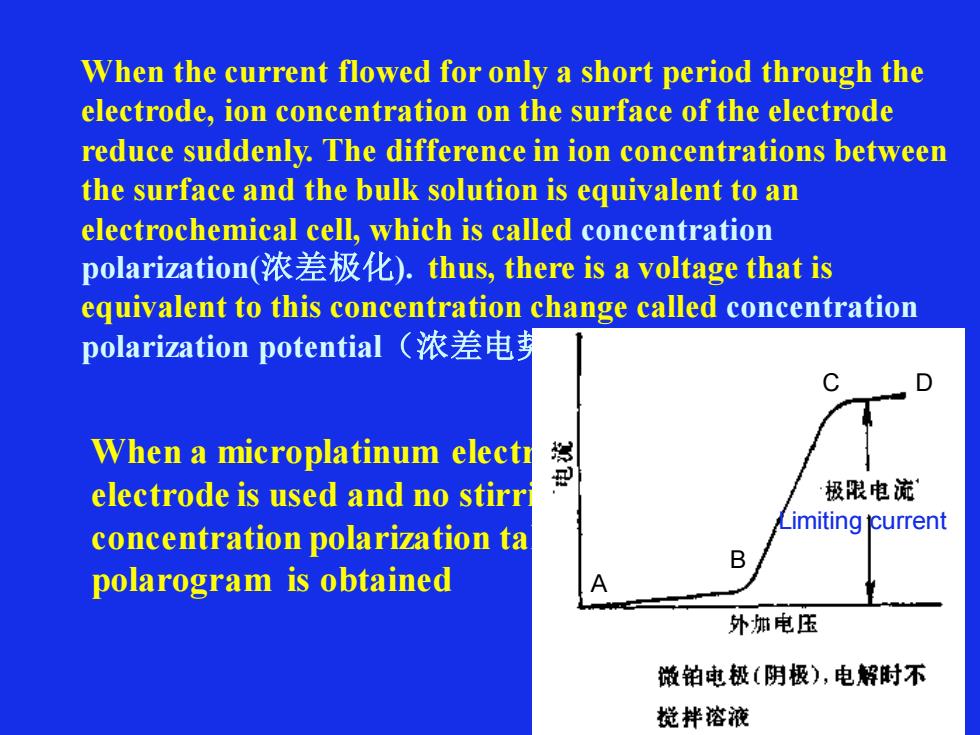
When the current flowed for only a short period through the electrode, ion concentration on the surface of the electrode reduce suddenly. The difference in ion concentrations between the surface and the bulk solution is equivalent to an electrochemical cell, which is called concentration polarization(浓差极化). thus, there is a voltage that is equivalent to this concentration change called concentration polarization potential(浓差电势) When a microplatinum electrode or dropping mercury electrode is used and no stirring is carried out, concentration polarization takes place soon, following polarogram is obtained Limiting current A B C D
When the current flowed for only a short period through the electrode, ion concentration on the surface of the electrode reduce suddenly. The difference in ion concentrations between the surface and the bulk solution is equivalent to an electrochemical cell, which is called concentration polarization(浓差极化). thus, there is a voltage that is equivalent to this concentration change called concentration polarization potential(浓差电势) When a microplatinum electrode or dropping mercury electrode is used and no stirring is carried out, concentration polarization takes place soon, following polarogram is obtained Limiting current A B C D
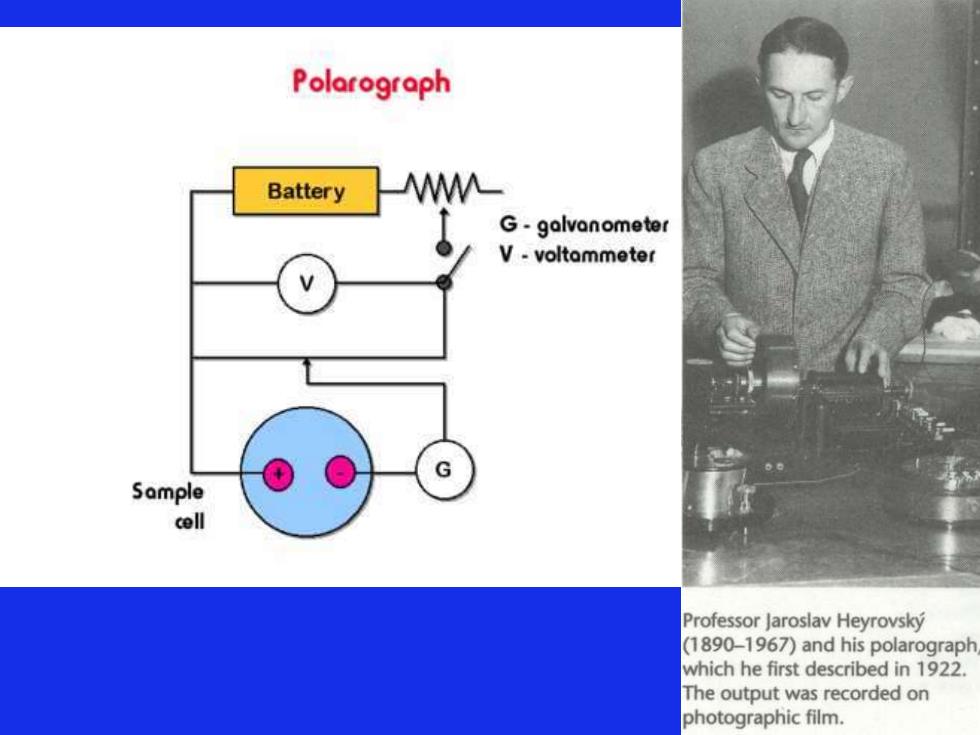
Polarograph Battery M G-galvanometer V-voltammeter Sample cell Professor Jaroslav Heyrovsky (1890-1967)and his polarograph which he first described in 1922. The output was recorded on photographic film
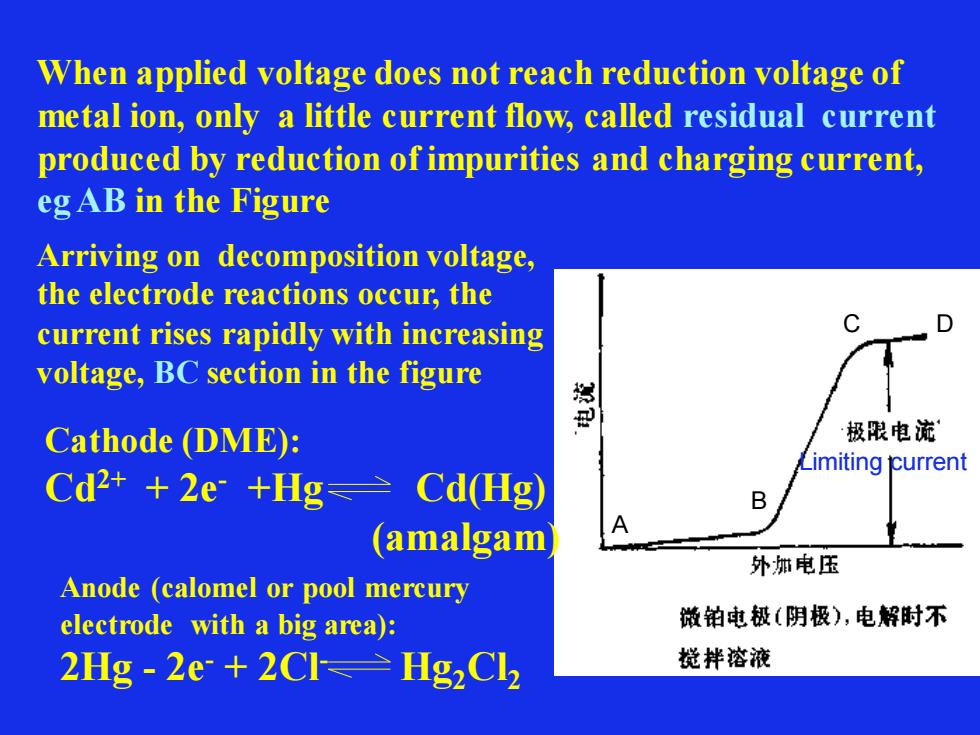
