
Ease of Use Estimating next year's dividend is straightforward,but estimating next year's price appears to be much more difficult The problem is that next year's price is obtained (eventually)by estimating,and discounting,every future dividend THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 16
Ease of Use Estimating next year’s dividend is straightforward, but estimating next year’s price appears to be much more difficult The problem is that next year’s price is obtained (eventually) by estimating, and discounting, every future dividend THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 16
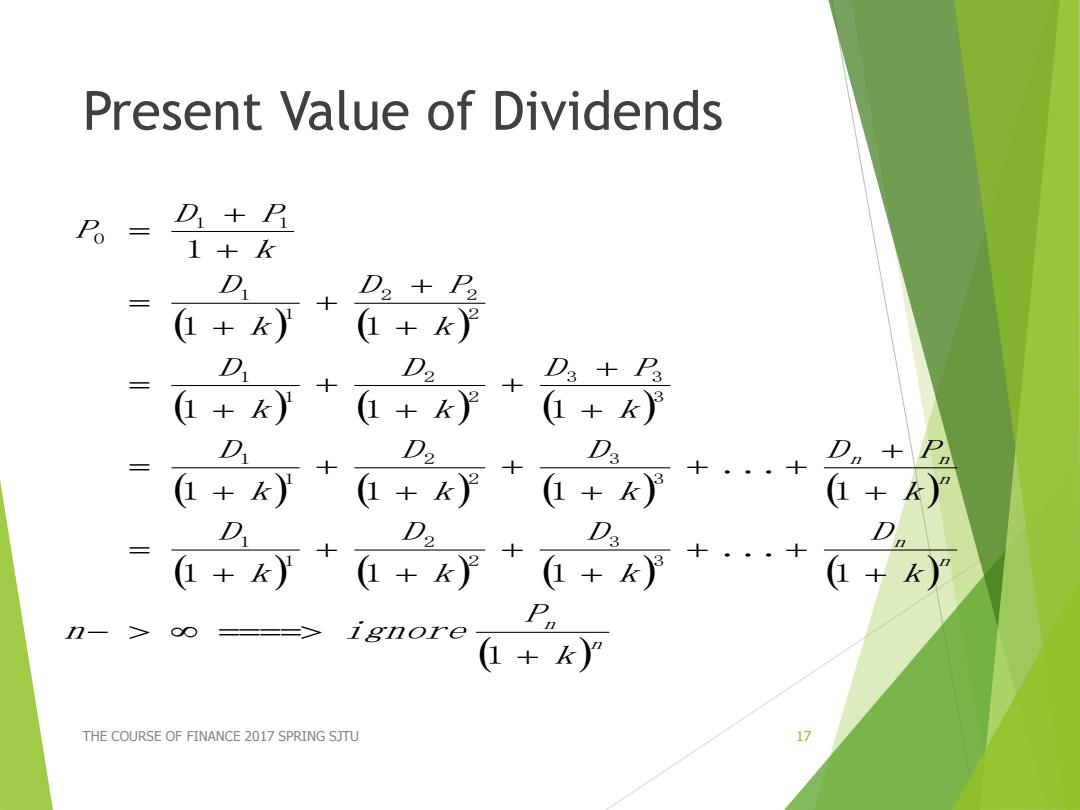
Present value of Dividends B = D+P 1+k D D2+2 三 十 (+k) (+k) D D2 十 D3+P3 三 1+k3 D D. D2 D+P 三 +)++y+十++ 1+k) D D2 D. D +)++k+++·++ P n-> ==> ignore(ky THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 17
Present Value of Dividends THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 17 n n n n n n n k P n ignore k D k D k D k D k D P k D k D k D k D P k D k D k D P k D k D P P 1 1 ... 1 1 1 1 ... 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 2 2 1 1 3 3 2 2 1 1 3 3 3 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 0
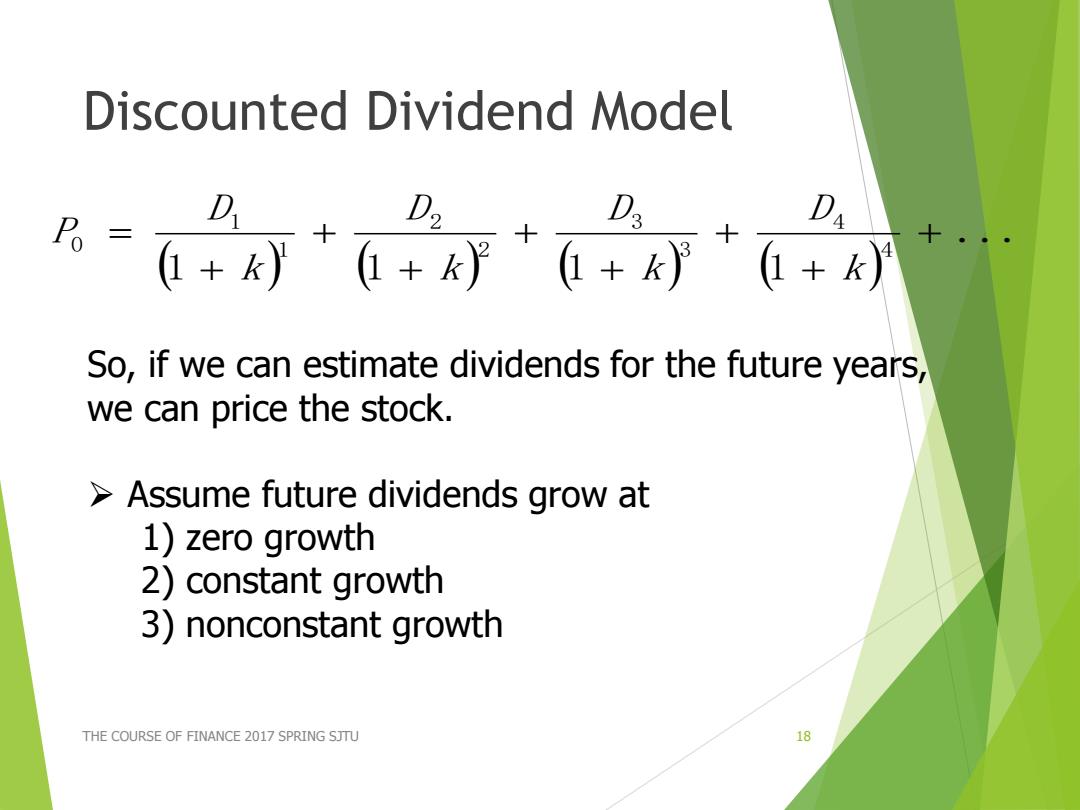
Discounted Dividend Model D D2 D D B=+灯++好+0+)+ So,if we can estimate dividends for the future years, we can price the stock. Assume future dividends grow at 1)zero growth 2)constant growth 3)nonconstant growth THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 18
