Outline Dynamics 3.1 Free Vibration of SDOF Systems Chapter 3 3.2 Forced Vibration of SDOF Systems 3-3 NumericalAnalysis of Seismic Response of SDOF Seismic Responses of Systems ( SDOF and MDOF Free Vibration of MDOF Systems 3-7 Response Specturm Method of MDOF 3-8 Earthquake Action and Responses of MDOF 3.9 Time History Method of MDO 2015/1020 国 20151020 Review Review Base excitati From the moment.(k-1) 4 x(t))) R+25ax+02x=-3 Then Method: nearaNewmak-andWilomethod to solve the differentialissue. 国 大01so0 Displacement spectra T-0.5s Computation of the response spectrum 1
1 Chapter 3 Seismic Responses of SDOF and MDOF 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 1 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 2 Outline 3.1 Free Vibration of SDOF Systems 3.2 Forced Vibration of SDOF Systems 3.3 Numerical Analysis of Seismic Response of SDOF 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*) 3.6 Free Vibration of MDOF Systems 3.7 Response Specturm Method of MDOF 3.8 Earthquake Action and Responses of MDOF 3.9 Time History Method of MDOF Dynamics g m x cx kx m x Then g x x x x 2 2 x t x e sin t d t t g 2 0 2 1 1 1 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 3 Base excitation (Earthquakes) x ground mass k c g x From the moment, (k-1) Derivate the moment, k Method: linear acceleration, Newmark-β, and Wilson-θ method to solve the differential issue. -1 -1 -1 ( ), ( ), ( ) kkk x t x t x t ( ), ( ), ( ) kkk x t x t x t x t x t x t ( ), ( ), ( ) -1 -1 -1 ( ), ( ), ( ) kkk x t x t x t( ), ( ), ( ) kkk x t x t x t t k -1 t kt 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 4 Assumption: linear acceleration increase No. 5 No. 6
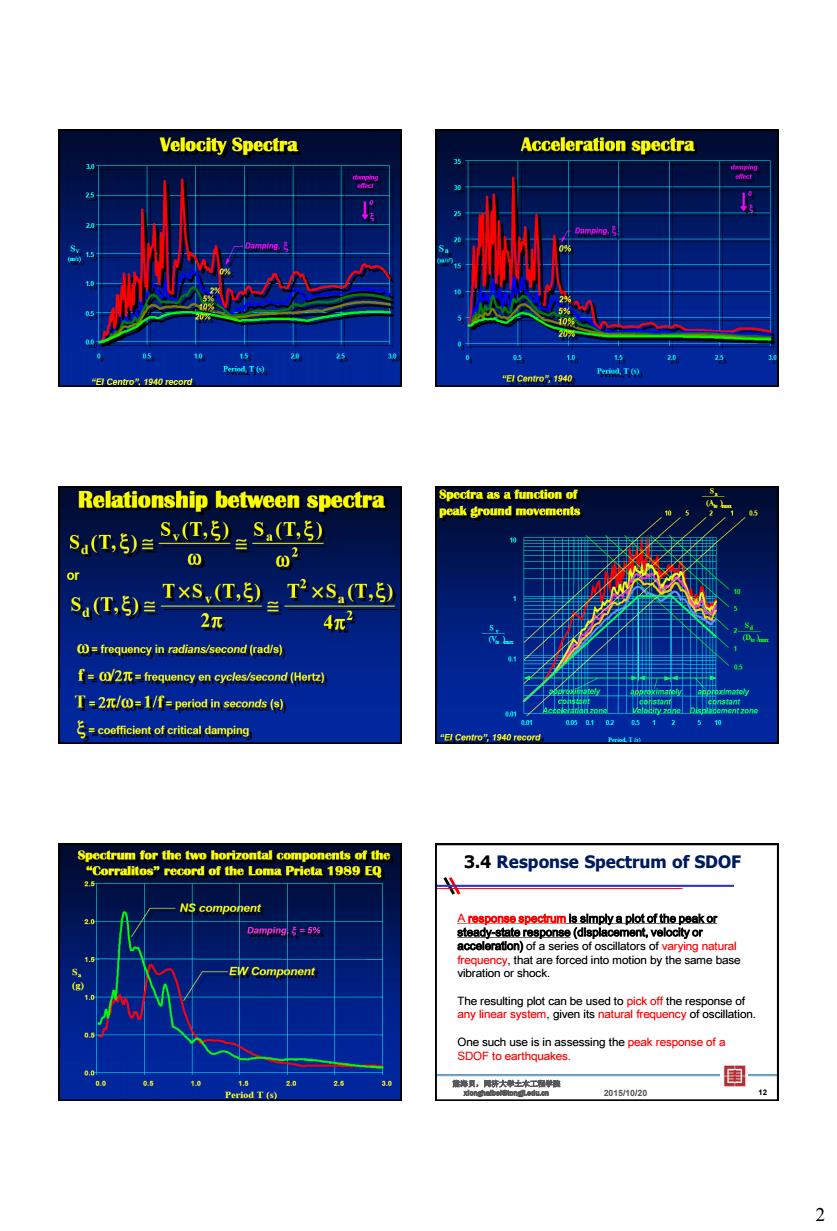
Velocity Spectra Acceleration spectra Relationship between spectra ST,5=S(C=S①,5) S(T)=TxS,(T)=TxS.(T.5) 2π 4π reqyin raians/secon (r) ==frequency en cycles/second (Hertz) T2=1/f=period in seconds ( cofficientof critica damping 194 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF ent Thceratcanetodoatheyr8r8o0ed 2 dT 大 2015t0/2
