
Contents 16 Hrs Introduction Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms Pulse amplitude modulation 2-d signal waveforms M-d signal waveforms ■Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN ■Optimal receivers and probs of err UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 2
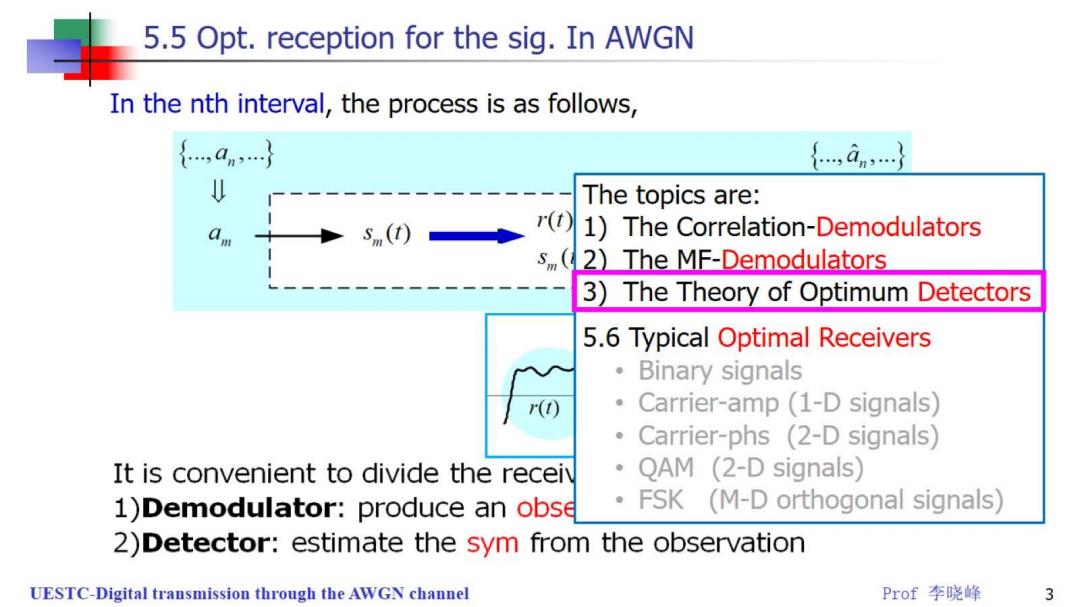
5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.In AWGN In the nth interval,the process is as follows, {,an,} {,an} The topics are: ()1)The Correlation-Demodulators s(2)The MF-Demodulators 3)The Theory of Optimum Detectors 5.6 Typical Optimal Receivers 。 Binary signals r(t) Carrier-amp(1-D signals) Carrier-phs (2-D signals) It is convenient to divide the receiv QAM (2-D signals) 1)Demodulator:produce an obse FSK (M-D orthogonal signals) 2)Detector:estimate the sym from the observation UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 3
