
(一)根与茎的联系分叉、转位、汇合 ·茎和根的维管组织的联系 转变区(过渡区)(transition region:在 植物幼苗时期的茎和根相接的部分, 出现双方各自特征性结构(即根的初 生维管组织为间隔排列,木质部为外 始式;茎的初生维管组织为内外排列, 木质部为内始式)的过渡,称为根茎过 渡区
(一)根与茎的联系 • 茎和根的维管组织的联系 转变区(过渡区) (transition region):在 植物幼苗时期的茎和根相接的部分, 出现双方各自特征性结构(即根的初 生维管组织为间隔排列,木质部为外 始式;茎的初生维管组织为内外排列, 木质部为内始式)的过渡,称为根茎过 渡区. 分叉、转位、汇合
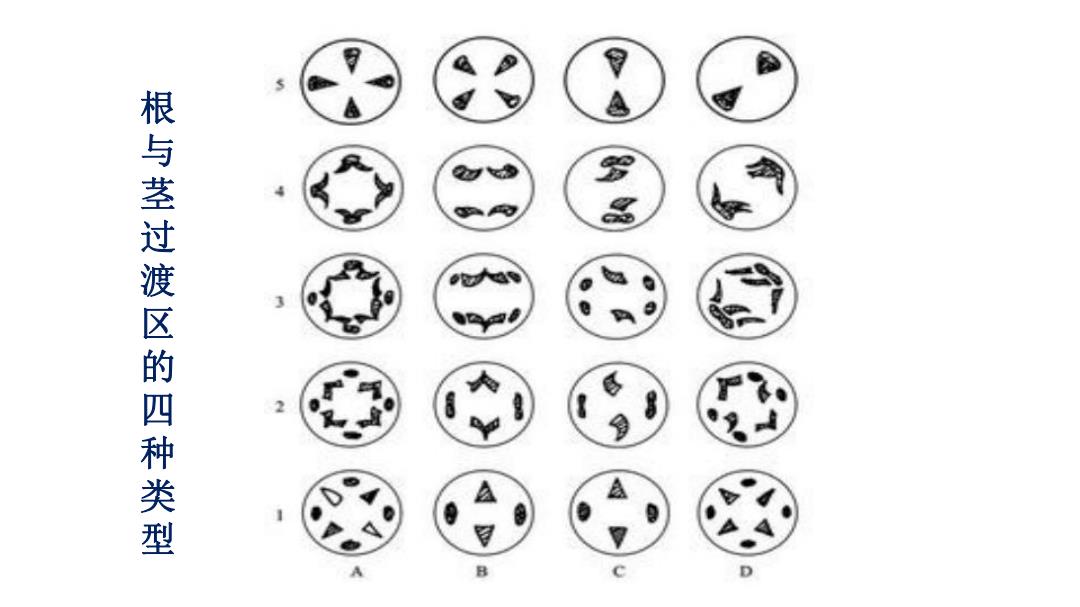
9 根与茎过渡区的四种类型
根与茎过渡区的四种类型
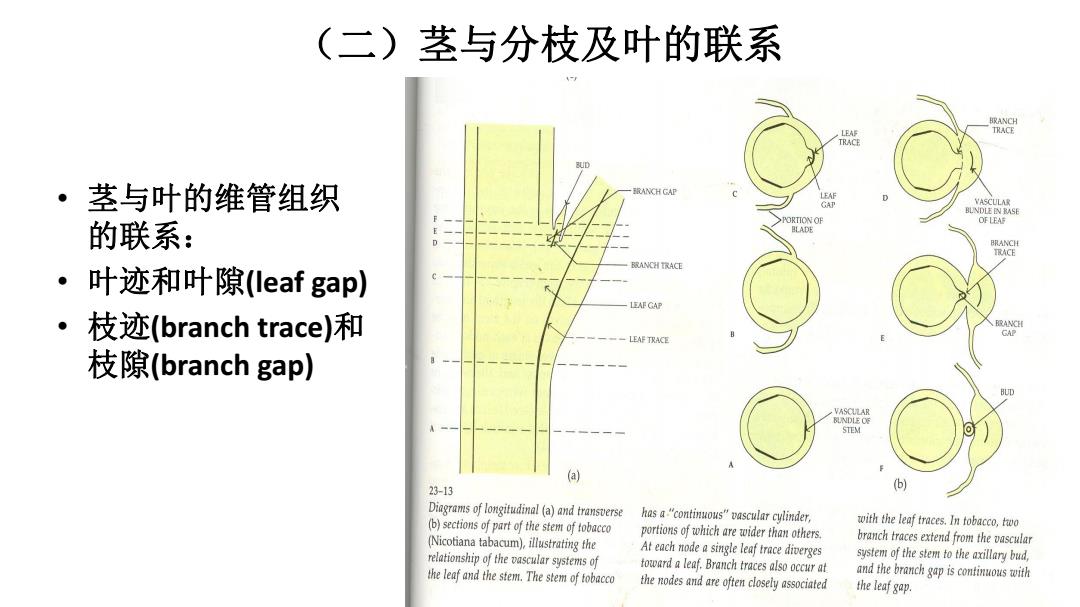
(二)茎与分枝及叶的联系 TRACE R ·茎与叶的维管组织 载ANCH GAP VASCULAR BLINDLE EN RASE PORTION OF OF LEAF 的联系: BLADE 藏NCH TRACE ·叶迹和叶隙(leaf gap) LEAF GAP ·枝迹(branch trace)和 LEAF TRACE 枝隙(branch gap) VASCULAR STEM (a) 23-13 b】 Diagrams of longitudinal (a)and transverse (b)sections of part of the stem of tobacco has a"continuous"vascular cylinder, (Nicotiana tabacum),illustrating the portions of which are wider than others. with the leaf traces.In tobacco,two