2 No. 7 No. 8 No. 9 No. 10 No. 11 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF A response spectrum is simply a plot of the peak or steady-state response (displacement, velocity or acceleration) of a series of oscillators of varying natural frequency, that are forced into motion by the same base vibration or shock. The resulting plot can be used to pick off the response of any linear system, given its natural frequency of oscillation. One such use is in assessing the peak response of a SDOF to earthquakes. 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 12
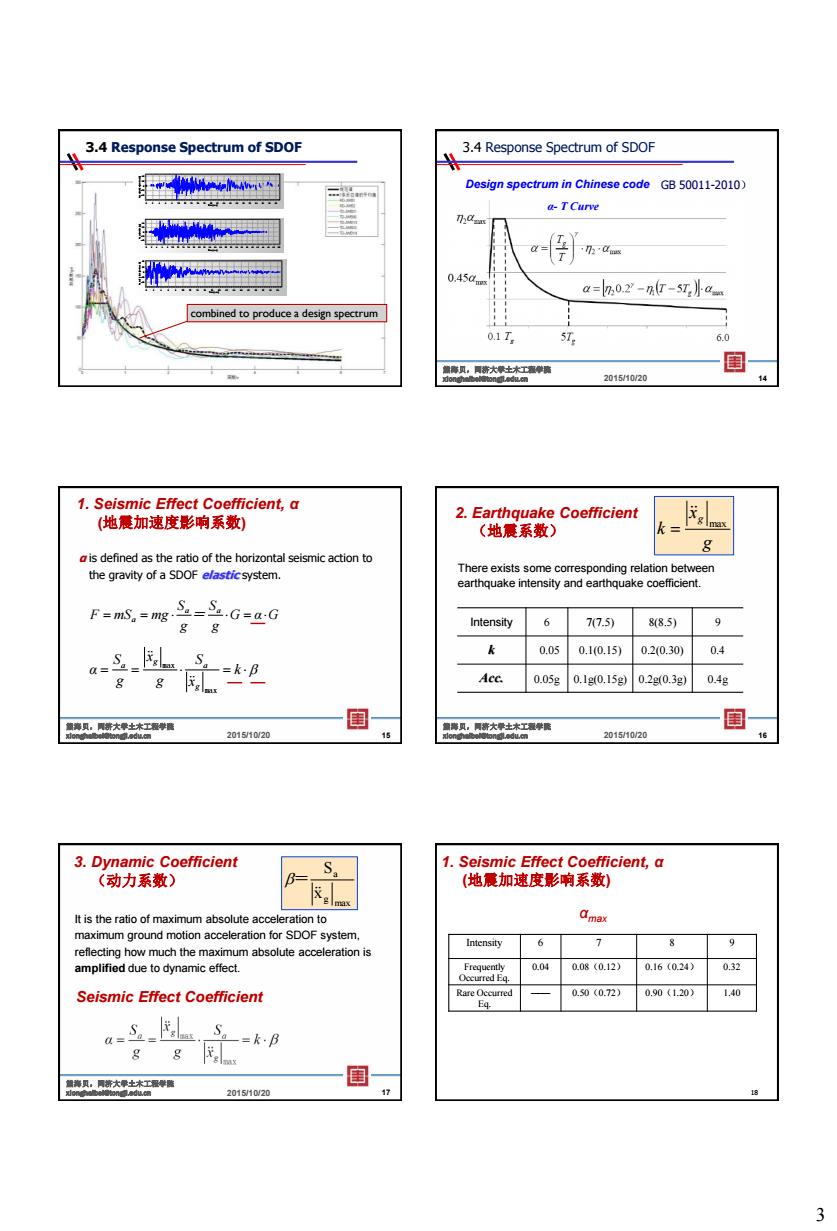
3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF spectrum in Chinese code GB50011-2010 a=.o--s可a combined to producea desn spectrum 01T 20151020 1.Seismic Effect Coefficient,a (地晨加速度影响系数) 2t8 Coomc1et人 只 ais defined as the ratio of the horizontal seismic action to the gravity of a SDOF elasticsystem. Intensity 6 7(7.5)8(85)9 斗t k0.050.10.15020.3004 4c005g01g0,15g02g0.3g04g8 大用 2015/10w20 20151020 3.Dynamic Coefficient 1.Seismic Effect Coefficient,a (动力系数) S, (地震加速度影响系数) 004 (0.12) 016(024)0.2 Seismic Effect Coefficient a-s- =kB 20110y20 3
3 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF Time [sec] 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 Acceleration [cm/sec2]40 20 0 -20 -40 Time [sec] 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 Acceleration [g] 40 20 0 -20 -40 Time [sec] 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 Acceleration [cm/sec2]40 20 0 -20 -40 combined to produce a design spectrum 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF Design spectrum in Chinese code 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 14 GB 50011-2010) α- T Curve α is