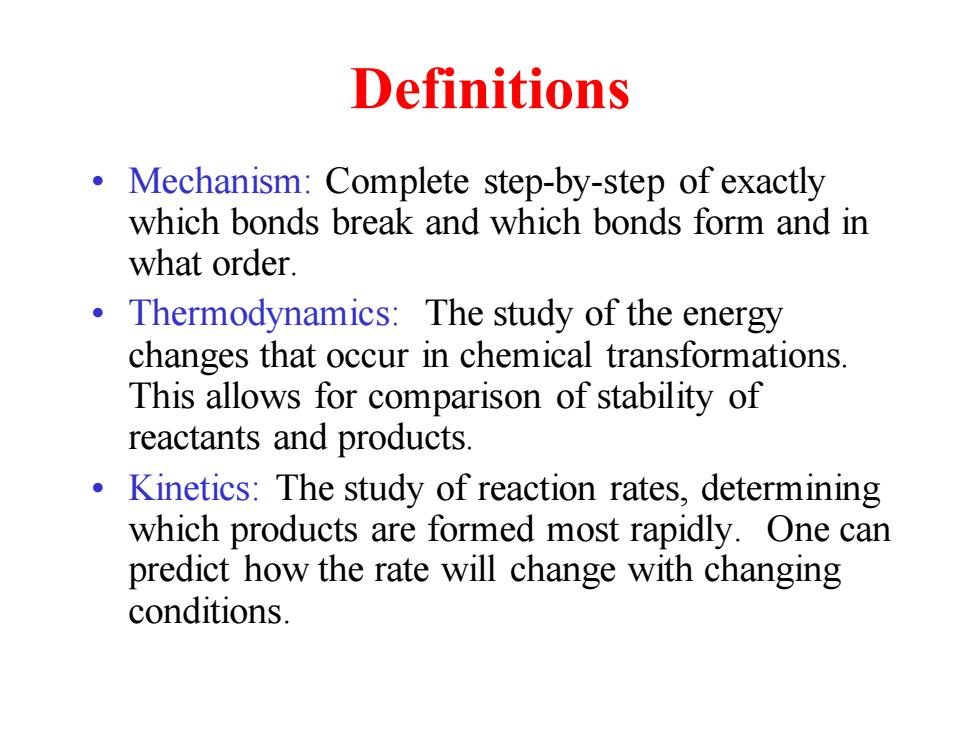
Definitions Mechanism:Complete step-by-step of exactly which bonds break and which bonds form and in what order. 。 Thermodynamics:The study of the energy changes that occur in chemical transformations. This allows for comparison of stability of reactants and products. Kinetics:The study of reaction rates,determining which products are formed most rapidly.One can predict how the rate will change with changing conditions
Definitions • Mechanism: Complete step-by-step of exactly which bonds break and which bonds form and in what order. • Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that