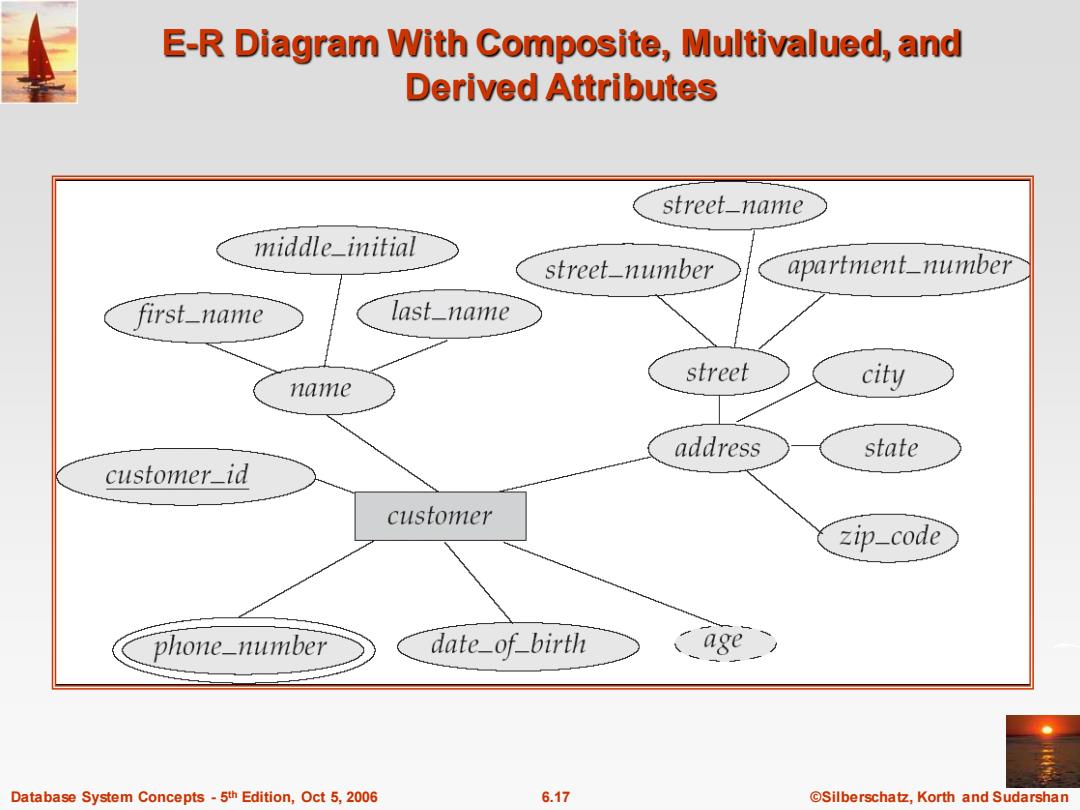
E-R Diagram With Composite,Multivalued,and Derived Attributes street_name middle_initial street_number apartment_number first_name last_name street name city address state customer_id customer zip_code phone_number date_of birth age Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 6.17 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 6.17 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 E-R Diagram With Composite, Multivalued, and Derived Attributes
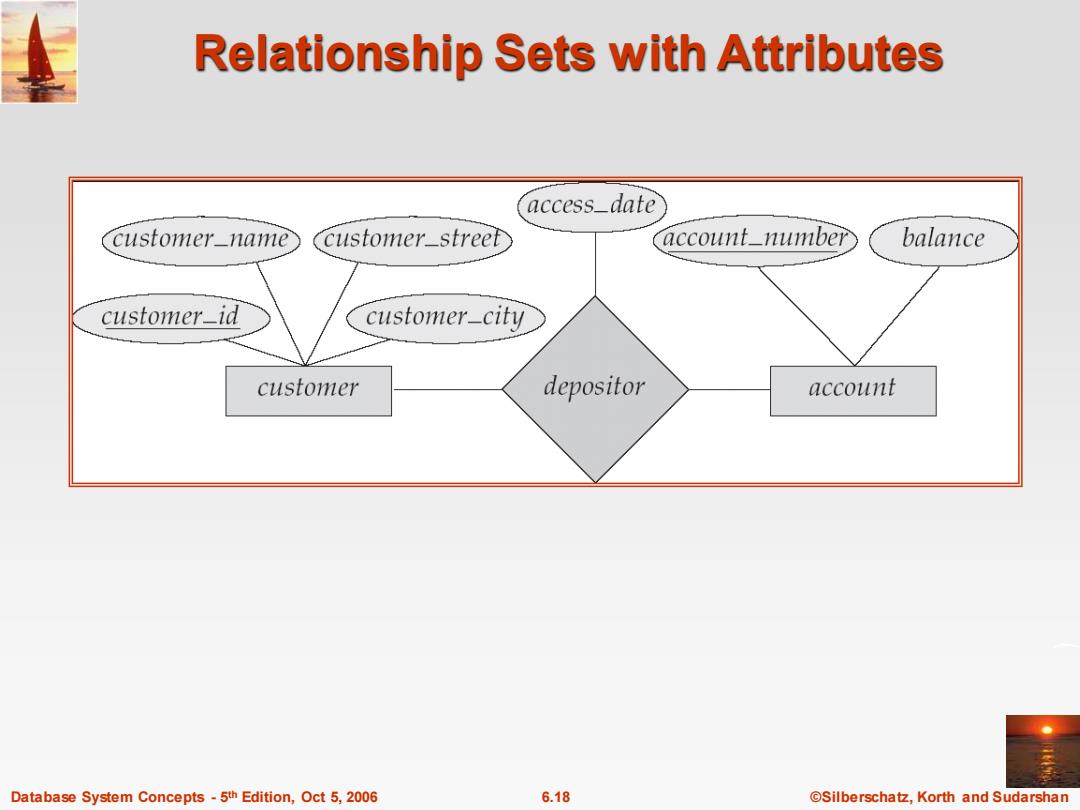
Relationship Sets with Attributes access_date customer_name Ccustomer_streef account_number balance customer_id customer-city customer depositor account Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 6.18 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 6.18 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Relationship Sets with Attributes
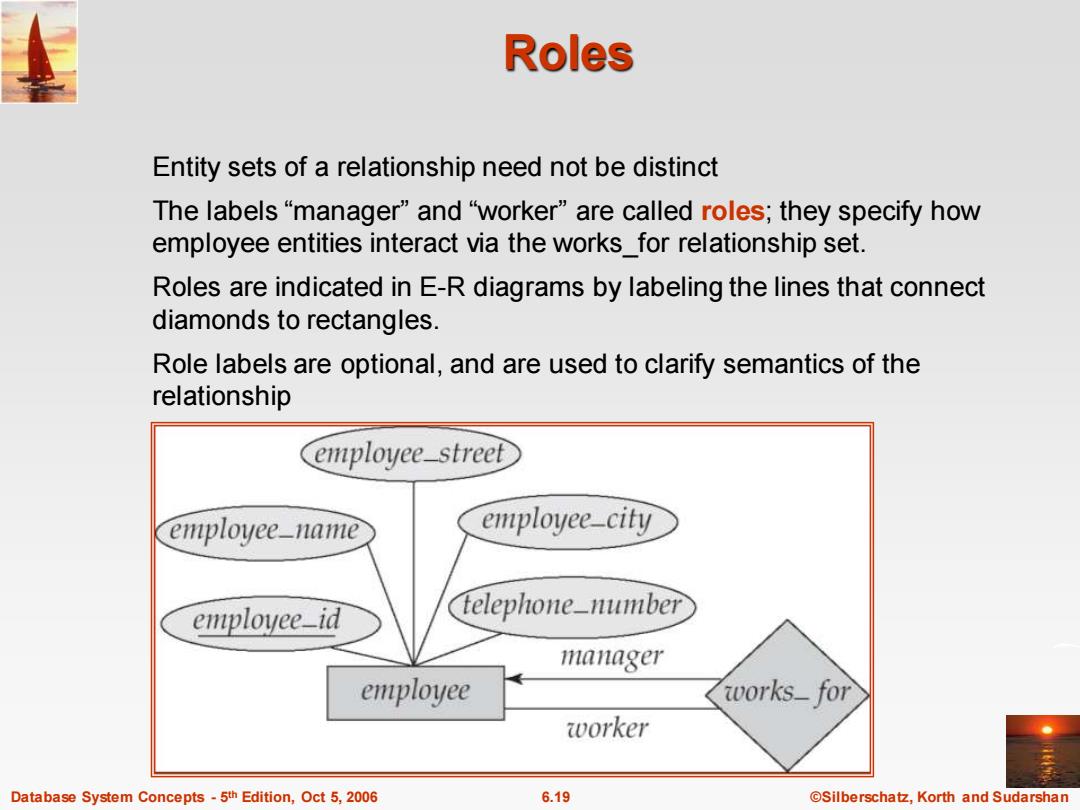
Roles Entity sets of a relationship need not be distinct The labels“manager”and“worker"”are called roles;they specify how employee entities interact via the works_for relationship set. Roles are indicated in E-R diagrams by labeling