Detailed Structure of a TP Monitor Queue manager handles incoming messages Some queue managers provide persistent or durable message queueing contents of queue are safe even if systems fails. Durable queueing of outgoing messages is important application server writes message to durable queue as part of a transaction once the transaction commits,the TP monitor guarantees message is eventually delevered,regardless of crashes. ACID properties are thus provided even for messages sent outside the database Many TP monitors provide locking,logging and recovery services, to enable application servers to implement ACID properties by themselves. Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 25.7 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 25.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. Detailed Structure of a TP Monitor Queue manager handles incoming messages Some queue managers provide persistent or durable message queueing contents of queue are safe even if systems fails. Durable queueing of outgoing messages is important application server writes message to durable queue as part of a transaction once the transaction commits, the TP monitor guarantees message is eventually delevered, regardless of crashes. ACID properties are thus provided even for messages sent outside the database Many TP monitors provide locking, logging and recovery services, to enable application servers to implement ACID properties by themselves
Application Coordination Using TP Monitors A TP monitor treats each subsystem as a resource manager that provides transactional access to some set of resources. The interface between the TP monitor and the resource manager is defined by a set of transaction primitives The resource manager interface is defined by the X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing standard. TP monitor systems provide a transactional remote procedure call (transactional RPC)interface to their service Transactional RPC provides calls to enclose a series of RPC calls within a transaction. Updates performed by an RPC are carried out within the scope of the transaction,and can be rolled back if there is any failure. Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 25.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 25.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. Application Coordination Using TP Monitors A TP monitor treats each subsystem as a resource manager that provides transactional access to some set of resources. The interface between the TP monitor and the resource manager is defined by a set of transaction primitives The resource manager interface is defined by the X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing standard. TP monitor systems provide a transactional remote procedure call (transactional RPC) interface to their service Transactional RPC provides calls to enclose a series of RPC calls within a transaction. Updates performed by an RPC are carried out within the scope of the transaction, and can be rolled back if there is any failure

Transactional Workflows Workflows are activities that involve the coordinated execution of multiple tasks performed by different processing entities. With the growth of networks,and the existence of multiple autonomous database systems,workflows provide a convenient way of carrying out tasks that involve multiple systems. Example of a workflow delivery of an email message,which goes through several mails systems to reach destination. Each mailer performs a tasks:forwarding of the mail to the next mailer. If a mailer cannot deliver mail,failure must be handled semantically (delivery failure message). Workflows usually involve humans:e.g.loan processing,or purchase order processing. Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 25.10 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 25.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. Transactional Workflows Workflows are activities that involve the coordinated execution of multiple tasks performed by different processing entities. With the growth of networks, and the existence of multiple autonomous database systems, workflows provide a convenient way of carrying out tasks that involve multiple systems. Example of a workflow delivery of an email message, which goes through several mails systems to reach destination. Each mailer performs a tasks: forwarding of the mail to the next mailer. If a mailer cannot deliver mail, failure must be handled semantically (delivery failure message). Workflows usually involve humans: e.g. loan processing, or purchase order processing
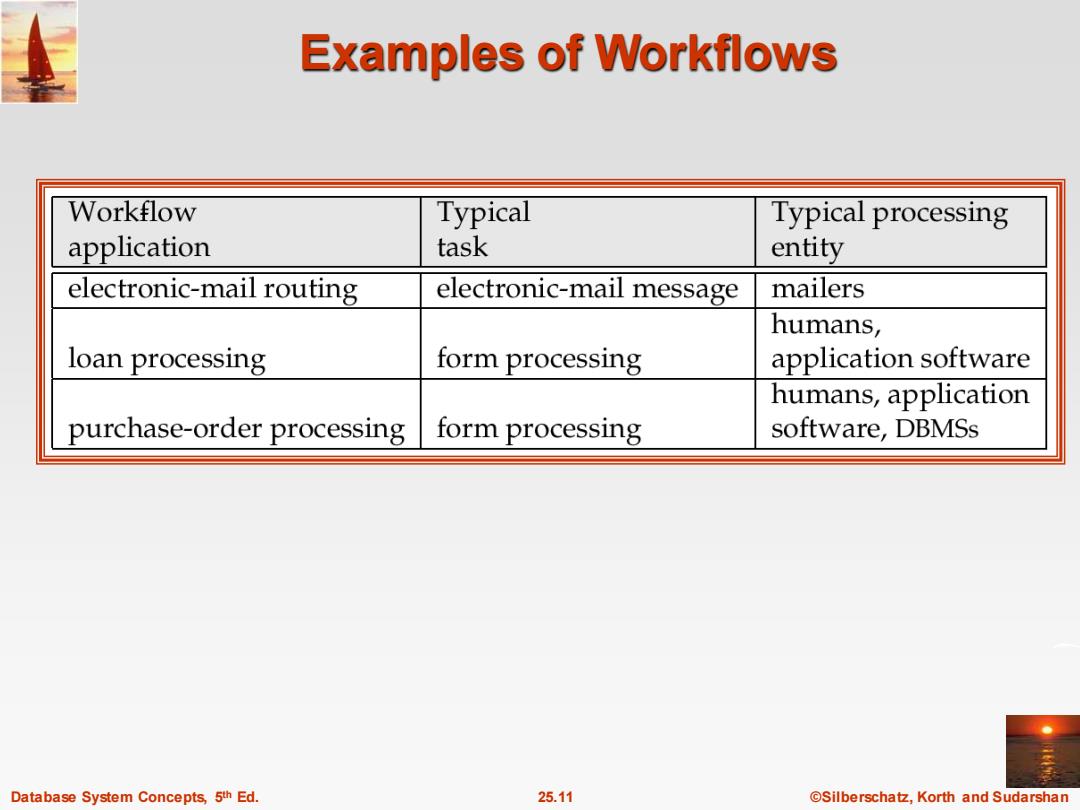
Examples of Workflows Workflow Typical Typical processing application task entity electronic-mail routing electronic-mail message mailers humans, loan processing form processing application software humans,application purchase-order processing form processing software,DBMSs Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 25.11 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 25.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. Examples of Workflows

Loan Processing Workflow loan application customer loan officer reject verification loan superior disbursement accept officer In the past,workflows were handled by creating and forwarding paper forms Computerized workflows aim to automate many of the tasks.But the humans still play role e.g.in approving loans. Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 25.12 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 25.12 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. Loan Processing Workflow In the past, workflows were handled by creating and forwarding paper forms Computerized workflows aim to automate many of the tasks. But the humans still play role e.g. in approving loans