
Saving Data in Android ·Internal Storage Shared Preferences ·File ·SQLite Database ·Network Connection 6
Saving Data in Android • Internal Storage • Shared Preferences • File • SQLite Database • Network Connection 6
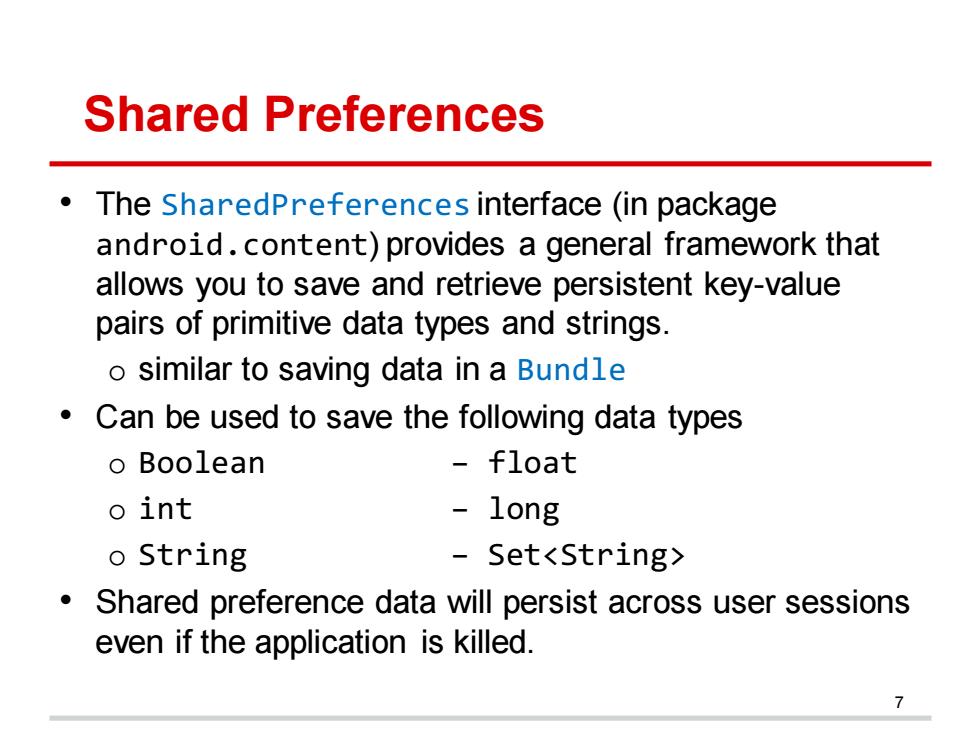
Shared Preferences The SharedPreferences interface (in package android.content)provides a general framework that allows you to save and retrieve persistent key-value pairs of primitive data types and strings. o similar to saving data in a Bundle Can be used to save the following data types o Boolean float o int long o String Set<String> Shared preference data will persist across user sessions even if the application is killed
Shared Preferences • The SharedPreferences interface (in package android.content) provides a general framework that allows you to save and retrieve persistent key-value pairs of primitive data types and strings. o similar to saving data in a Bundle • Can be used to save the following data types o Boolean – float o int – long o String − Set<String> • Shared preference data will persist across user sessions even if the application is killed. 7
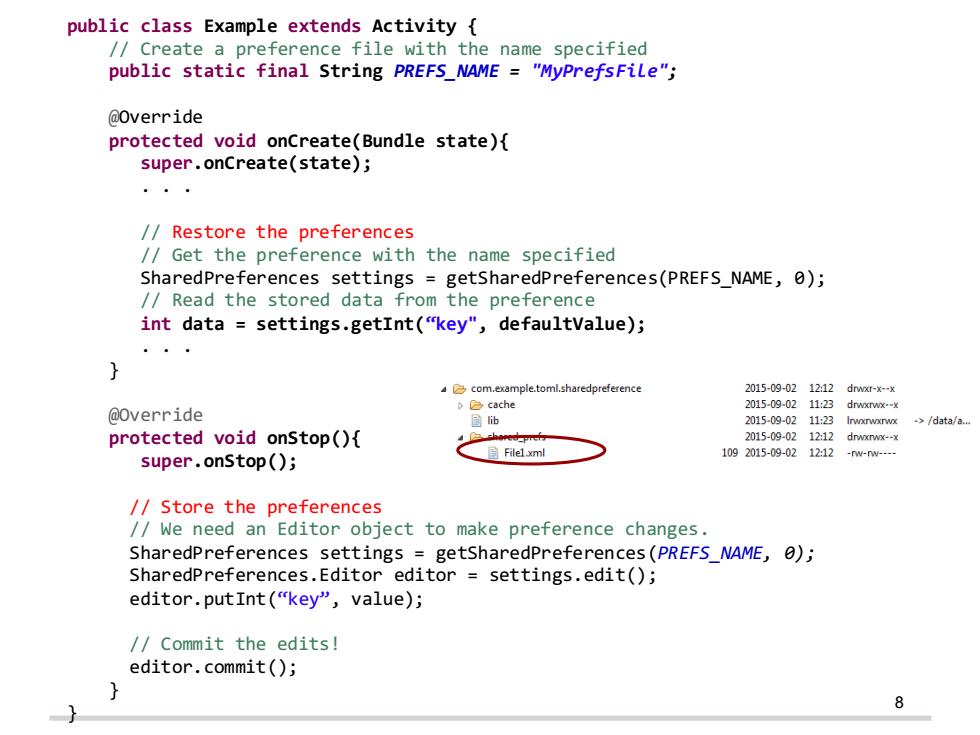
public class Example extends Activity /Create a preference file with the name specified public static final String PREFS_NAME "MyPrefsFile"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle state){ super.onCreate(state); /Restore the preferences //Get the preference with the name specified SharedPreferences settings getsharedPreferences(PREFS_NAME,0); /Read the stored data from the preference int data settings.getInt("key",defaultvalue); com.example.toml.sharedpreference 2015-09-0212:12dw0-x-x cache 2015-09-02 11:23 drwxrwx--x @Override 三ib 2015-09-0211:23 Irwxnwxrwx >/data/a... protected void onStop(){ 2015-09-02 1212 drwxrwx--x 目Filel.xml 1092015-09-0212:12 super.onstop(); -nw-n---- /Store the preferences /We need an Editor object to make preference changes. SharedPreferences settings getsharedPreferences(PREFS_NAME,0); SharedPreferences.Editor editor settings.edit(); editor.putInt("key",value); //Commit the edits! editor.commit(); 8
8 public class Example extends Activity { // Create a preference file with the name specified public static final String PREFS_NAME = "MyPrefsFile"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle state){ super.onCreate(state); . . . // Restore the preferences // Get the preference with the name specified SharedPreferences settings = getSharedPreferences(PREFS_NAME, 0); // Read the stored data from the preference int data = settings.getInt(“key", defaultValue); . . . } @Override protected void onStop(){ super.onStop(); // Store the preferences // We need an Editor object to make preference changes. SharedPreferences settings = getSharedPreferences(PREFS_NAME, 0); SharedPreferences.Editor editor = settings.edit(); editor.putInt(“key”, value); // Commit the edits! editor.commit(); } }
