
密码学的演变历史(3) Feistel,Whitfield Diffie,Matin Hellman ●1971,IBM发明Luciffer Cipher,128位密钥作 分组加密。这项发明是由Horst Feistel(Jan.30,1915-Nov.14,1990)领导的, 他是密码学家,当时在BM负责设计加密器, 他的工作最终激发了7O年代Data Encryption Standard(DES)的研发高潮 ·1976-1977,美国国家标准局正式公布实施 DES ●1975,Vhitfield Diffie和Matin Hellman,发 表A New Direction in Cryptography,首次提 出适应网络保密通信的公开密钥思想,揭开 现代密码学研究的序幕,具有划时代的意义 ¥ 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security -2 7/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 7/81 密码学的演变历史(3) Feistel, Whitfield Diffie, Matin Hellman ⚫ 1971, IBM发明Luciffer Cipher, 128位密钥作 分组加密。这项发明是由Horst Feistel(Jan.30, 1915–Nov.14,1990)领导的, 他是密码学家,当时在IBM负责设计加密器, 他的工作最终激发了70年代Data Encryption Standard (DES)的研发高潮 ⚫ 1976-1977,美国国家标准局正式公布实施 DES ⚫ 1975, Whitfield Diffie 和 Matin Hellman, 发 表A New Direction in Cryptography, 首次提 出适应网络保密通信的公开密钥思想,揭开 现代密码学研究的序幕,具有划时代的意义

密码学的演变历史(4) 海车不 105 R.S.A..Abbas El Gamal,Lai Xuejia 1977-1978,Ronald Rivest,Adi Shamir,.Len Adleman:第一次提出公 开密钥密码系统的实现方法RSA 1981,成立International Association for Cryptology Research 1985,Abbas El Gamal提出概率密 码系统EIGamal方法 1990-1992,Lai Xuejia and James: IDEA,The International Data Encryption Algorithm 0 2000,AES,Advanced Encryption Standard 平N两 婚道 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 8/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 8/81 密码学的演变历史(4) R.S.A., Abbas El Gamal, Lai Xuejia ⚫ 1977-1978,Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, Len Adleman第一次提出公 开密钥密码系统的实现方法RSA ⚫ 1981,成立International Association for Cryptology Research ⚫ 1985,Abbas El Gamal提出概率密 码系统ElGamal方法 ⚫ 1990-1992,Lai Xuejia and James: IDEA, The International Data Encryption Algorithm ⚫ 2000, AES, Advanced Encryption Standard

