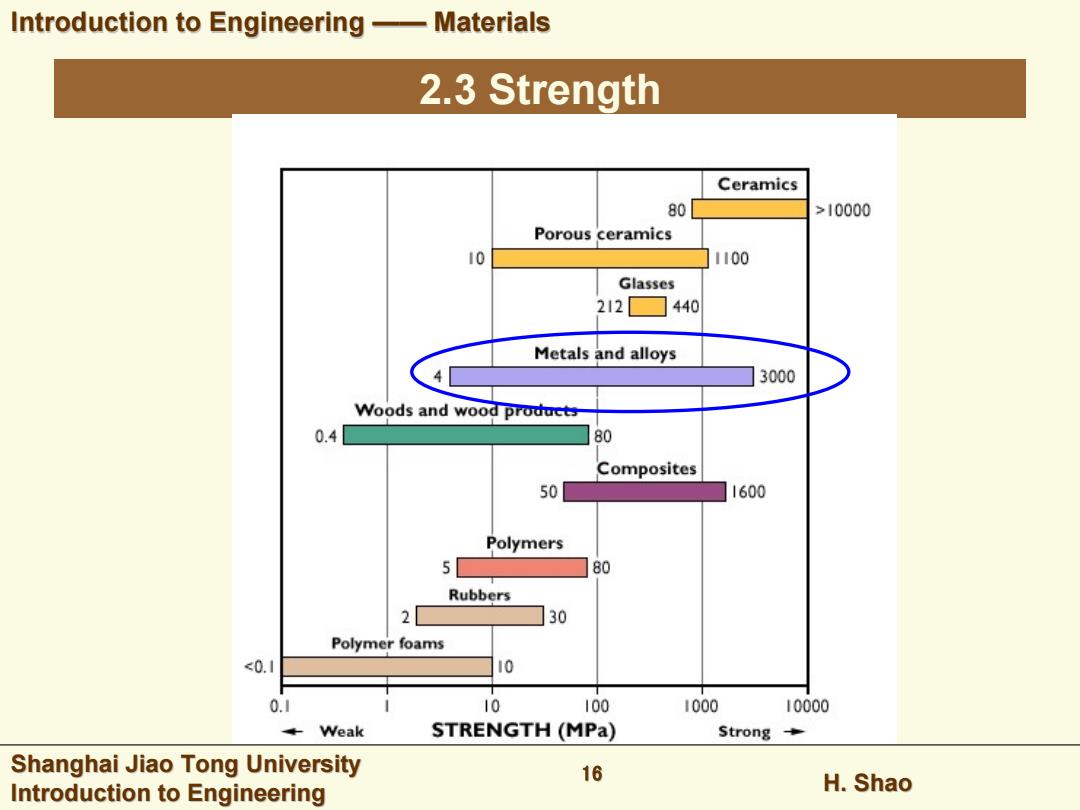
Introduction to Engineering-Materials 2.3 Strength Ceramics 80 >10000 Porous ceramics 10 1100 Glasses 212☐440 Metals and alloys 3000 Woods and wood products 0.4 80 Composites 50 1600 Polymers 5 80 Rubbers 2 30 Polymer foams <0.1 10 0.1 10 100 1000 10000 Weak STRENGTH(MPa) Strong Shanghai Jiao Tong University 16 Introduction to Engineering H.Shao
Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering —— Materials Materials Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai Jiao Tong University Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering H. Shao 16 2.3 Strength

Introduction to Engineering-Materials 2.4 Toughness(韧性) ■Toughness The resistance of a material to being broken in two A crack(fracture)running across the material absorbs energy ■A tough material Requires a lot of energy to break it Usually because the fracture process causes a lot of plastic deformation ■A brittle material ■May be strong But once a crack has started,the material fractures easily Because little energy is absorbed (e.g.glass). Shanghai Jiao Tong University 17 Introduction to Engineering H.Shao
Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering —— Materials Materials Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai Jiao Tong University Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering H. Shao 17 2.4 Toughness (韧性) Toughness The resistance of a material to being broken in two A crack (fracture) running across the material absorbs energy A tough material Requires a lot of energy to break it Usually because the fracture process causes a lot of plastic deformation A brittle material May be strong But once a crack has started, the material fractures easily Because little energy is absorbed (e.g. glass)

Introduction to Engineering-Materials 2.4 Toughness (韧性) Measurement (Compact Tension Test) Load Crack Fracture Shanghai Jiao Tong University 18 Introduction to Engineering H.Shao
Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering —— Materials Materials Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai Jiao Tong University Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering H. Shao 18 2.4 Toughness (韧性) Measurement (Compact Tension Test) Crack Load Fracture

Introduction to Engineering-Materials 2.4 Toughness ,(韧性) Ceramics 0.003L 0.2 Porous ceramics <0.001 0.04 Glasses 0.004 0.008 Metals and alloys 0.34 145 Composites 8 60 Woods and wood products 0.005 3.4 Polymers 0.1 100 Rubbers 200 Polymer foams 0.001 5 0.001 0.01 0.1 10 100 1000 Brittle TOUGHNESS (kJ/m2) Tough Shanghai Jiao Tong University 19 Introduction to Engineering H.Shao
Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering —— Materials Materials Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai Jiao Tong University Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering H. Shao 19 2.4 Toughness (韧性)

Introduction to Engineering-Materials 2.5 Elongation (延展性) Elongation to failure A measure of the ductility of a materials It is the amount of strain it can experience before failure in tensile testing. A ductile material(most metals and polymers)will record a high elongation ■ Brittle materials like ceramics tend to show very low elongation because they do not plastically deform Shanghai Jiao Tong University 20 Introduction to Engineering H.Shao
Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering —— Materials Materials Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai Jiao Tong University Introduction to Engineering Introduction to Engineering H. Shao 20 2.5 Elongation (延展性) Elongation to failure – A measure of the ductility of a materials – It is the amount of strain it can experience before failure in tensile testing. A ductile material (most metals and polymers) will record a high elongation Brittle materials like ceramics tend to show very low elongation because they do not plastically deform