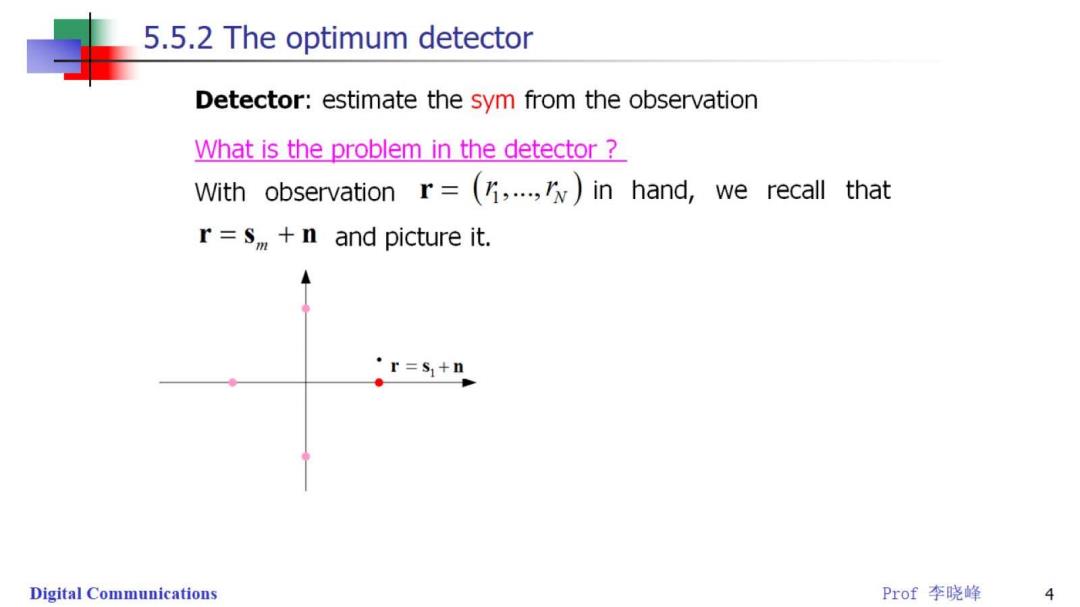
5.5.2 The optimum detector Detector:estimate the sym from the observation What is the problem in the detector With observation r=(,..,)in hand,we recall that r=s +n and picture it. ·r=s1+n Digital Communications Prof李晓峰 4
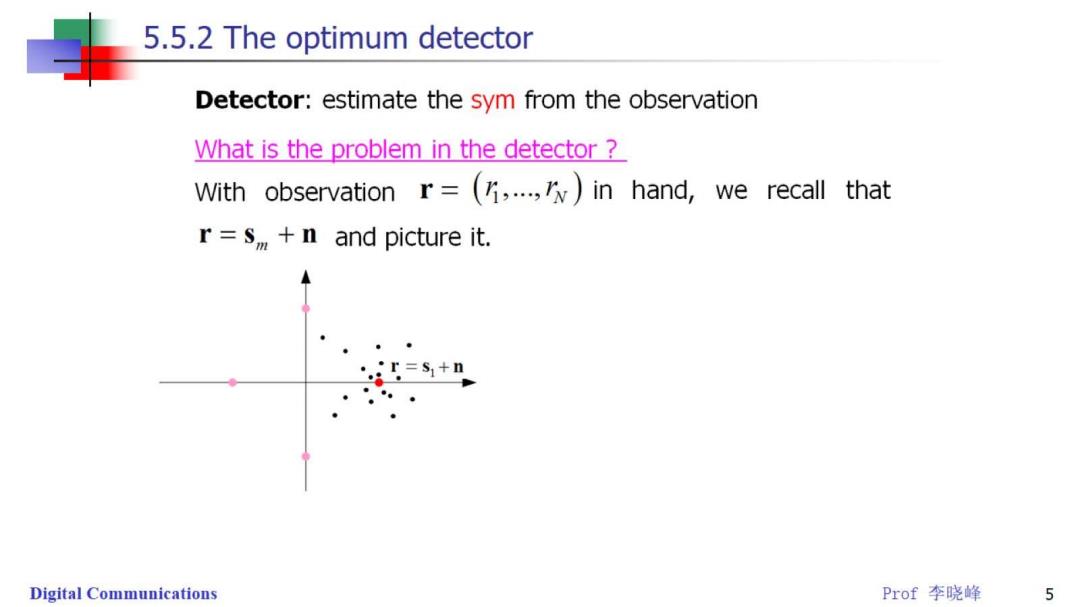
5.5.2 The optimum detector Detector:estimate the sym from the observation What is the problem in the detector With observation r=(,..,)in hand,we recall that r=s,+n and picture it. r=s+n Digital Communications Prof李晓峰 5
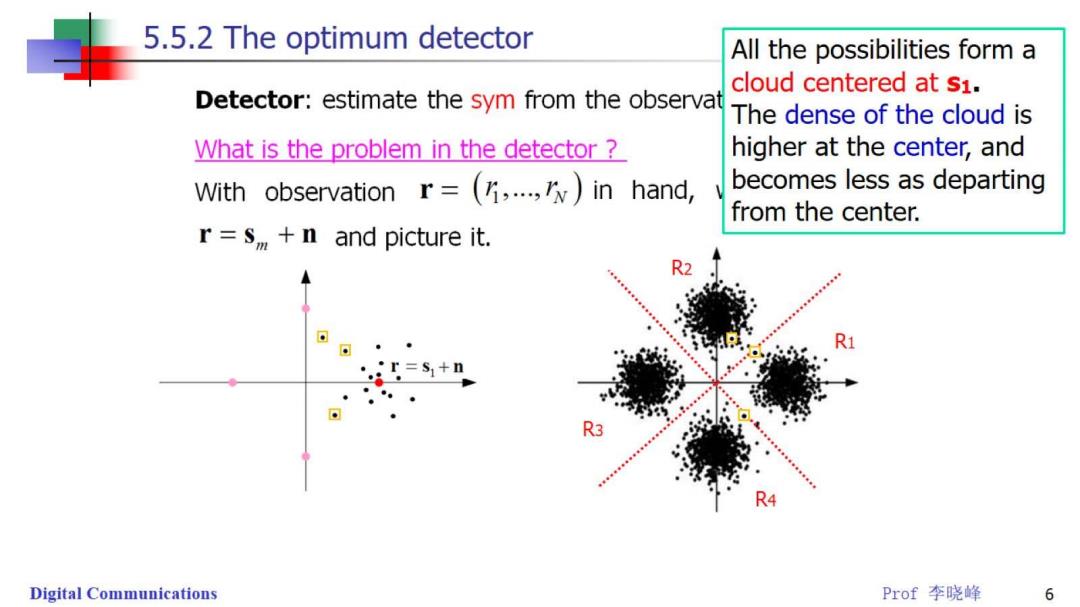
5.5.2 The optimum detector All the possibilities form a cloud centered at s1. Detector:estimate the sym from the observat The dense of the cloud is What is the problem in the detector higher at the center,and With observation r=(,..in hand, becomes less as departing from the center. r=s +n and picture it. R2 。r=s1+n R3 Digital Communications Prof李晓峰 6