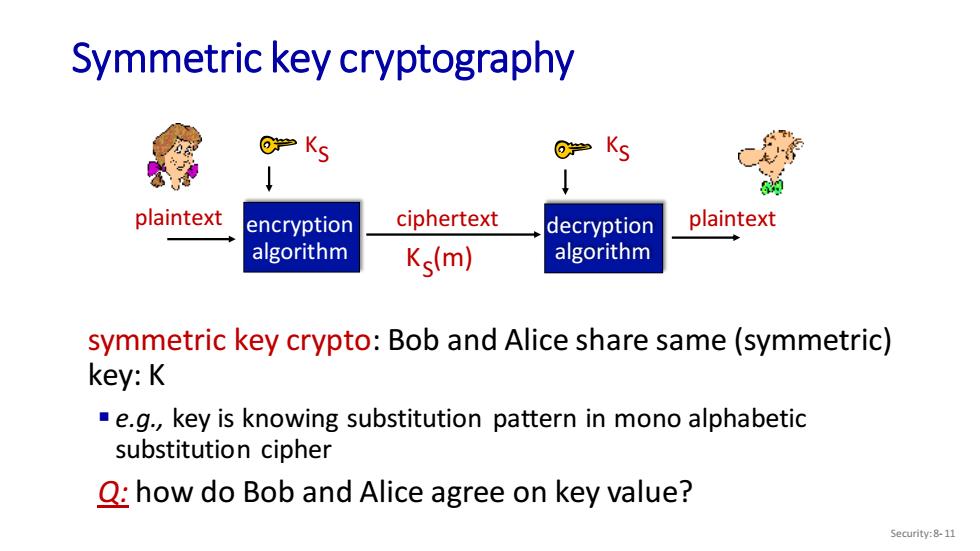
Symmetric key cryptography ⑥学Ks ≥Ks plaintext encryption ciphertext decryption plaintext algorithm Ks(m) algorithm symmetric key crypto:Bob and Alice share same(symmetric) key:K "e.g.,key is knowing substitution pattern in mono alphabetic substitution cipher Q:how do Bob and Alice agree on key value? Security:8-11
Symmetric key cryptography plaintext plaintext K S encryption algorithm decryption algorithm KS ciphertext K (m) S symmetric key crypto: Bob and Alice share same (symmetric) key: K ▪ e.g., key is knowing substitution pattern in mono alphabetic substitution cipher Q: how do Bob and Alice agree on key value? Security: 8- 11

Simple encryption scheme substitution cipher:substituting one thing for another monoalphabetic cipher:substitute one letter for another plaintext:abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ciphertext:mnbvcxzasdfghjklpoiuytrewq e.g.:Plaintext:bob.i love you.alice ciphertext:nkn.s gktc wky.mgsbc Encryption key:mapping from set of 26 letters to set of 26 letters Security:8-12
Simple encryption scheme substitution cipher: substituting one thing for another ▪ monoalphabetic cipher: substitute one letter for another plaintext: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ciphertext: mnbvcxzasdfghjklpoiuytrewq Plaintext: bob. i love you. alice ciphertext: nkn. s gktc wky. mgsbc e.g.: Encryption key: mapping from set of 26 letters to set of 26 letters Security: 8- 12
A more sophisticated encryption approach n substitution ciphers,M,M2,...,M cycling pattern: ·eg,n=4:M1,M3M4a,M3,M2iM1vM3,M4M3,M2i… -for each new plaintext symbol,use subsequent substitution pattern in cyclic pattern dog:d from M,o from M3,g from Ma Encryption key:n substitution ciphers,and cyclic pattern key need not be just n-bit pattern Security:8-13
A more sophisticated encryption approach Security: 8- 13 ▪n substitution ciphers, M1 ,M2 ,…,Mn ▪cycling pattern: • e.g., n=4: M1 ,M3 ,M4 ,M3 ,M2 ; M1 ,M3 ,M4 ,M3 ,M2 ; .. ▪for each new plaintext symbol, use subsequent substitution pattern in cyclic pattern • dog: d from M1 , o from M3 , g from M4 Encryption key: n substitution ciphers, and cyclic pattern • key need not be just n-bit pattern

Symmetric key crypto:DES DES:Data Encryption Standard US encryption standard [NIST 1993] 56-bit symmetric key,64-bit plaintext input -block cipher with cipher block chaining ■now secure is DES? DES Challenge:56-bit-key-encrypted phrase decrypted(brute force) in less than a day no known good analytic attack making DES more secure: 3DES:encrypt 3 times with 3 different keys Security:8-14
Symmetric key crypto: DES Security: 8- 14 DES: Data Encryption Standard ▪ US encryption standard [NIST 1993] ▪ 56-bit symmetric key, 64-bit plaintext input ▪ block cipher with cipher block chaining ▪ how secure is DES? • DES Challenge: 56-bit-key-encrypted phrase decrypted (brute force) in less than a day • no known good analytic attack ▪ making DES more secure: • 3DES: encrypt 3 times with 3 different keys

AES:Advanced Encryption Standard symmetric-key NIST standard,replaced DES(Nov 2001) processes data in 128 bit blocks ■128,192,or256 bit keys brute force decryption(try each key)taking 1 sec on DES, takes 149 trillion years for AES Security:8-15
AES: Advanced Encryption Standard Security: 8- 15 ▪symmetric-key NIST standard, replaced DES (Nov 2001) ▪processes data in 128 bit blocks ▪128, 192, or 256 bit keys ▪brute force decryption (try each key) taking 1 sec on DES, takes 149 trillion years for AES