occur in chemical transformations. This allows for comparison of stability of reactants and products. • Kinetics: The study of reaction rates, determining which products are formed most rapidly. One can predict how the rate will change with changing conditions
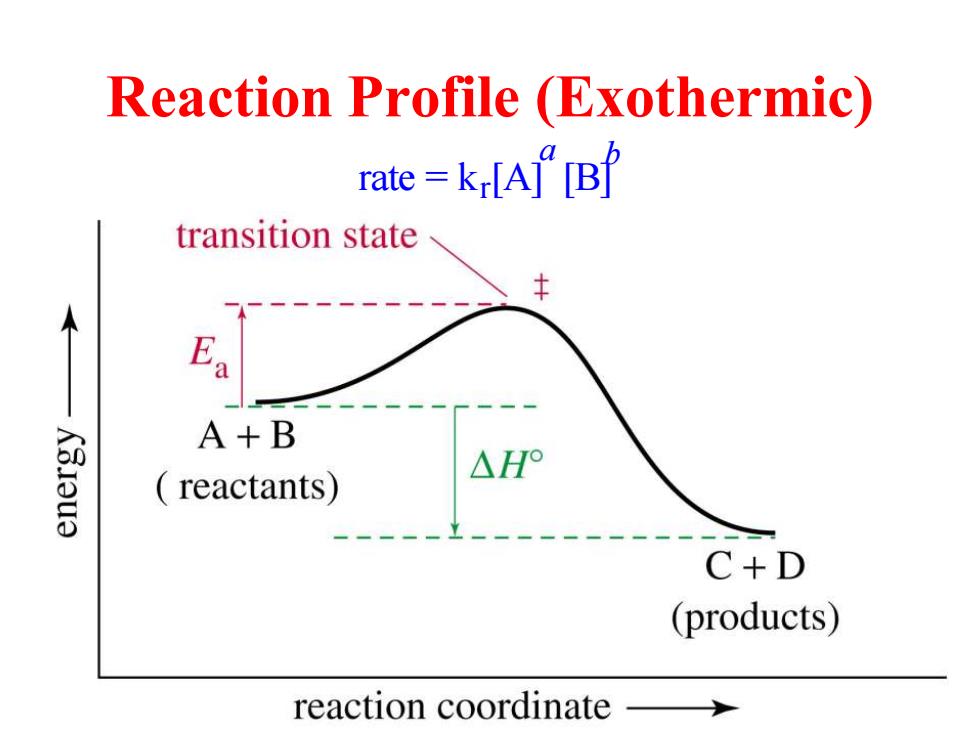
Reaction Profile (Exothermic) rate=krA”B transition state A+B K3.Iu3 △H reactants) C+D (products) reaction coordinate
Reaction Profile (Exothermic) rate = kr [A] [B] a b
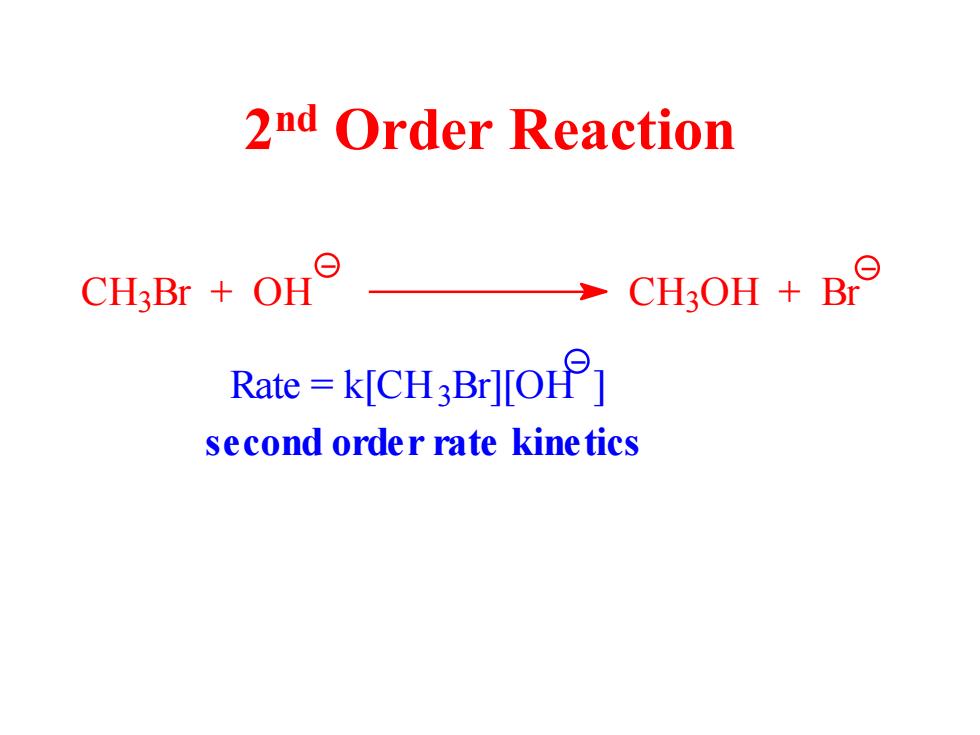
2nd Order Reaction CH3Br OH CH3OH B Rate=kICH3Br][O] second order rate kinetics
