形式化开发过程 ·建立需求与系统模型之间的映射关系 -模型获取 Requirement △△△ ·从现实世界向模型表示的转化过程 capture ·形式规约 System 一模型验证 modelling ·判断模型表示是否符合需求 System ·形式证明与验证 synthesis -模型变换 ·从模型表示向计算机系统的转化过程 一一对多关系,即一个模型对应多种实现 》一致性检查 ·设计求精 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 6/112
形式化开发过程 • 建立需求与系统模型之间的映射关系 – 模型获取 • 从现实世界向模型表示的转化过程 • 形式规约 – 模型验证 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 6/112 • 判断模型表示是否符合需求 • 形式证明与验证 – 模型变换 • 从模型表示向计算机系统的转化过程 – 一对多关系,即一个模型对应多种实现 » 一致性检查 • 设计求精

规格说明技术 USTC 。 描述系统对象,对象的操作方法,以及对象的行为 -非形式化方法,称“规格说明” 一形式化方法,称“形式规约” 形式规约(Formal Specification) -描述类 ·基于数学公理和概念,通过逻辑或代数,给出系统的状态空 间,采用自动工具进行验证。 -基于代数的方法:Z、VDM、Larch -基于逻辑:一阶线性时态逻辑(FOLTL)、计算树逻辑(CTL) 一操作类:操作语义 ·基于状态和迁移,通过可执行模型描述系统,采用静态分析 和模型执行进行验证。 -基于模型:图示化,直观 一基于语言:程序,一种可执行的形式规约 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/112
规格说明技术 • 描述系统对象,对象的操作方法,以及对象的行为 – 非形式化方法,称“规格说明” – 形式化方法,称“形式规约” • 形式规约(Formal Specification) – 描述类 • 基于数学公理和概念,通过逻辑或代数,给出系统的状态空 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/112 • 基于数学公理和概念,通过逻辑或代数,给出系统的状态空 间,采用自动工具进行验证。 – 基于代数的方法:Z、VDM、Larch – 基于逻辑:一阶线性时态逻辑(FOLTL)、计算树逻辑(CTL) – 操作类:操作语义 • 基于状态和迁移,通过可执行模型描述系统,采用静态分析 和模型执行进行验证。 – 基于模型:图示化,直观 – 基于语言:程序,一种可执行的形式规约
形式证明与验证(Formal Verification&Validation) ,定理证明:可以处理无限状态空间问题 -演绎验证(deductive verification) ·采用逻辑公式表示系统规约及其性质 -工具(定理证明器,Theorem Prover) ·用户引导自动推演工具:ACL2、LP、Eves ·证明检验器:HOL、LCF、LEGO ·符合证明器:PVS ·基于分离逻辑+交互式证明:Coq 模型检验model--checking:适用于有穷状态系统 -完全自动化,验证速度快 ·检验性质不满足时,给出反例。 ·状态空间爆炸 一工具 ·时态逻辑模型检验工具:SMV/NuSMV、SPIN、UPPAAL ·行为一致性检验工具:FDR、Cospan/Formal Checker ·复合检验工具:HSIS、METAFrame 8/112
