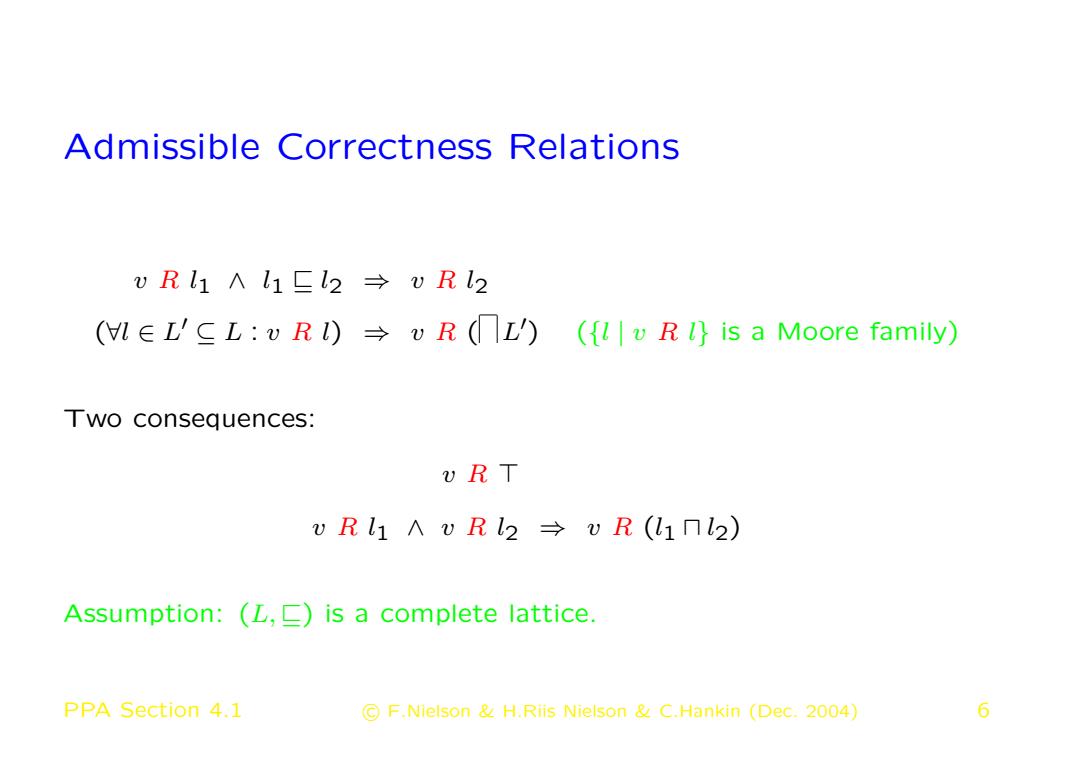
Admissible Correctness Relations vRl1∧l1El2→vRl2 (l∈L'≤L:vRl)→vR(L)({l|vR}is a Moore family) Two consequences: U RT vRl1∧vRl2→vR(l1nl2) Assumption:(L,is a complete lattice. PPA Section 4.1 C F.Nielson H.Riis Nielson C.Hankin (Dec.2004) 6
Admissible Correctness Relations v R l1 ∧ l1 v l2 ⇒ v R l2 (∀l ∈ L 0 ⊆ L : v R l) ⇒ v R ( L 0 ) ({l | v R l} is a Moore family) Two consequences: v R > v R l1 ∧ v R l2 ⇒ v R (l1 u l2) Assumption: (L, v) is a complete lattice. PPA Section 4.1 c F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (Dec. 2004) 6
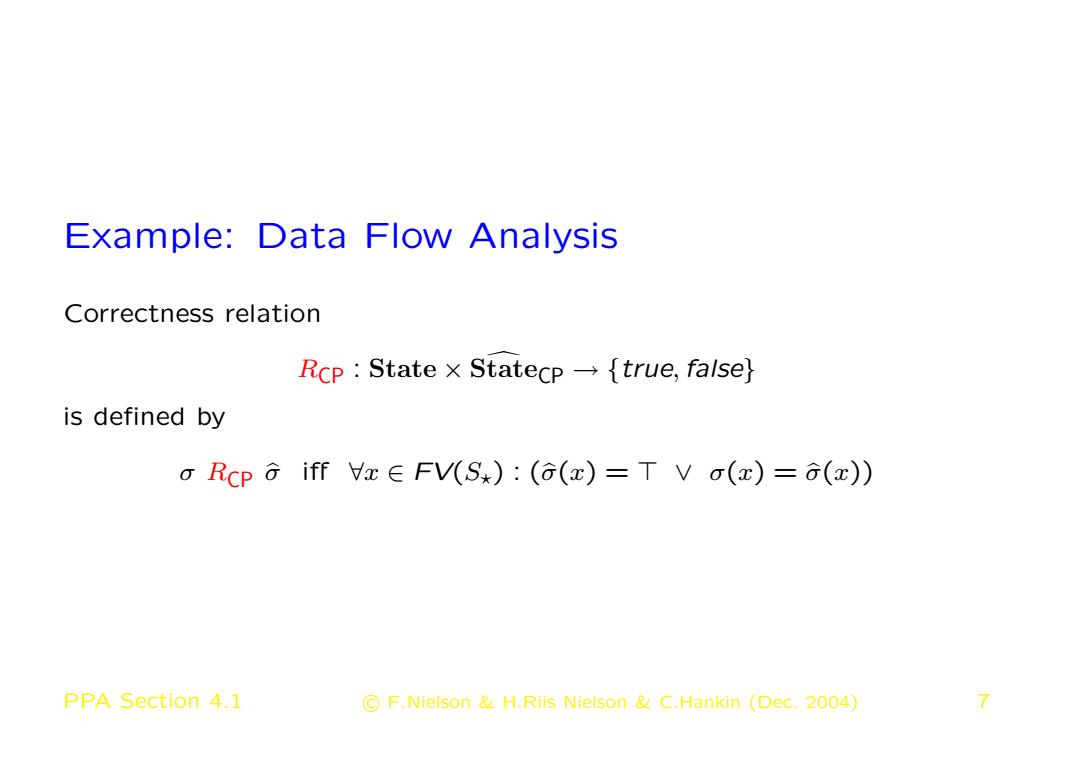
Example:Data Flow Analysis Correctness relation Rcp State x Statecp-{true,false) is defined by o Rcp a iff VxEFV(S):((x)=T V o(z)=(x)) PPA Section 4.1 C F.Nielson H.Riis Nielson C.Hankin (Dec.2004) 7
Example: Data Flow Analysis Correctness relation RCP : State × State d CP → {true,false} is defined by σ RCP σb iff ∀x ∈ FV(S?) : (σb(x) = > ∨ σ(x) = σb(x)) PPA Section 4.1 c F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (Dec. 2004) 7