2 nd Order Reaction C H3 Br + OH C H3 OH + Br Rate = k[CH3 Br][OH ] second order rate kinetics
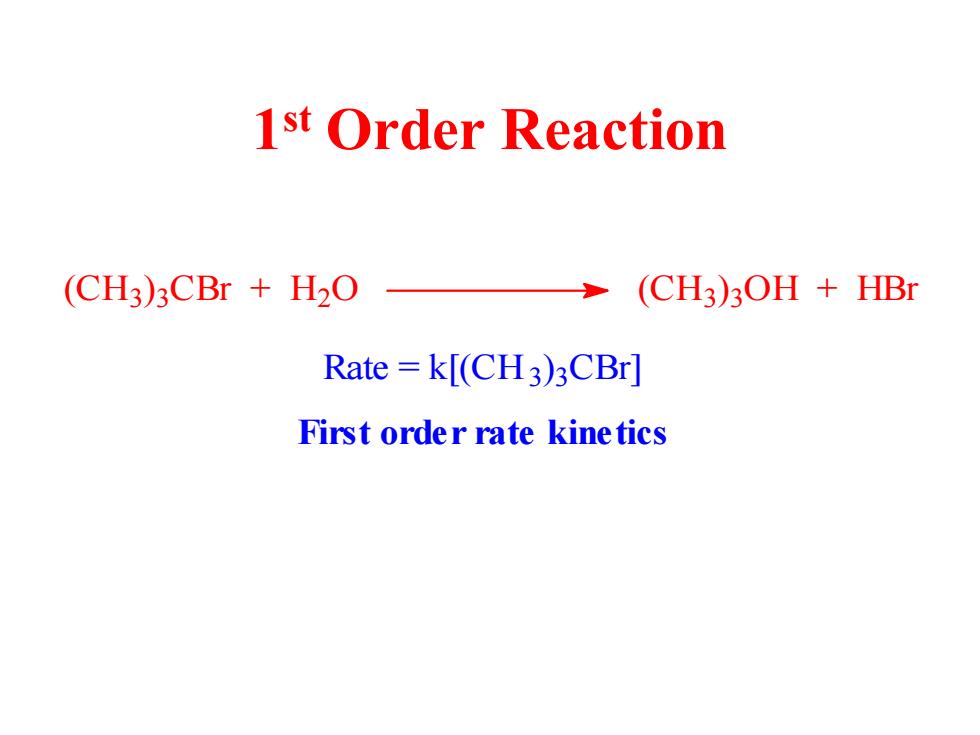
1st Order Reaction (CH3)3CBr H2O (CH3)3OH +HBr Rate=k[(CH3)3CBr] First order rate kinetics
1 st Order Reaction (CH3) 3 CBr + H2 O (CH3) 3 OH + HBr Rate = k[(CH3) 3 CBr] First order rate kinetics
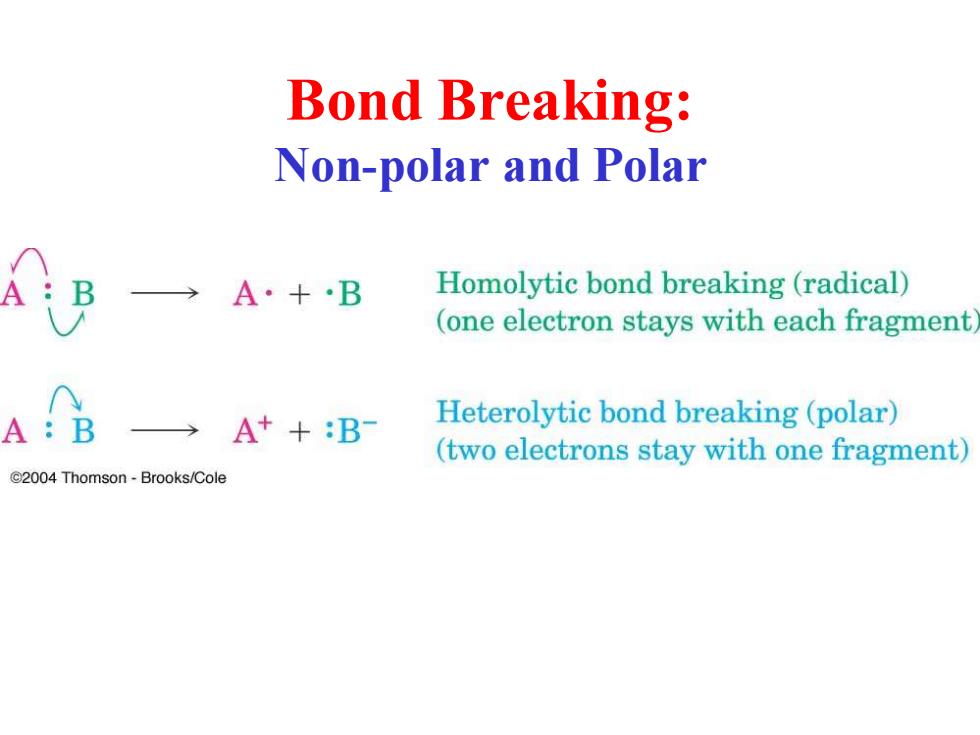
Bond Breaking: Non-polar and Polar →A·+·B Homolytic bond breaking (radical) (one electron stays with each fragment A:B →A++:B Heterolytic bond breaking(polar) (two electrons stay with one fragment) 2004 Thomson-Brooks/Cole
Bond Breaking: Non-polar and Polar