the lines that connect diamonds to rectangles. Role labels are optional,and are used to clarify semantics of the relationship employee street employee-name employee-city employee-id telephone_number manager employee works_for worker Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 6.19 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 6.19 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Roles Entity sets of a relationship need not be distinct The labels “manager” and “worker” are called roles; they specify how employee entities interact via the works_for relationship set. Roles are indicated in E-R diagrams by labeling the lines that connect diamonds to rectangles. Role labels are optional, and are used to clarify semantics of the relationship

Cardinality Constraints We express cardinality constraints by drawing either a directed line (> signifying“one,”or an undirected line(-),signifying“many,”between the relationship set and the entity set. One-to-one relationship: A customer is associated with at most one loan via the relationship borrower A loan is associated with at most one customer via borrower Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 6.20 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 6.20 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Cardinality Constraints We express cardinality constraints by drawing either a directed line (→), signifying “one,” or an undirected line (—), signifying “many,” between the relationship set and the entity set. One-to-one relationship: A customer is associated with at most one loan via the relationship borrower A loan is associated with at most one customer via borrower
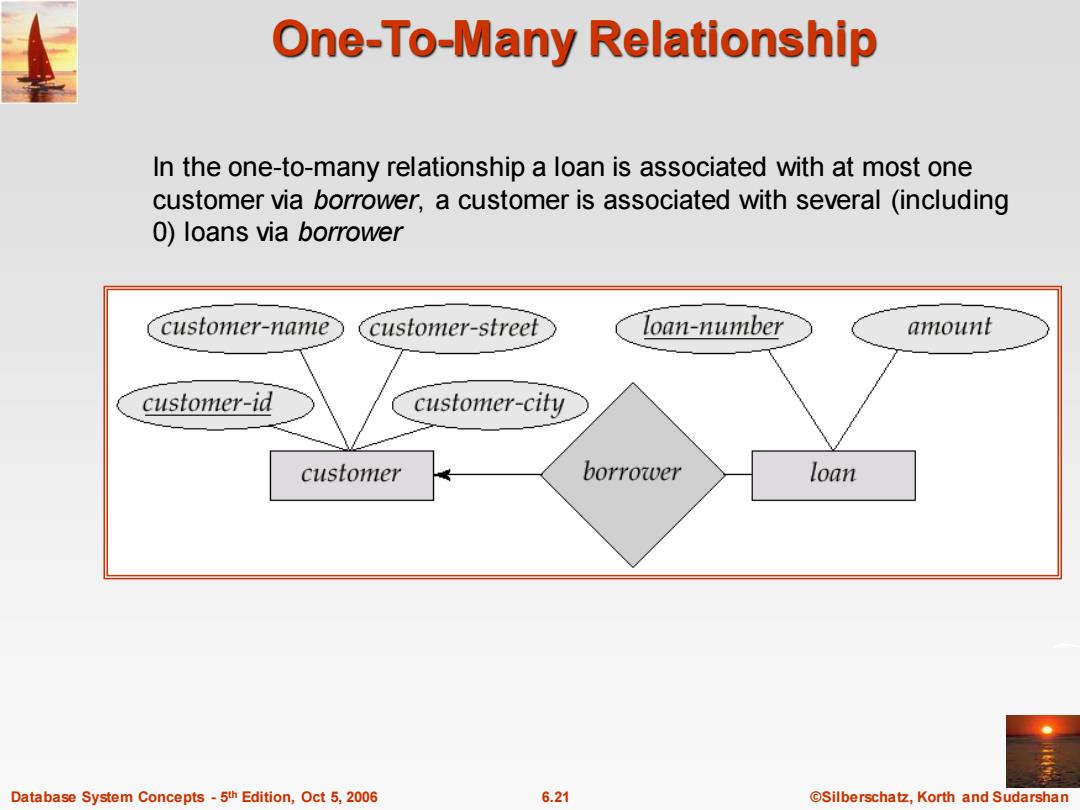
One-To-Many Relationship In the one-to-many relationship a loan is associated with at most one customer via borrower,a customer is associated with several (including 0)loans via borrower customer-name customer-street loan-number amount customer-id customer-city customer borrower loan Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 6.21 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 6.21 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 One-To-Many Relationship In the one-to-many relationship a loan is associated with at most one customer via borrower, a customer is associated with several (including 0) loans via borrower