Example:Control Flow Analysis Correctness relation RCFA Val x (Env x Val){true,false} is defined by RCEA (p,)iff v(p,) where 1 is given by: true if v=c (ffE dom(o)p()(()ifv=closet in PPA Section 4.1 C F.Nielson H.Riis Nielson C.Hankin (Dec.2004) 8
Example: Control Flow Analysis Correctness relation RCFA : Val × (Env d × Val d ) → {true,false} is defined by v RCFA (ρb, vb) iff v V (ρb, vb) where V is given by: v V (ρb, vb) iff ( true if v = c t ∈ vb ∧ ∀x ∈ dom(ρ) : ρ(x) V (ρb, ρb(x)) if v = close t in ρ PPA Section 4.1 c F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (Dec. 2004) 8
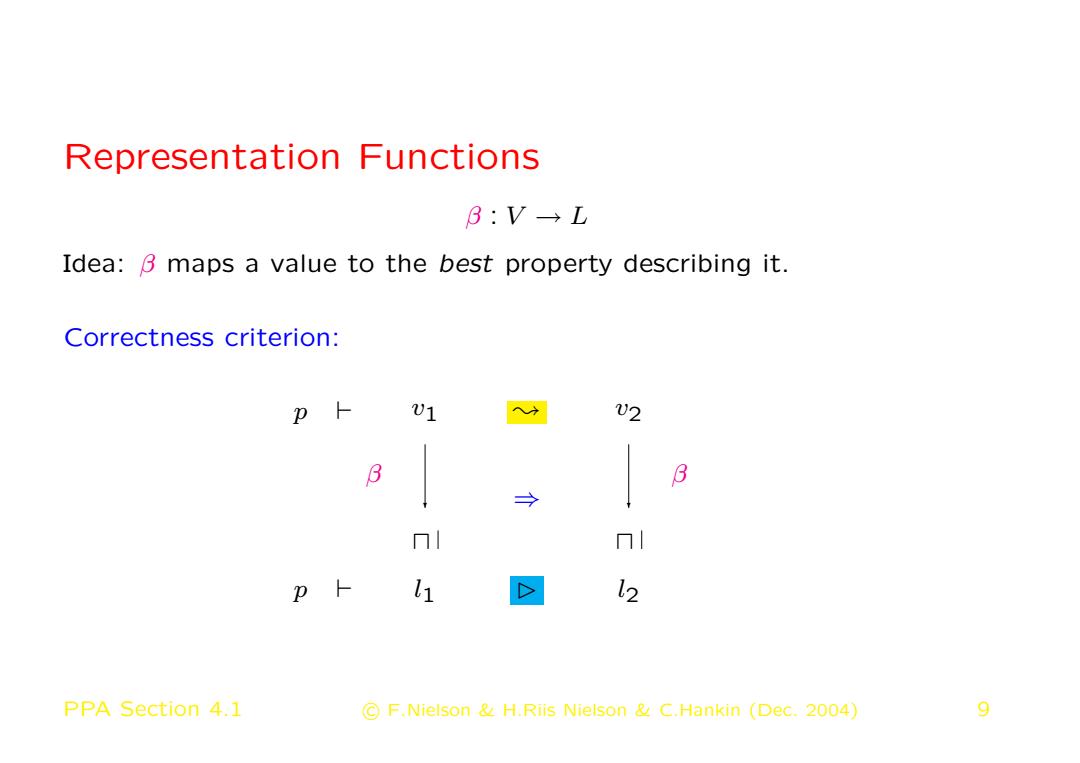
Representation Functions B:V→L Idea:3 maps a value to the best property describing it. Correctness criterion: U1 v2 3 → 冂 p卜 li D 12 PPA Section 4.1 C F.Nielson H.Riis Nielson C.Hankin (Dec.2004) 9
Representation Functions β : V → L Idea: β maps a value to the best property describing it. Correctness criterion: p ` v1 ❀ v2 u u p ` l1 ✄ l2 ❄ ❄ β β ⇒ PPA Section 4.1 c F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (Dec. 2004) 9
