
Implications of Asymmetric Information Adverse selection-form of market failure resulting from asymmetric information:if insurance companies must charge a single premium because they can not distinguish between high-risk and low-risk individuals,more high-risk individuals will insure,making it unprofitable to sell insurance
Implications of Asymmetric Information Adverse selection - form of market failure resulting from asymmetric information: if insurance companies must charge a single premium because they can not distinguish between high-risk and low-risk individuals, more high-risk individuals will insure, making it unprofitable to sell insurance

2 Market Signaling Market Signaling-Process by which sellers send signals to buyers conveying information about product quality. Note:Michael Spence:Market Signaling(1974)
2 Market Signaling Market Signaling– Process by which sellers send signals to buyers conveying information about product quality. Note: Michael Spence: Market Signaling(1974)
$200000 $20,000 C1)=$40,00y S100000 000 $10,000 CT)=$20,000y B(w) By) 0 123 45 Years of Colleg Optimal Choice of y for group I Optimal Choice ofy for group II Signaling
$200000 $100000 Optimal Choice of y for group I Optimal Choice of y for group II y* Years of College y* Signaling

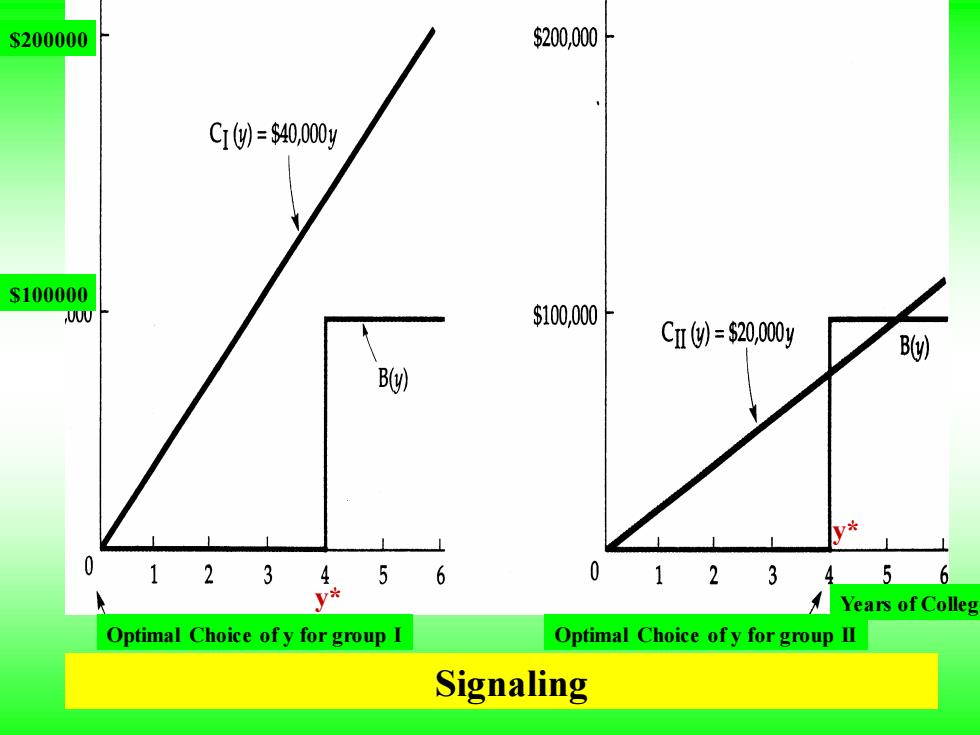
Education can be a useful signal of the high productivity of a group of workers if education is easier to obtain for this group than for a low-productivity group. In (a),the low-productivity group will choose an education level of y=0 because the cost of education is greater than the increased earnings resulting from education. However in (b),the high-productivity group will choose an education level of y*=4 because the gain in earnings is greater than the cost
Education can be a useful signal of the high productivity of a group of workers if education is easier to obtain for this group than for a low-productivity group. In (a), the low-productivity group will choose an education level of y = 0 because the cost of education is greater than the increased earnings resulting from education. However in (b), the high-productivity group will choose an education level of y* = 4 because the gain in earnings is greater than the cost

3 Moral hazard Moral hazard-when an insured party whose actions are unobserved can affect the probability or magnitude of a payment associated with an event
3 Moral hazard Moral hazard – when an insured party whose actions are unobserved can affect the probability or magnitude of a payment associated with an event