形式证明与验证(Formal Verification & Validation) • 定理证明:可以处理无限状态空间问题 – 演绎验证(deductive verification) • 采用逻辑公式表示系统规约及其性质 – 工具(定理证明器,Theorem Prover) • 用户引导自动推演工具:ACL2、LP、Eves • 证明检验器:HOL、LCF、LEGO • 符合证明器:PVS 8/112 • 符合证明器:PVS • 基于分离逻辑+交互式证明:Coq • 模型检验model-checking:适用于有穷状态系统 – 完全自动化,验证速度快 • 检验性质不满足时,给出反例。 • 状态空间爆炸 – 工具 • 时态逻辑模型检验工具:SMV/NuSMV、SPIN 、UPPAAL • 行为一致性检验工具:FDR、Cospan/Formal Checker • 复合检验工具:HSIS、METAFrame
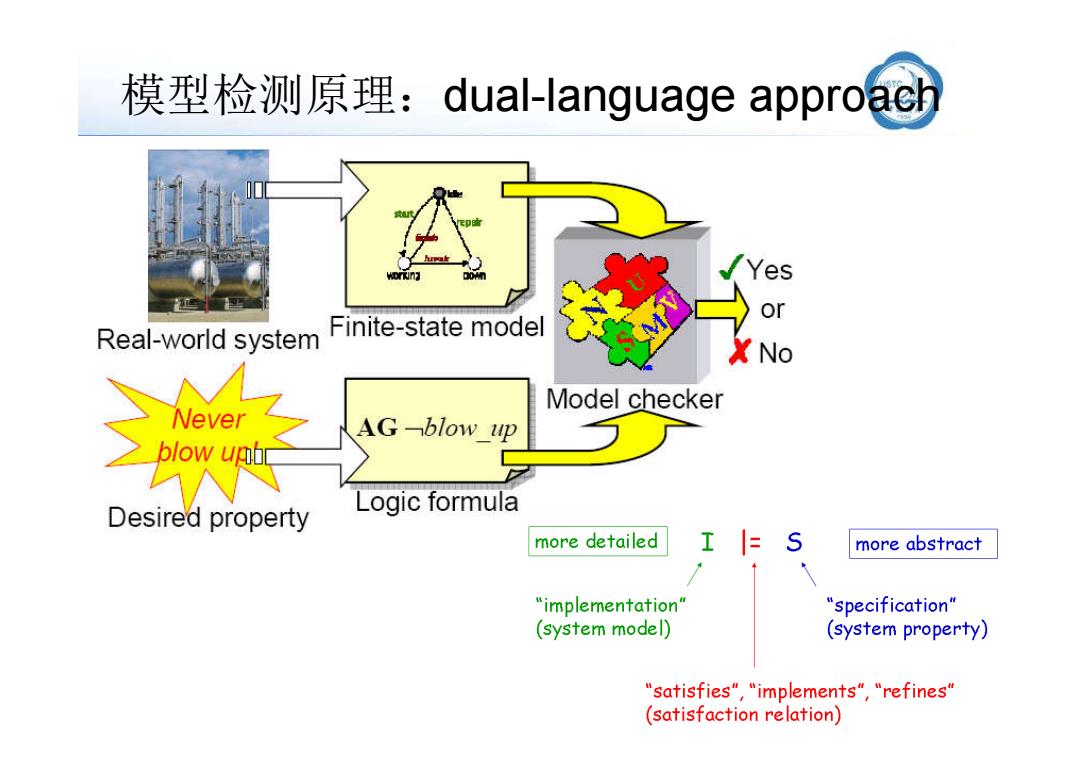
模型检测原理:dual-language approach Yes or Real-world system Finite-state model X No Model checker AGb1ow吧 Desired property Logic formula more detailed 工 more abstract “implementation" “specification'" (system model) (system property) 'satisfies","implements","refines" (satisfaction relation)
模型检测原理:dual-language approach 9/112
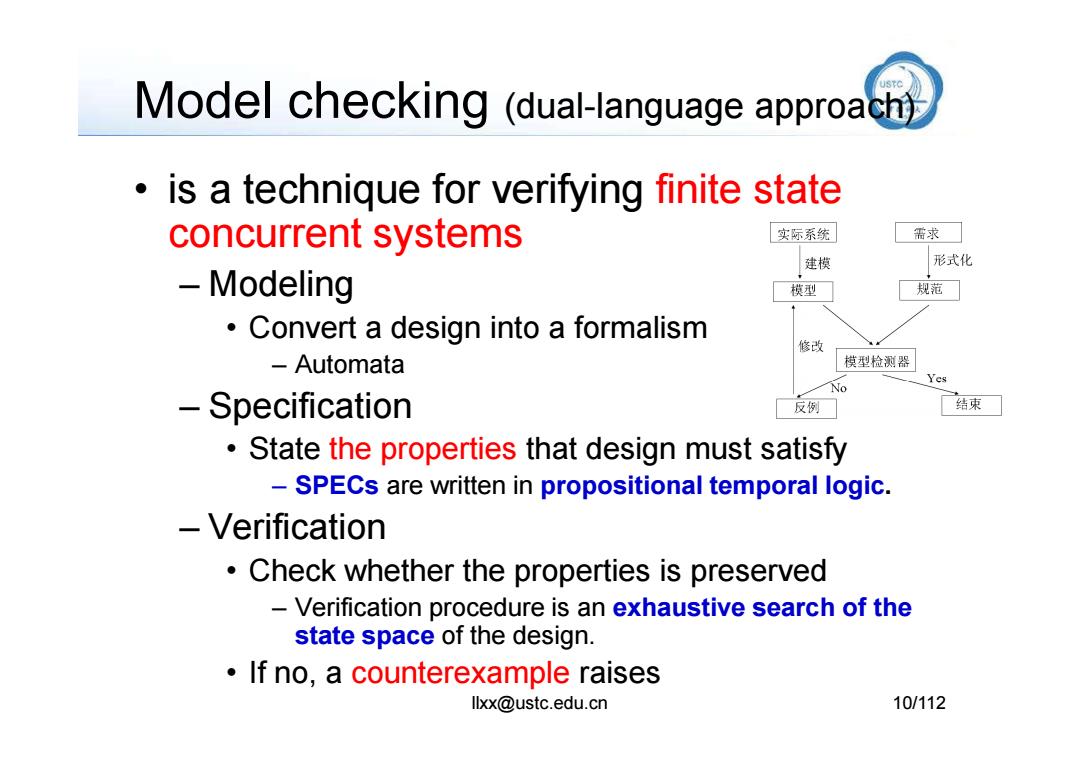
Model checking (dual-language approacm is a technique for verifying finite state concurrent systems 实际系统 需求 建模 形式化 -Modeling 模型 规范 Convert a design into a formalism 修改 -Automata 模型检测器 Yes No -Specification 反例 结束 State the properties that design must satisfy SPECs are written in propositional temporal logic. Verification Check whether the properties is preserved Verification procedure is an exhaustive search of the state space of the design. If no,a counterexample raises llxx@ustc.edu.cn 10/112
Model checking (dual-language approach) • is a technique for verifying finite state concurrent systems – Modeling • Convert a design into a formalism – Automata llxx@ustc.edu.cn 10/112 – Specification • State the properties that design must satisfy – SPECs are written in propositional temporal logic. – Verification • Check whether the properties is preserved – Verification procedure is an exhaustive search of the state space of the design. • If no, a counterexample raises