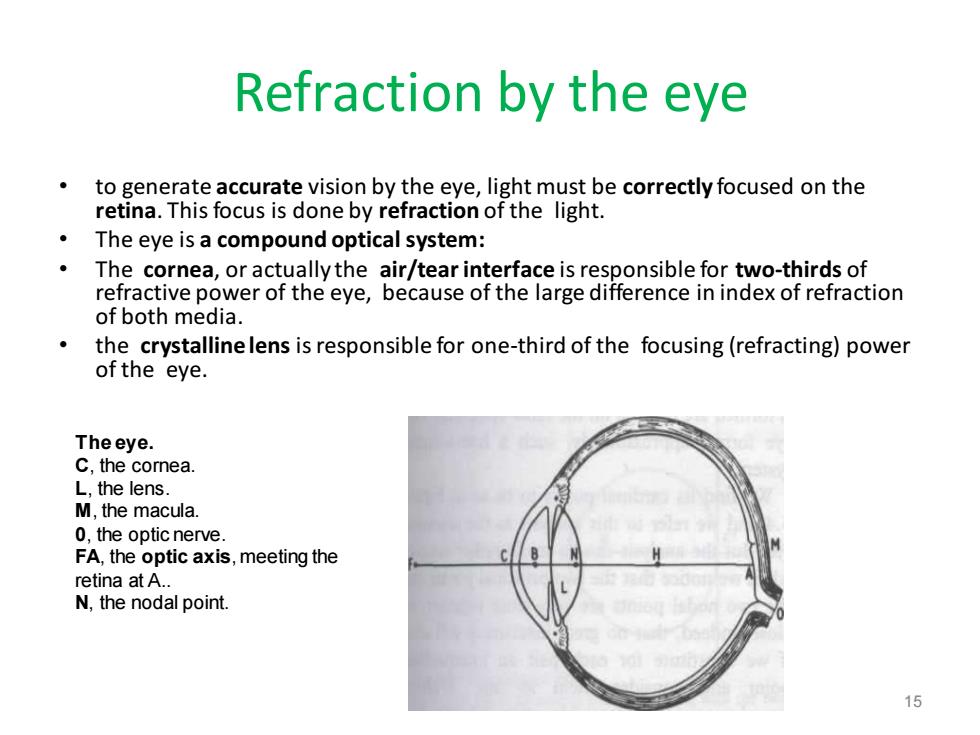
Refraction by the eye to generate accurate vision by the eye,light must be correctly focused on the retina.This focus is done by refraction of the light. The eye is a compound optical system: The cornea,or actually the air/tear interface is responsible for two-thirds of refractive power of the eye,because of the large difference in index of refraction of both media. the crystalline lens is responsible for one-third of the focusing(refracting)power of the eye. Theeye. C,the cornea L,the lens. M,the macula. 0.the optic nerve FA,the optic axis,meeting the retina at A.. N,the nodal point. 15
Refraction by the eye • to generate accurate vision by the eye, light must be correctly focused on the retina. This focus is done by refraction of the light. • The eye is a compound optical system: • The cornea, or actually the air/tear interface is responsible for two-thirds of refractive power of the eye, because of the large difference in index of refraction of both media. • the crystalline lens is responsible for one-third of the focusing (refracting) power of the eye. 15 The eye. C, the cornea. L, the lens. M, the macula. 0, the optic nerve. FA, the optic axis, meeting the retina at A.. N, the nodal point