defined as the ratio of the horizontal seismic action to the gravity of a SDOF elastic system. G α G g S = g S F mS mg a a a k x S g x g S α g a g a max max 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 15 1. Seismic Effect Coefficient, α (地震加速度影响系数) 2. Earthquake Coefficient (地震系数) There exists some corresponding relation between earthquake intensity and earthquake coefficient. Intensity 6 7(7.5) 8(8.5) 9 k 0.05 0.1(0.15) 0.2(0.30) 0.4 Acc. 0.05g 0.1g(0.15g) 0.2g(0.3g) 0.4g 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 16 g x k g max 3. Dynamic Coefficient (动力系数) It is the ratio of maximum absolute acceleration to maximum ground motion acceleration for SDOF system, reflecting how much the maximum absolute acceleration is amplified due to dynamic effect. max g a x S = 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 17 Seismic Effect Coefficient 18 αmax Intensity 6 7 8 9 Frequently Occurred Eq. 0.04 0.08(0.12) 0.16(0.24) 0.32 Rare Occurred Eq. —— 0.50(0.72) 0.90(1.20) 1.40 1. Seismic Effect Coefficient, α (地震加速度影响系数)

4.Site Predominant Period场地卓越周期 Earthquake wave is influenced with soil profile Active faults nearby, Regional geology influenc sidence(下陷性地震) 2015y10w20 几大生大 30151020 4.Site Predominant Period,Ta To emress site characteristics and the distance to epicanter Based on Chinese Seismic Code (0012010). Site Predominant oup 025.0.350.450.65 @ 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (* Response spectra are very useful tools 1 Nonlinearity of Materia If we know a singie story building's natural period,and the 2.Motion Equations of SDOF Nonlinear ding const n ste,we can find the s System(K e the the Nonlinear Motion Equations 4.Hystorosis(回)Model If we can resolve a MDOF to a family of equivalent SDOF skeletor system,then we canc e multi-story buldng's Eq.loads using 大