branch traces extend from the vascular relationship of the vascular systems of At each node a single leaf trace diverges system of the stem to the axillary bud, the leaf and the stem.The stem of tobacco toward a leaf.Branch traces also occur at the nodes and are often closely associated and the branch gap is continouswith the lea时gap
(二)茎与分枝及叶的联系 • 茎与叶的维管组织 的联系: • 叶迹和叶隙(leaf gap) • 枝迹(branch trace)和 枝隙(branch gap)
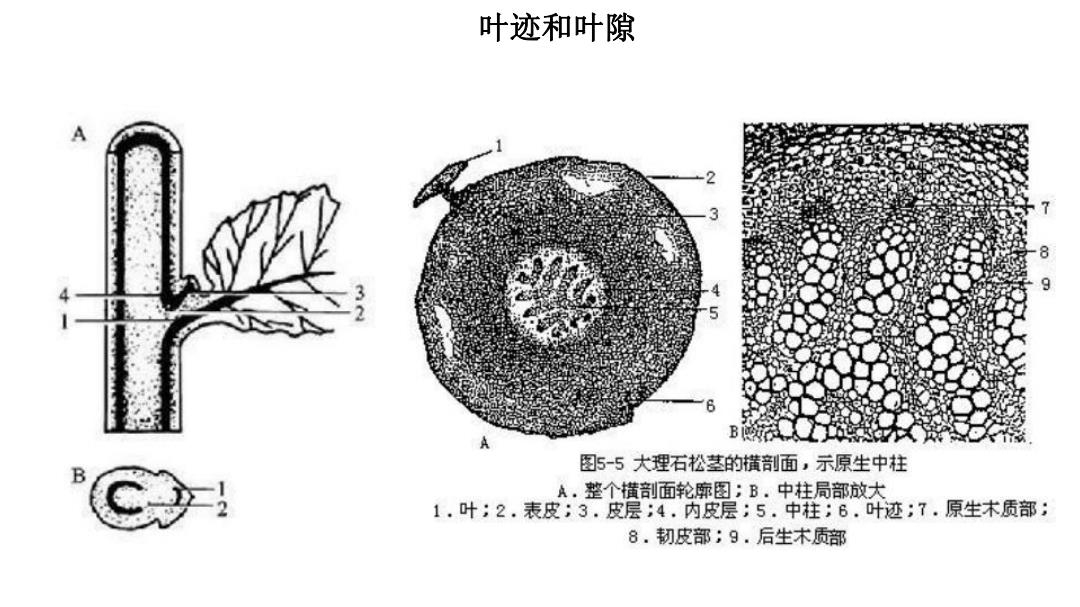
叶迹和叶隙 A B 图5-5大理石松茎的横剖面,示原生中柱 A,整个横剖面轮廓图;B.中柱局部放大 1.叶;2,表皮;3,皮层;4.内皮层;5.中柱;6,叶迹;7.原生木质部: 8.韧皮部;9.后生木质部
叶迹和叶隙
三、营养器官生长的相关性 Windy Sun Shade (一)枝叶系统与根系的相关性 Gravity:weight is a proolem (地下部分与地上部分的相互关系) 根深叶茂 Shade GaV商y:Wy eay制upp0ed (二)主干与侧枝的生长相关性 根深叶茂 Lees windy (主根与侧根) 顶端优势 0bd海 Poor soll upported by sol bodract
三、营养器官生长的相关性 (一)枝叶系统与根系的相关性 (地下部分与地上部分的相互关系) 根深叶茂 (二)主干与侧枝的生长相关性 (主根与侧根) 顶端优势