When applied voltage does not reach reduction voltage of metal ion, only a little current flow, called residual current produced by reduction of impurities and charging current, eg AB in the Figure Limiting current A B C D Arriving on decomposition voltage, the electrode reactions occur, the current rises rapidly with increasing voltage, BC section in the figure Cathode (DME): Cd2+ + 2e- +Hg Cd(Hg) (amalgam) Anode (calomel or pool mercury electrode with a big area): 2Hg - 2e- + 2Cl- Hg2Cl2
When applied voltage does not reach reduction voltage of metal ion, only a little current flow, called residual current produced by reduction of impurities and charging current, eg AB in the Figure Limiting current A B C D Arriving on decomposition voltage, the electrode reactions occur, the current rises rapidly with increasing voltage, BC section in the figure Cathode (DME): Cd2+ + 2e- +Hg Cd(Hg) (amalgam) Anode (calomel or pool mercury electrode with a big area): 2Hg - 2e- + 2Cl- Hg2Cl2

When it reaches C point voltage, due to concentration polarization, the current arrives at a limiting value and does not rise markedly, called limiting current, consisting of residual current and diffusion current 极谱波可以用i~ U外表示曲线表示,也可以用i ~ Ede曲线来表示,从下 面的讨论可以看出,二者是基本重合的。 U = ( ESCE -Ede ) + i R ∵ i and R are very little in polarographic electrolysis U = ESCE -Ede = -Ede( vs. SCE) To remove completely influence of iR, three electrode system is usually used
When it reaches C point voltage, due to concentration polarization, the current arrives at a limiting value and does not rise markedly, called limiting current, consisting of residual current and diffusion current 极谱波可以用i~ U外表示曲线表示,也可以用i ~ Ede曲线来表示,从下 面的讨论可以看出,二者是基本重合的。 U = ( ESCE -Ede ) + i R ∵ i and R are very little in polarographic electrolysis U = ESCE -Ede = -Ede( vs. SCE) To remove completely influence of iR, three electrode system is usually used
Very little oscillation
Very little oscillation