4 4. Site Predominant Period 场地卓越周期 Tg 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 19 Earthquake wave is influenced with soil profile: • Active faults nearby, • Soil dynamic response • Regional geology influence • Liquefaction • Landslide • Subsidence (下陷性地震) 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 20 Site Category Site Group I II III IV Group 1 0.25 0.35 0.45 0.65 Group 2 0.30 0.40 0.55 0.75 Group 3 0.35 0.45 0.65 0.90 Site Predominant Period Tg (s) 4. Site Predominant Period, Tg To express site characteristics and the distance to epicanter, It is divided to three groups, Group 1 to 3 for near-earthquake (近震) to far-earthquake (远震). Based on Chinese Seismic Code (GB 50011-2010), 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 21 0.3 6 0.05 0.9 4 32 0.05 1 0.02 ς 0.08 1.6 0.05 2 1 Attenuation index number declined slope coefficient Damping adjusting coefficient • Response spectra are very useful tools If we know a single story building’s natural period, and the building construction site, we can find the seismic effective coefficient to determine the equivalent static force (earthquake load), the we can combine the Eq. load with other loads. Then we can check the system if it meets the requirements. If we can resolve a MDOF to a family of equivalent SDOF system, then we can calculate multi-story building’s Eq. loads using Response Spectra of SDOF. 3.4 Response Spectrum of SDOF 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 23 1. Nonlinearity of Materials 2. Motion Equations of SDOF Nonlinear System (K(t)) 3. Solutions of Nonlinear Motion Equations 4. Hysteresis (滞回) Model ( ; skeleton curve (骨架曲线) and hysteretic curve (滞回曲线)) ,M ,F 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*)
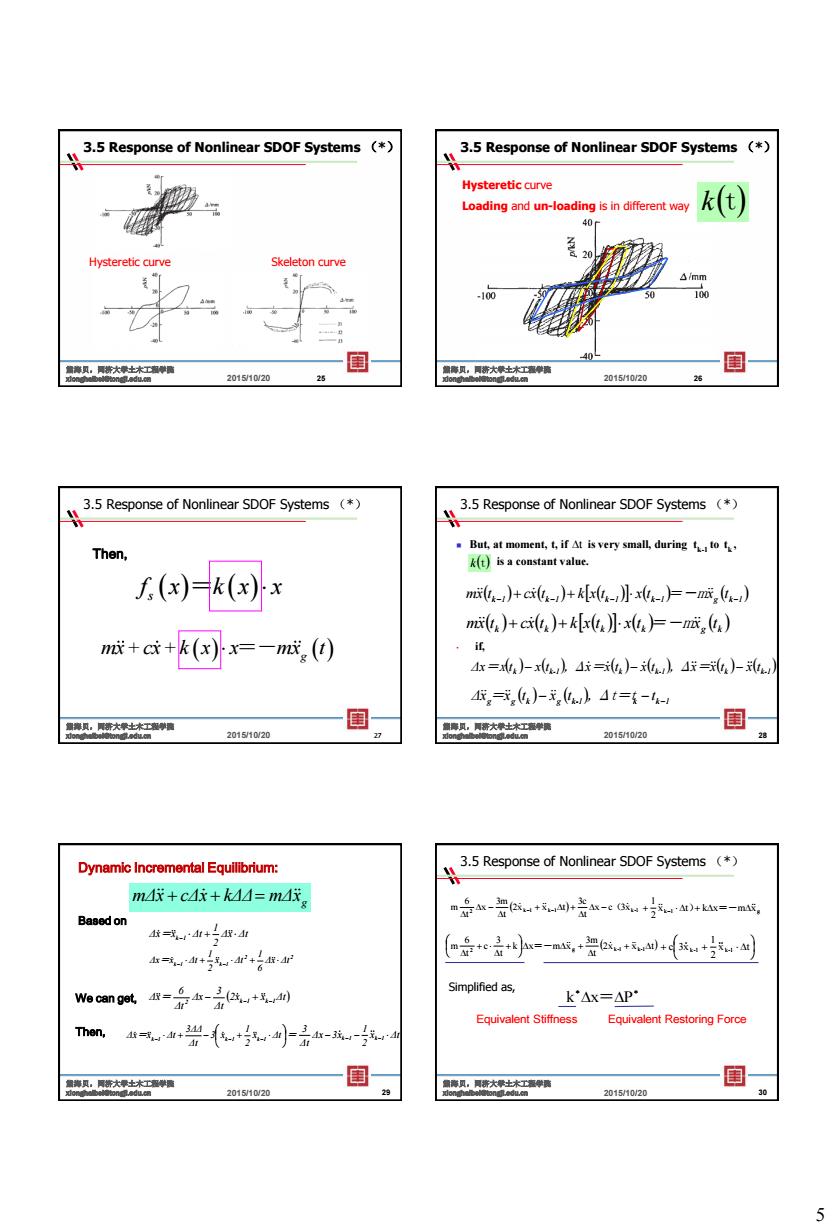
