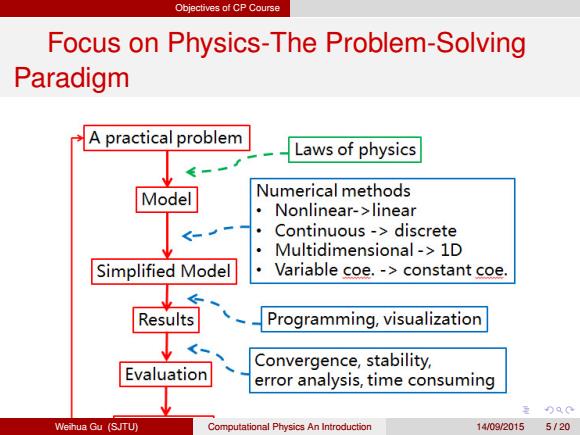
Objectives of CP Course Focus on Physics-The Problem-Solving Paradigm A practical problem Laws of physics Model Numerical methods Nonlinear->linear Continuous->discrete Multidimensional->1D Simplified Model Variable coe.->constant coe. Results Programming,visualization Convergence,stability, Evaluation error analysis,time consuming 重00C Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 5120
Objectives of CP Course Focus on Physics-The Problem-Solving Paradigm Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 5 / 20
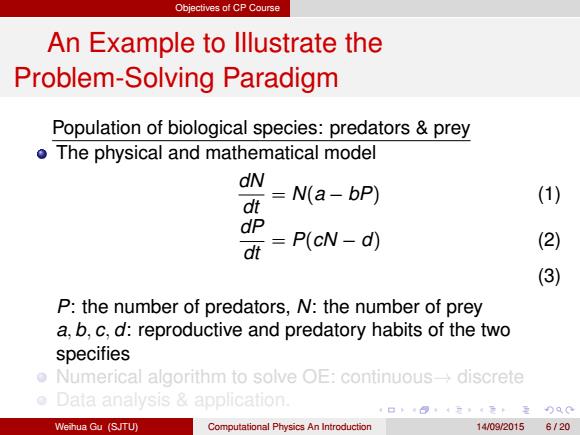
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN dt N(a-bP) (1) dP dt =P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuousdiscrete Data analysis application. ¥口,4元4元卡重)90 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
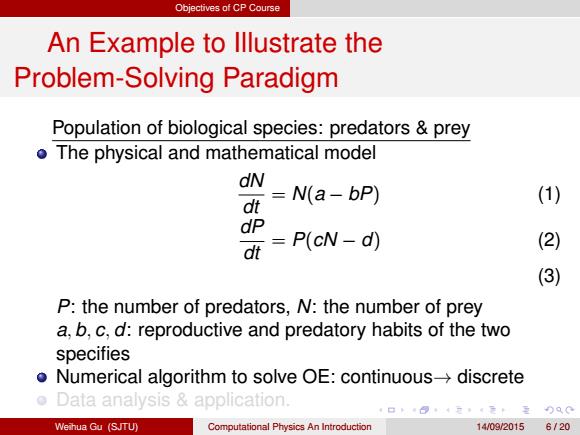
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN N(a-bP) (1) dt dP dt P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuous->discrete o Data analysis application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/092015 6120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
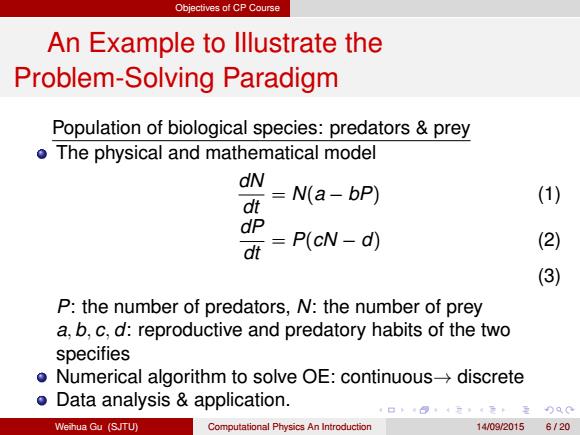
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN N(a-bP) (1) dt dP dt =P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies o Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuous->discrete o Data analysis application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20156120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
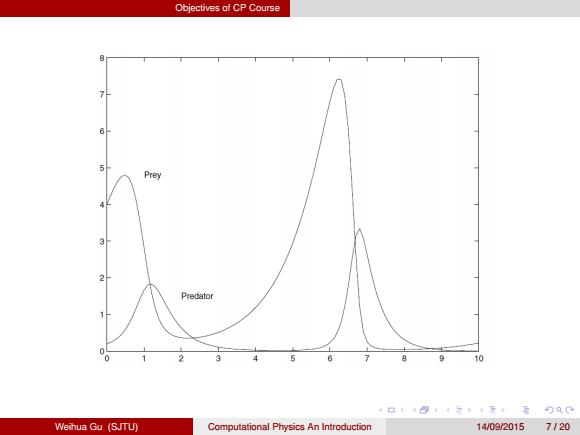
Objectives of CP Course Pre倒 3 2 Predator 0 10 4口404元,4无:至分Q0 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20157120
Objectives of CP Course Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 7 / 20