
Friends and enemies:Alice,Bob,Trudy Who might Bob and Alice be? ..well,real-life Bobs and Alices! Web browser/server for electronic transactions(e.g.,on-line purchases) on-line banking client/server ■DNS servers BGP routers exchanging routing table updates ■other examples?
Friends and enemies: Alice, Bob, Trudy Who might Bob and Alice be? ▪ … well, real-life Bobs and Alices! ▪ Web browser/server for electronic transactions (e.g., on-line purchases) ▪ on-line banking client/server ▪ DNS servers ▪ BGP routers exchanging routing table updates ▪ other examples?

There are bad guys(and girls)out therel Q:What can a"bad guy"do? A:A lot!(recall section 1.6) eavesdrop:intercept messages actively insert messages into connection impersonation:can fake(spoof)source address in packet (or any field in packet) hijacking:"take over"ongoing connection by removing sender or receiver,inserting himself in place denial of service:prevent service from being used by others(e.g., by overloading resources)
There are bad guys (and girls) out there! Q: What can a “bad guy” do? A: A lot! (recall section 1.6) • eavesdrop: intercept messages • actively insert messages into connection • impersonation: can fake (spoof) source address in packet (or any field in packet) • hijacking: “take over” ongoing connection by removing sender or receiver, inserting himself in place • denial of service: prevent service from being used by others (e.g., by overloading resources)

Chapter 8 outline What is network security? Principles of cryptography Message integrity,authentication Securing e-mail Securing TCP connections:TLS Network layer security:IPsec -Security in wireless and mobile networks -Operational security:firewalls and IDS Security:8-8
Chapter 8 outline ▪ What is network security? ▪ Principles of cryptography ▪ Message integrity, authentication ▪ Securing e-mail ▪ Securing TCP connections: TLS ▪ Network layer security: IPsec ▪ Security in wireless and mobile networks ▪Operational security: firewalls and IDS Security: 8- 8
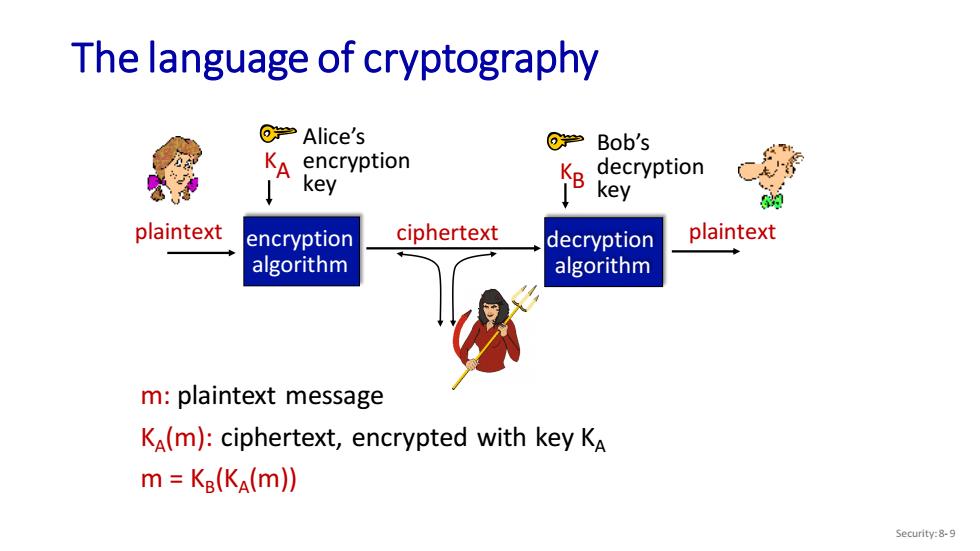
The language of cryptography @→Alice's @学Bob's KA encryption decryption key key plaintext encryption ciphertext decryption plaintext algorithm algorithm m:plaintext message KA(m):ciphertext,encrypted with key KA m KB(KA(m)) Security:8-9
The language of cryptography m: plaintext message KA (m): ciphertext, encrypted with key KA m = KB (KA (m)) plaintext ciphertext plaintext KA encryption algorithm decryption algorithm Alice’s encryption key Bob’s decryption key KB Security: 8- 9
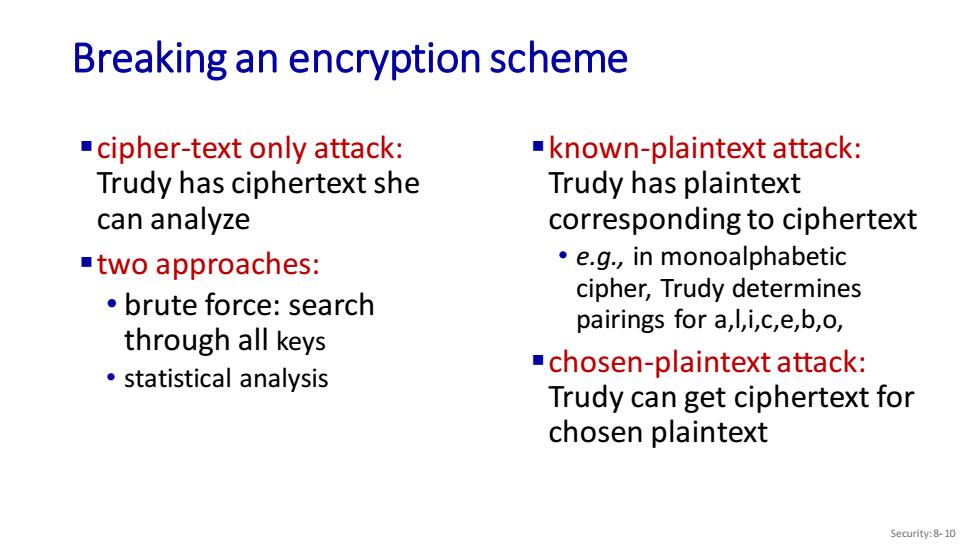
Breaking an encryption scheme cipher-text only attack: known-plaintext attack: Trudy has ciphertext she Trudy has plaintext can analyze corresponding to ciphertext two approaches: e.g.,in monoalphabetic cipher,Trudy determines 。brute force:search pairings for a,l,i,c,e,b,o, through all keys statistical analysis chosen-plaintext attack: Trudy can get ciphertext for chosen plaintext Security:8-10
Breaking an encryption scheme ▪cipher-text only attack: Trudy has ciphertext she can analyze ▪two approaches: • brute force: search through all keys • statistical analysis ▪known-plaintext attack: Trudy has plaintext corresponding to ciphertext • e.g., in monoalphabetic cipher, Trudy determines pairings for a,l,i,c,e,b,o, ▪chosen-plaintext attack: Trudy can get ciphertext for chosen plaintext Security: 8- 10