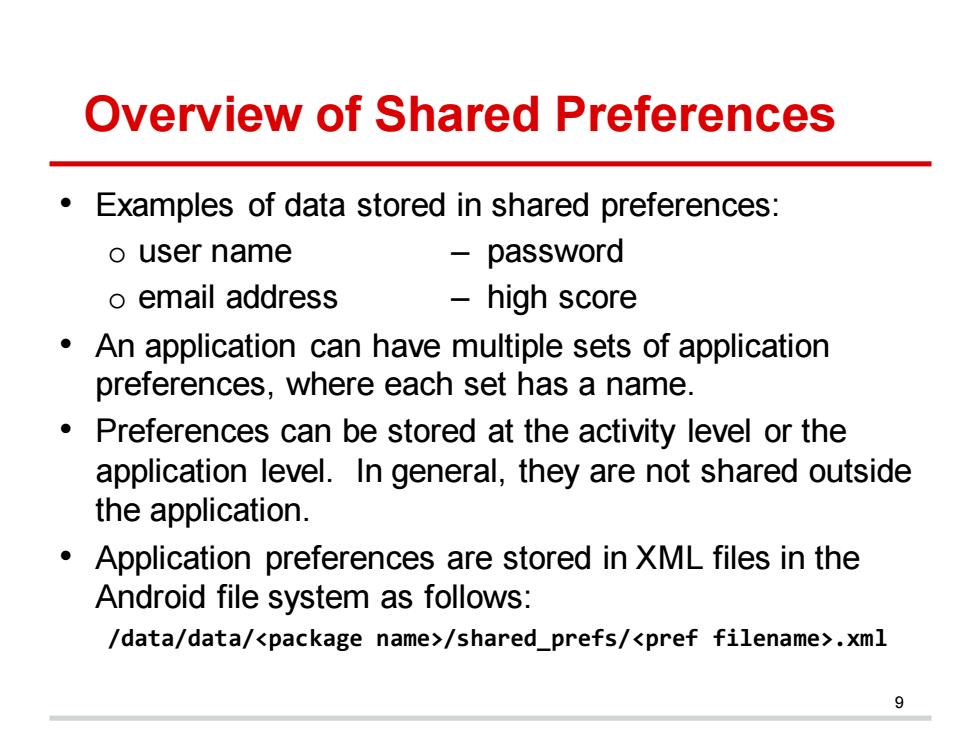
Overview of Shared Preferences Examples of data stored in shared preferences: o user name -password o email address high score An application can have multiple sets of application preferences,where each set has a name Preferences can be stored at the activity level or the application level.In general,they are not shared outside the application. Application preferences are stored in XML files in the Android file system as follows: /data/data/<package name>/shared_prefs/<pref filename>.xml
Overview of Shared Preferences • Examples of data stored in shared preferences: o user name – password o email address – high score • An application can have multiple sets of application preferences, where each set has a name. • Preferences can be stored at the activity level or the application level. In general, they are not shared outside the application. • Application preferences are stored in XML files in the Android file system as follows: /data/data/<package name>/shared_prefs/<pref filename>.xml 9

Obtaining a SharedPreferences Object Two methods that return a SharedPreferences object: getSharedPreferences(String name,int mode) o Use if you need multiple preferences files identified by name. o Name is specified as the first parameter. o If a preferences file by this name does not exist,it will be created when you retrieve an editor. o Preferences can be accessed by all activities in the application. getPreferences(int mode) o Use if you need only one preferences file for your Activity. o Only one preferences file for an Activity-don't supply a name. o Calls method getsharedPreferences(String,int)passing in this activity's class name as the preferences name. o Preferences are not shared with other activities in the application. 10
Obtaining a SharedPreferences Object Two methods that return a SharedPreferences object: • getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) o Use if you need multiple preferences files identified by name. o Name is specified as the first parameter. o If a preferences file by this name does not exist, it will be created when you retrieve an editor. o Preferences can be accessed by all activities in the application. • getPreferences(int mode) o Use if you need only one preferences file for your Activity. o Only one preferences file for an Activity – don't supply a name. o Calls method getSharedPreferences(String, int) passing in this activity’s class name as the preferences name. o Preferences are not shared with other activities in the application. 10