密码学基本术语TERMINOLOGIES Cryptology保密学),源自希腊语(Greek) Kryptos:hidden;logos:word,是密码学和密码处理过程的研究 Cryptography:The Science and Study of Secret Writing, 编码学 ● Cryptanalysis:The Science and Study of Secret Breaking, 码破译学 ● Cipher:A secret method of writing加密方法 ● Encipher(encipherment),encryption:将明文转换成密文的过程 ● Decipher(decipherment),decryption:将密文还原成明文的过程 Plaintext(cleartext):原始的可读数据,明文 ● Ciphertext(Cryptogram):加密后的不可解读之文件,密文 ● Ky:密钥,对加密与解密过程进行控制的参数 E(m):Encryption Transformation加密变换 D(c):Decryption Transformation解密变换 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 9/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 9/81 ⚫ Cryptology(保密学),源自希腊语(Greek) Kryptós: hidden; logos: word, 是密码学和密码处理过程的研究 ⚫ Cryptography: The Science and Study of Secret Writing,密码 编码学 ⚫ Cryptanalysis: The Science and Study of Secret Breaking,密 码破译学 ⚫ Cipher: A secret method of writing 加密方法 ⚫ Encipher (encipherment), encryption: 将明文转换成密文的过程 ⚫ Decipher (decipherment), decryption: 将密文还原成明文的过程 ⚫ Plaintext (cleartext): 原始的可读数据,明文 ⚫ Ciphertext (Cryptogram): 加密后的不可解读之文件,密文 ⚫ Key: 密钥,对加密与解密过程进行控制的参数 ⚫ E(m): Encryption Transformation 加密变换 ⚫ D(c): Decryption Transformation 解密变换 密码学基本术语 Terminologies
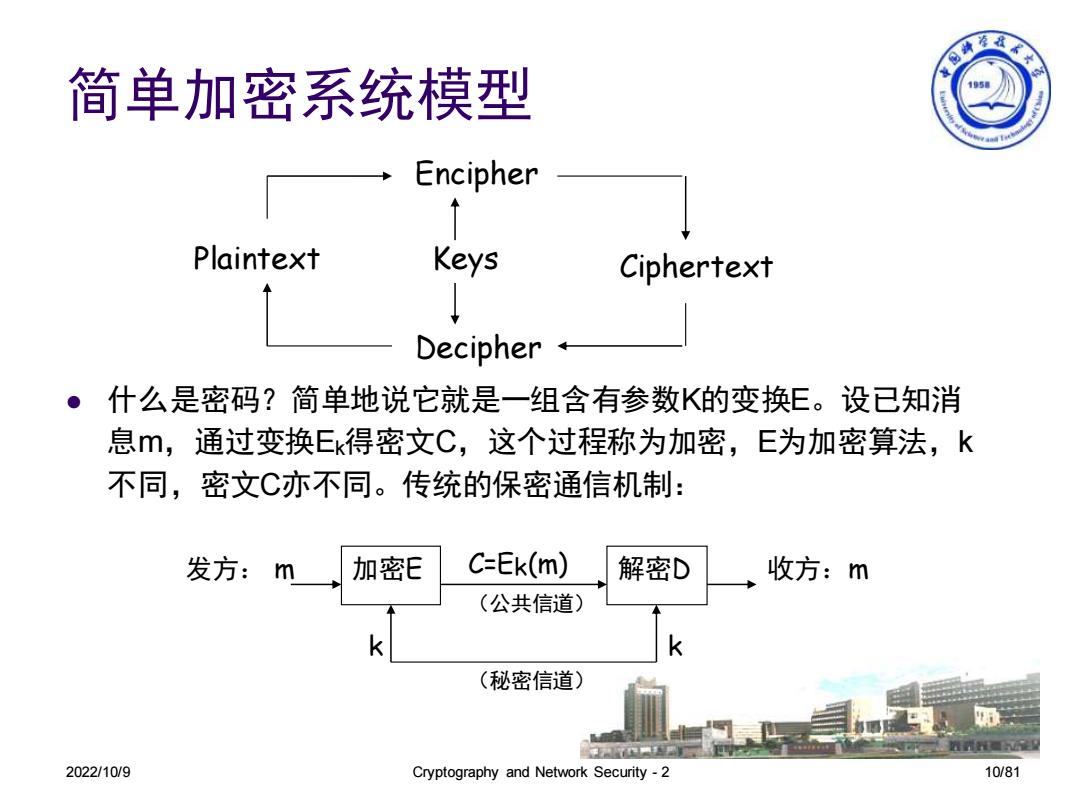
海拳家大 简单加密系统模型 15 Encipher Plaintext Keys Ciphertext Decipher 什么是密码?简单地说它就是一组含有参数K的变换E。设已知消 息m,通过变换Ek得密文C,这个过程称为加密,E为加密算法,k 不同,密文C亦不同。传统的保密通信机制: 发方:m 加密E C=Ek(m) 解密D 收方:m (公共信道) (秘密信道) 甲= 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security-2 10/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 10/81 ⚫ 什么是密码?简单地说它就是一组含有参数K的变换E。设已知消 息m,通过变换Ek得密文C,这个过程称为加密,E为加密算法,k 不同,密文C亦不同。传统的保密通信机制: Encipher Plaintext Keys Ciphertext Decipher 发方: m C=Ek(m) 收方:m k k (公共信道) 加密E 解密D (秘密信道) 简单加密系统模型

理论安全和实际安全 理论安全,或无条件安全Theoretical Secure(or Perfect Secure) 攻击者无论截获多少密文,都无法得到足够的信息来唯 地决定明文。Shannon用理论证明:欲达理论安全,加密 密钥长度必须大于等于明文长度,密钥只用一次,用完即 丢,即一次一密,One--time Pad,不实用。 实际安全,或计算上安全Practical Secure(or Computationally Secure) 如果攻击者拥有无限资源,任何密码系统都是可以被破译 的;但是在有限的资源范围内,攻击者都不能通过系统的 分析方法来破解系统,则称这个系统是计算上安全的或破 译这个系统是计算上不可行(Computationally Infeasible)。 道道 2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security -2 11/81
2022/10/9 Cryptography and Network Security - 2 11/81 ⚫ 理论安全,或无条件安全Theoretical Secure (or Perfect Secure) 攻击者无论截获多少密文,都无法得到足够的信息来唯一 地决定明文。Shannon用理论证明:欲达理论安全,加密 密钥长度必须大于等于明文长度,密钥只用一次,用完即 丢,即一次一密,One-time Pad,不实用。 ⚫ 实际安全,或计算上安全Practical Secure (or Computationally Secure) 如果攻击者拥有无限资源,任何密码系统都是可以被破译 的;但是在有限的资源范围内,攻击者都不能通过系统的 分析方法来破解系统,则称这个系统是计算上安全的或破 译这个系统是计算上不可行(Computationally Infeasible)。 理论安全和实际安全