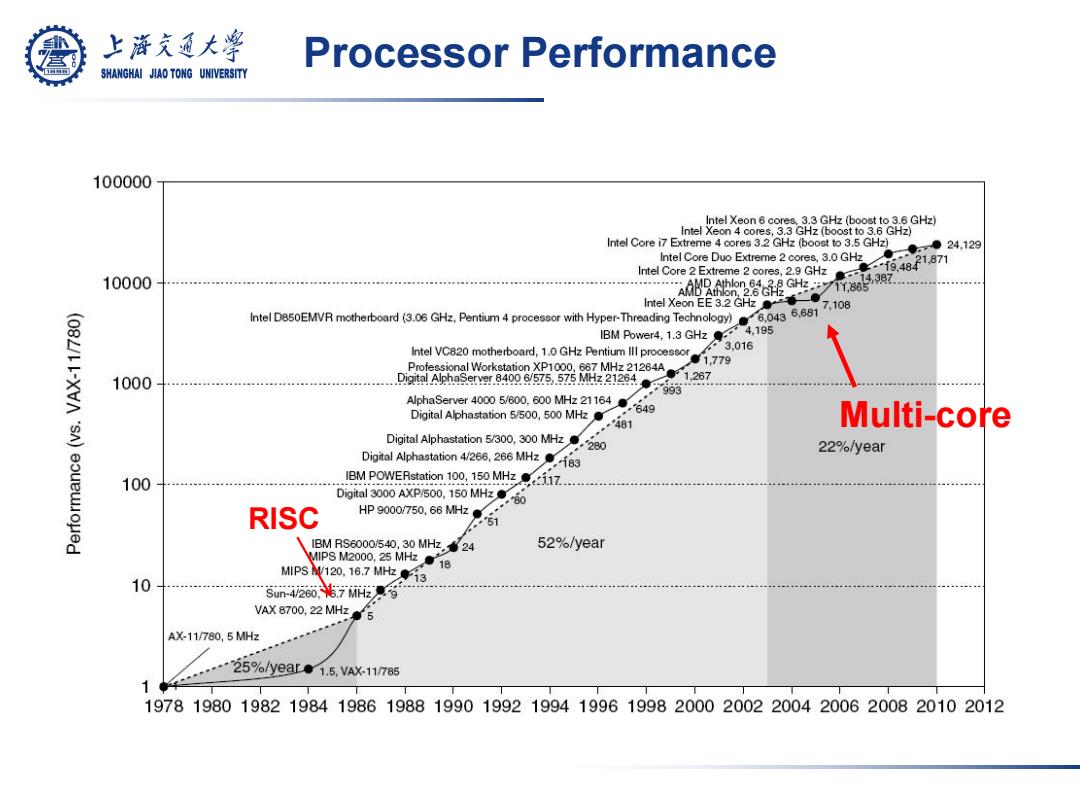
上游充通大 Processor Performance SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 100000 Intel Xeon 6 cores,3.3 GHz(boost to 3.6 GHz) Intel Xeon 4 cores,3.3 GHz (boost to 3.6 GHz) Intel Core i7 Extreme 4 cores 3.2 GHz(boost to 3.5 GHz) Intel Core Duo Extreme 2 cores,3.0 GHz .-●24,129 9,4821,871 10000 Intel Core 2 Extreme 2 cores,2.9 GHz …A8982%6混Gy1m,883 4387.… 26G2 Intel XeonEE32Ge●, ID850EMVR motherboard(3.06 GHz.Pentium 4 processor with Hyper-Threading Technology).0436.681 IBM Power4,1.3 GHz4.195 Intel VC820 motherboard,1.GHz Pentium 3.016 Professional Workstation XP1000,667 MHz 21264A 1000 D98Aa9eNr.840025.iM212463 1.267 AlphaServer00 5/0.00 MHz21164 Digital Alphastation 5/500,500 MHz 481 Multi-core Digital Alphastation 5/300,300 MHz Digital Alphastation 4/2 MHz +280 22%/year 100 Sanon 100 150 NAZ8117.. Digital 3000 AXP/500,150 MHz RISC HP9000750,66MH● 51 IBM RS6000540,30MH,24 VIPS M2000,25 MHz18 52%/year MPS120,16.7MH3 10 5Un4280老7i.兮 VAX 8700,22 MHzs AX-11/780,5MHz -25%/yeae1.5,VaX-11785 197819801982198419861988199019921994199619982000200220042006200820102012
Processor Performance RISC Multi-core
Current Trends in Architecture Introduction Cannot continue to leverage Instruction-Level parallelism (ILP) ·6 Single processor performance improvement ended in2003 ⊕ New models for performance: Data-level parallelism(DLP) Thread-level parallelism(TLP) Request-level parallelism(RLP) These require explicit restructuring of the application
Current Trends in Architecture Cannot continue to leverage Instruction-Level parallelism (ILP) • Single processor performance improvement ended in 2003 New models for performance: • Data-level parallelism (DLP) • Thread-level parallelism (TLP) • Request-level parallelism (RLP) These require explicit restructuring of the application Introduction
Classes of Computers © Personal Mobile Device (PMD) e.g.start phones,tablet computers Classes of Computers Emphasis on energy efficiency and real-time ©Desktop Computing Emphasis on price-performance © Servers Emphasis on availability,scalability,throughput © Clusters /Warehouse Scale Computers ·Used for“Software as a Service(SaaS)" Emphasis on availability and price-performance e Sub-class:Supercomputers,emphasis:floating-point performance and fast internal networks Embedded Computers 。Emphasis:price
Classes of Computers Personal Mobile Device (PMD) • e.g. start phones, tablet computers • Emphasis on energy efficiency and real-time Desktop Computing • Emphasis on price-performance Servers • Emphasis on availability, scalability, throughput Clusters / Warehouse Scale Computers • Used for “Software as a Service (SaaS)” • Emphasis on availability and price-performance • Sub-class: Supercomputers, emphasis: floating-point performance and fast internal networks Embedded Computers • Emphasis: price Classes of Computers
Parallelism Classes of parallelism in applications: ·Data-Level Parallelism(DLP) Classes of Computers Task-Level Parallelism (TLP) Classes of architectural parallelism: Instruction-Level Parallelism(ILP) Vector architectures/Graphic Processor Units (GPUs) Thread-Level Parallelism Request-Level Parallelism
Parallelism Classes of parallelism in applications: • Data-Level Parallelism (DLP) • Task-Level Parallelism (TLP) Classes of architectural parallelism: • Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) • Vector architectures/Graphic Processor Units (GPUs) • Thread-Level Parallelism • Request-Level Parallelism Classes of Computers
Flynn's Taxonomy Classes Single instruction stream,single data stream (SISD) Single instruction stream,multiple data streams(SIMD) Computers Vector architectures Multimedia extensions Graphics processor units Multiple instruction streams,single data stream(MISD) No commercial implementation Multiple instruction streams,multiple data streams (MIMD) Tightly-coupled MIMD Loosely-coupled MIMD
Flynn’s Taxonomy Single instruction stream, single data stream (SISD) Single instruction stream, multiple data streams (SIMD) • Vector architectures • Multimedia extensions • Graphics processor units Multiple instruction streams, single data stream (MISD) • No commercial implementation Multiple instruction streams, multiple data streams (MIMD) • Tightly-coupled MIMD • Loosely-coupled MIMD Classes of Computers