3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (* 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (* tic curve skeleton curve 国 20110/20 20151020 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (* 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (* Then, ‘的h四o ∫(x)=k(x)x mt+ct+kt}xt上-m,) mt,)+ct)+t小上一成) m成+c+k()x=一n成,() 4,=式,)-,b4t={-4- 2015/1020 国 20151020 Dynamic Incremental Equllibrium: 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems ( m4+c4+k4=m4优 Basodon 核=3M+二A·d (+e是小小=-m4+++u+ We can0--+ Simplified as. k△x=△P· Then, 兴4小-号血-玩 国 20151020 5
5 Hysteretic curve 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*) 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 25 Skeleton curve Hysteretic curve Loading and un-loading is in different way 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*) 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 26 kt 27 Then, f x k x x s = mx+cx+k x x mx t =- g 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*) 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn But, at moment, t, if is very small, during tk-1 to t k , is a constant value. k 1 k 1 k 1 k 1 g k 1 mx t cx t k x t x t =-mx t k k k k g k m x t cx t k x t x t =-m x t • if, k k-1 k k-1 k k-1 Δx=x t x t ,Δx =x t x t ,Δ x = x t x t g g k g k-1 k k 1 Δx =x t x t ,Δt=t t 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*) t kt 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 28 g mΔ x cΔx kΔΔ mΔ x Based on Δx Δt 2 1 Δx=x Δt k 1 2 2 k 1 k 1 Δx Δt 6 1 x Δt 2 1 Δx=x Δt We can get, 2x x Δt Δt 3 Δx Δt 6 Δx= 2 k1 k1 Then, x Δt 2 1 3 x Δt 3ΔΔ Δx=x Δt k 1 k 1 k 1 x Δt 2 1 Δx 3x Δt 3 = k 1 k 1 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 29 Dynamic Incremental Equilibrium: 2 k 1 k 1 3xk-1 x c t 3c 2x x t t 3m x t 6 m ( k 1 k x m xg x t 2 1 ) =- 2x x t t 3m k x m x t 3 c t 6 m 2 g k-1 k-1 =- x t 2 1 c 3x k-1 k-1 k x=P Simplified as, Equivalent Stiffness Equivalent Restoring Force 2015/10/20 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 30 3.5 Response of Nonlinear SDOF Systems (*)