R H R2 HN-CH-C-OH +H-N-CH-COO w H,0 R H R2 HgN-CH-C-N-CH-COO

Protein Sequence (Primary structure) The amino acid sequence of a protein is an unique characteristic of the protein is encoded by the nucleotide sequence of DNA,is thus a form of genetic information is read from the amino terminus to the carboxyl terminus
Protein Sequence (Primary structure) The amino acid sequence of a protein is an unique characteristic of the protein is encoded by the nucleotide sequence of DNA, is thus a form of genetic information is read from the amino terminus to the carboxyl terminus

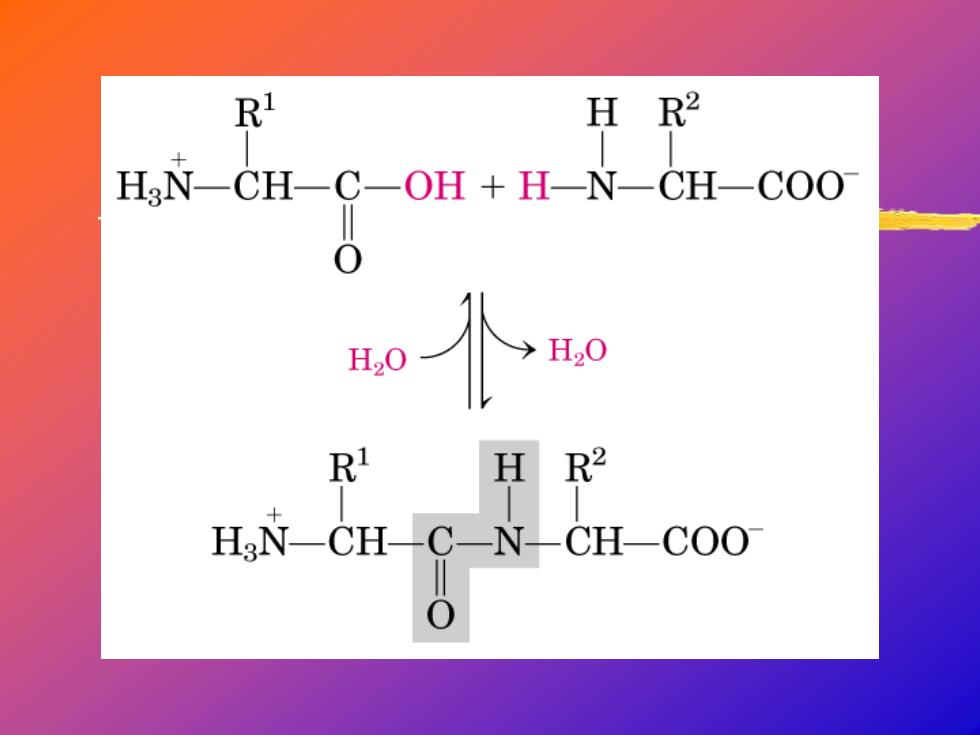
Structure of peptide bond Two amino acids are joined by the peptide bond,a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme called ribosome in all cells: H O H H R R R HR Due to the double bond character,the six atoms of the peptide bond group are always planar!
Structure of peptide bond Two amino acids are joined by the peptide bond, a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme called ribosome in all cells: Due to the double bond character, the six atoms of the peptide bond group are always planar! C C N C O H C C N C O H C C N C OH H H2N C C O R H N C C OH O R' H H H2N C C O R H NH3 C C OH O R' H OH + + H2O

Analysis of Protein Sequences Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: real amino acid sequencing sequencing the corresponding DNA in the gene Amino Acid Analysis of Proteins 6mol/L HCI@110 C for 24,48,72 hours in sealed glass vials(Trp is destroyed,must be analyzed by other means) Each reaction mixture is loaded on an ion-exchange column where each amino acid can be eluted according to their charge Eluted amino acids are quantified by reacting to ninhydrin(postcolumn derivatization) This method has been automated (amino acid analyzer)and allows analysis of only the amount of each type of amino acids,but gives no information on the order of amino acids nor the absolute amount of each amino acid
Analysis of Protein Sequences Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: real amino acid sequencing sequencing the corresponding DNA in the gene Amino Acid Analysis of Proteins 6mol/L HCl @ 110°C for 24, 48, 72 hours in sealed glass vials (Trp is destroyed, must be analyzed by other means) Each reaction mixture is loaded on an ion-exchange column where each amino acid can be eluted according to their charge Eluted amino acids are quantified by reacting to ninhydrin (postcolumn derivatization) This method has been automated (amino acid analyzer) and allows analysis of only the amount of each type of amino acids, but gives no information on the order of amino acids nor the absolute amount of each amino acid

Edman Degradation Method Edman degradation uses Edman reagent to determine the order of amino acids from the N-terminal end of a protein. mild alkali condition N=C=S+N与 N一C-NH HS H weak aqueous acid Analyzed by ion-exchange chromotography NH phenylthiohydantion(PTH)derivative Thiazolinone derivative
Edman Degradation Method Edman degradation uses Edman reagent to determine the order of amino acids from the N-terminal end of a protein. N C S + NH3 N O R H R' O mild alkali condition N C NH H N O R H R' O S H phenylthiohydantion (PTH) derivative Thiazolinone derivative TFA N H NH3 R R' O S N O N NH + O S R Analyzed by ion-exchange chromotography weak aqueous acid