Discounted Dividend Model THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 18 ... 1 1 1 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 k D k D k D k D P So, if we can estimate dividends for the future years, we can price the stock. Assume future dividends grow at 1) zero growth 2) constant growth 3) nonconstant growth

Zero Growth If dividends are expected at regular intervals forever,then this is a perpetuity and the present value of expected future dividends can be found using the perpetuity formula Po=D/K D Suppose stock is expected to pay a $0.50 dividend every quarter and the required return is 10%with quarterly compounding. What is the price? DP0=.50/(.1/4)=$20 8-19
Zero Growth If dividends are expected at regular intervals forever, then this is a perpetuity and the present value of expected future dividends can be found using the perpetuity formula P0 = D / K Suppose stock is expected to pay a $0.50 dividend every quarter and the required return is 10% with quarterly compounding. What is the price? P0 = .50 / (.1 / 4) = $20 8-19
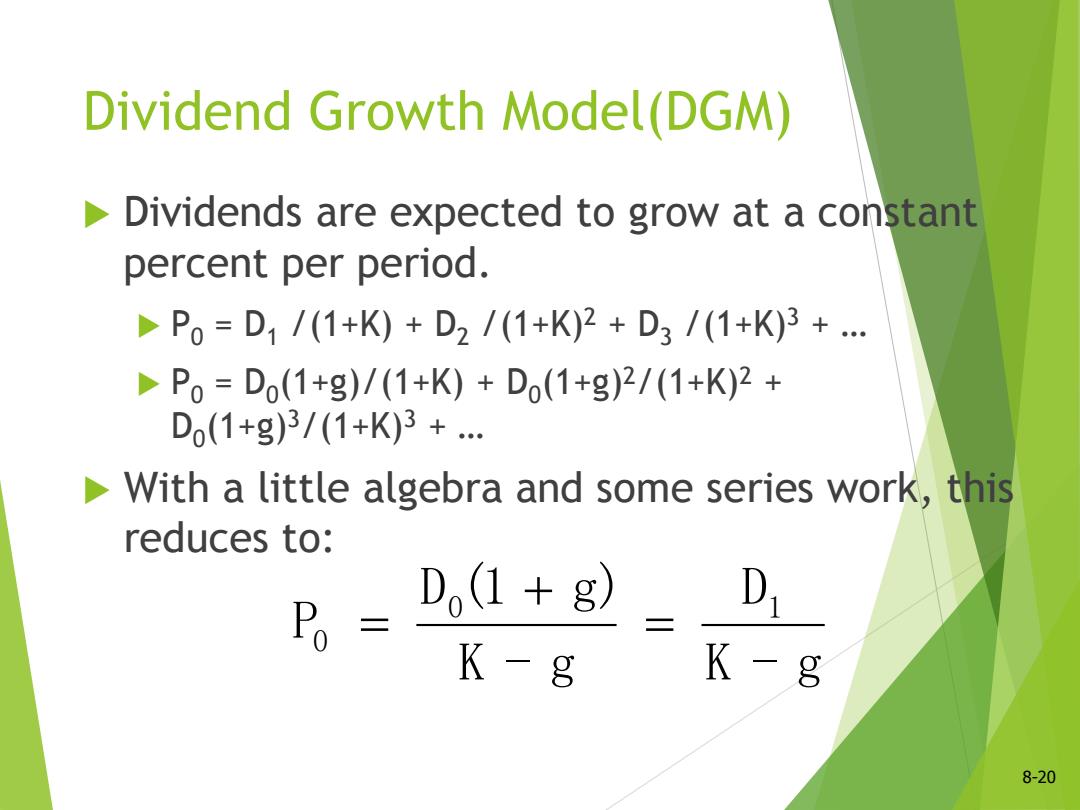
Dividend Growth Model(DGM) Dividends are expected to grow at a constant percent per period. DP0=D1/(1+K)+D2/(1+K)2+D3/(1+K)3+… DP0=D(1+g)/(1+K)+Do(1+g)2/(1+K)2+ D(1+g)3/(1+K)3+… With a little algebra and some series work,this reduces to: D(1+g) K-8 K-8 8-20
Dividend Growth Model(DGM) Dividends are expected to grow at a constant percent per period. P0 = D1 /(1+K) + D2 /(1+K)2 + D3 /(1+K)3 + … P0 = D0 (1+g)/(1+K) + D0 (1+g)2/(1+K)2 + D0 (1+g)3/(1+K)3 + … With a little algebra and some series work, this reduces to: K - g D K - g D (1 g) P 0 1 0 8-20