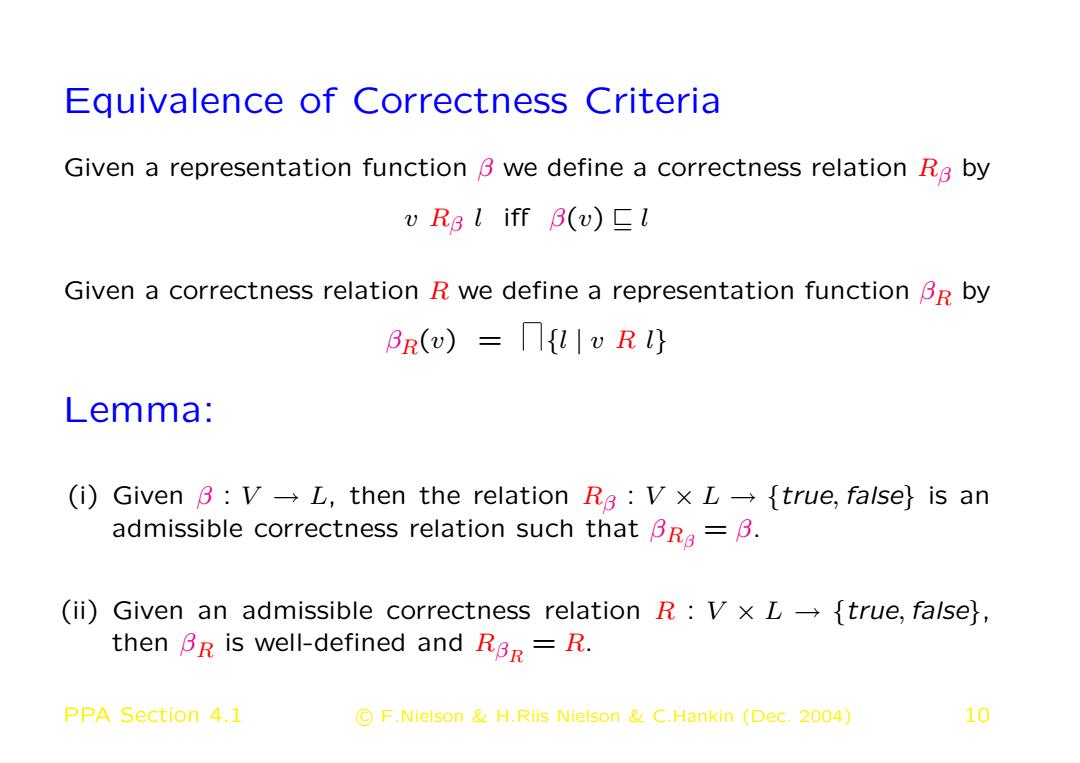
Equivalence of Correctness Criteria Given a representation function B we define a correctness relation Ra by v RB l iff B(v)l Given a correctness relation R we define a representation function BR by BR(v)=v R1} Lemma: (i)Given B:V-L,then the relation RB:VxL-{true,false}is an admissible correctness relation such that Br-B. (ii)Given an admissible correctness relation R:V x L-{true,falsel, then Br is well-defined and RBr=R. PPA Section 4.1 F.Nielson H.Riis Nielson C.Hankin (Dec.2004) 10
Equivalence of Correctness Criteria Given a representation function β we define a correctness relation Rβ by v Rβ l iff β(v) v l Given a correctness relation R we define a representation function βR by βR(v) = {l | v R l} Lemma: (i) Given β : V → L, then the relation Rβ : V × L → {true,false} is an admissible correctness relation such that βRβ = β. (ii) Given an admissible correctness relation R : V × L → {true,false}, then βR is well-defined and RβR = R. PPA Section 4.1 c F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (Dec. 2004) 10