
2.阅读的眼动研究 /96 心理学家对阅读的眼动研究可以追溯到19 世纪,较著名的书有1897年Quantzl的《阅读 心理学中的问题》,1906年Dearborn的《阅 读心理学》和1908年Huey的《阅读心理学 和教育学》。 最近二十多年来,随着认知心理学的兴起, 心理学家开始重视眼动与知觉及其认知之 间的关系。在阅读的研究中,心理学家利 用眼动参数来反映认知加工的过程
2. 阅读的眼动研究 心理学家对阅读的眼动研究可以追溯到19 世纪,较著名的书有1897年Quantz的《阅读 心理学中的问题》,1906年Dearborn的《阅 读心理学》和1908年Huey的《阅读心理学 和教育学》。 最近二十多年来,随着认知心理学的兴起, 心理学家开始重视眼动与知觉及其认知之 间的关系。在阅读的研究中,心理学家利 用眼动参数来反映认知加工的过程
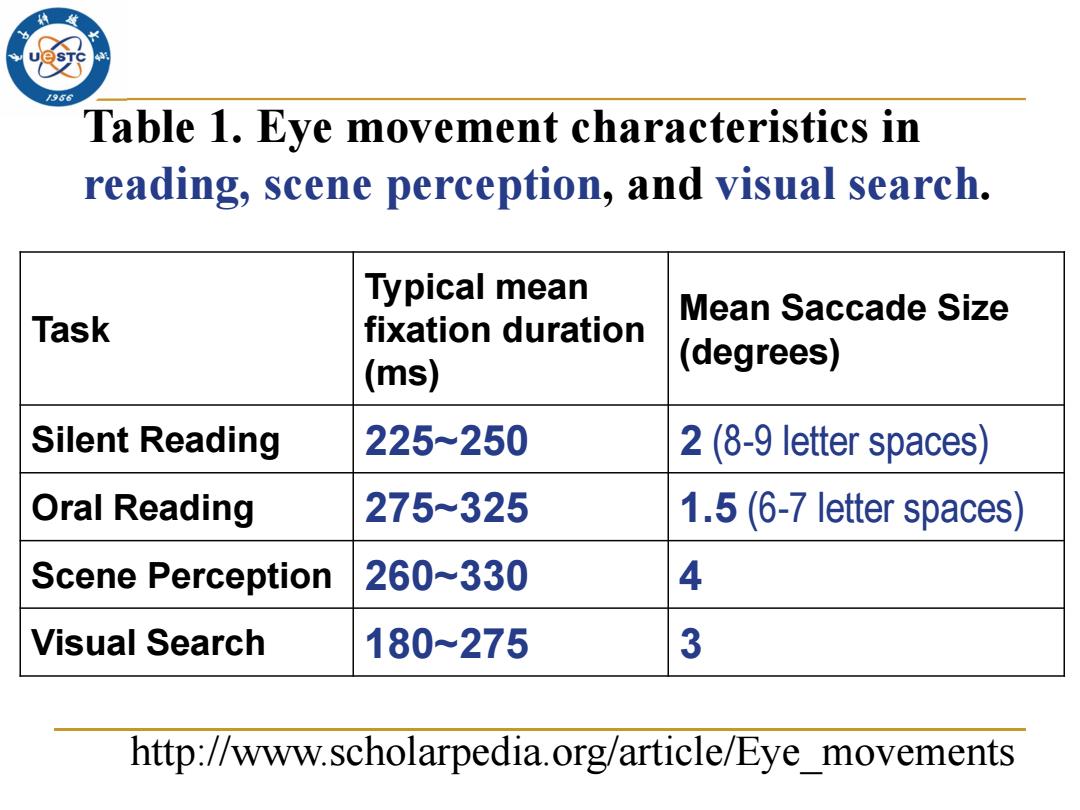
Table 1.Eye movement characteristics in reading,scene perception,and visual search. Typical mean Mean Saccade Size Task fixation duration (ms) (degrees) Silent Reading 225~250 2(8-9 letter spaces) Oral Reading 275-325 1.5 (6-7 letter spaces) Scene Perception 260~330 4 Visual Search 180~275 3 http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Eye_movements
Task Typical mean fixation duration (ms) Mean Saccade Size (degrees) Silent Reading 225~250 2 (8-9 letter spaces) Oral Reading 275~325 1.5 (6-7 letter spaces) Scene Perception 260~330 4 Visual Search 180~275 3 Table 1. Eye movement characteristics in reading, scene perception, and visual search. http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Eye_movements

Reading Example: This person is reading the text for understanding So even though not every word is fixated,the amount of time spent on each-word is indicative of the processing of the word. Skimming Example: This person is skimming the text.This is most obvious from the pattern of fixations that are more dispersed and shorter fixation durations that is typical for this type of reading.The main gist maybe understood,but poorer memory for the text usually results

/956 While reading,about 10-15%of the time readers move their eyes back (regress)to previously read material in the text.These regressions,as they are called,tend to depend on the difficulty of the text. As would be expected,saccade size and fixation duration are also both modulated by text difficulty:as the text becomes more difficult,saccade size decreases,fixation durations increase,and regressions increase
While reading, about 10-15% of the time readers move their eyes back (regress) to previously read material in the text. These regressions, as they are called, tend to depend on the difficulty of the text. As would be expected, saccade size and fixation duration are also both modulated by text difficulty: as the text becomes more difficult, saccade size decreases, fixation durations increase, and regressions increase

/956 Studies have demonstrated that English readers acquire useful information from an asymmetrical region around the fixation point:extending 3-4 character spaces to the left of fixation and about 14-15 character spaces to the right. Research has also found that readers do not utilize information from the words on the line below the currently fixated line (Pollatsek,Raney,LaGasse,Rayner, 1993)
Studies have demonstrated that English readers acquire useful information from an asymmetrical region around the fixation point: extending 3-4 character spaces to the left of fixation and about 14-15 character spaces to the right. Research has also found that readers do not utilize information from the words on the line below the currently fixated line (Pollatsek, Raney, LaGasse, & Rayner, 1993)