Objective-VlI 上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Open question: >What is the impact of mobility on connectivity of clustered networks subject to delay constraints? ▣Ve study The critical transmission range for connectivity >K-hop mobile clustered networks (delay guarantee) >Random walk mobility model with non-trivial velocity >iid.mobility model (fast mobility) Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 6
Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 6 Objective – I/II ❑Open question: ➢What is the impact of mobility on connectivity of clustered networks subject to delay constraints? ❑We study ➢The critical transmission range for connectivity ➢K-hop mobile clustered networks (delay guarantee) ➢Random walk mobility model with non-trivial velocity ➢i.i.d. mobility model (fast mobility)
Objective-ll/II 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY We compare with the critical transmission range for connectivity in stationary k-hop clustered networks. ▣Implications on >the power-delay trade-off the energy efficiency Our results show that: Mobility does improve connectivity in k-hop clustered networks,and it also significantly decreases the energy consumption and the power-delay trade-off. Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 7
Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 7 Objective – II/II ❑ We compare with the critical transmission range for connectivity in stationary k-hop clustered networks. ❑ Implications on ➢the power-delay trade-off ➢the energy efficiency ❑ Our results show that: Mobility does improve connectivity in k-hop clustered networks, and it also significantly decreases the energy consumption and the power-delay trade-off
Outline 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Introduction K-hop Clustered Network Models >An overview of flat networks >K-hop clustered network models QMain Results and Intuitions QThe Impact of Mobility QConcluding Remarks Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 8
8 Outline ❑Introduction ❑K-hop Clustered Network Models ➢An overview of flat networks ➢K-hop clustered network models ❑Main Results and Intuitions ❑The Impact of Mobility ❑Concluding Remarks Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks
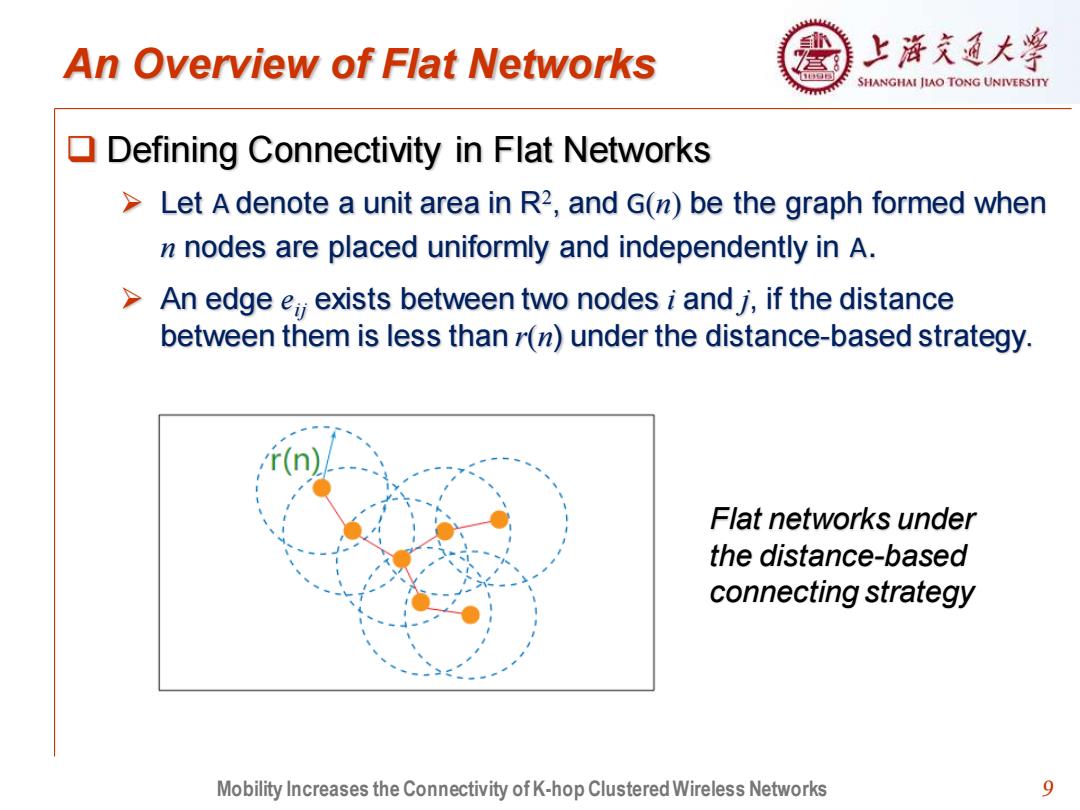
An Overview of Flat Networks 上浒充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Defining Connectivity in Flat Networks Let A denote a unit area in R2,and G(n)be the graph formed when n nodes are placed uniformly and independently in A. An edge e;exists between two nodes i and j,if the distance between them is less than r(n)under the distance-based strategy. Flat networks under the distance-based connecting strategy Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 9
9 An Overview of Flat Networks ❑ Defining Connectivity in Flat Networks ➢ Let A denote a unit area in R2 , and G(n) be the graph formed when n nodes are placed uniformly and independently in A. ➢ An edge eij exists between two nodes i and j, if the distance between them is less than r(n) under the distance-based strategy. Flat networks under the distance-based connecting strategy Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks
K-hop Clustered Network Models 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Clustered networks >n normal nodes and nd cluster-head nodes >Static or mobile ▣Mobility Model Random Walk Mobility Model with Non-Trivial Velocity -Uniformly chosen direction -Constantvelocity (continuous path) >I.I.D.Mobility Model -Independently and uniformly reshuffled -Staticwithin a single time slot Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks 10
10 K-hop Clustered Network Models ❑Clustered networks ➢n normal nodes and n d cluster-head nodes ➢Static or mobile ❑Mobility Model ➢Random Walk Mobility Model with Non-Trivial Velocity – Uniformly chosen direction – Constant velocity (continuous path) ➢I.I.D. Mobility Model – Independently and uniformly reshuffled – Static within a single time slot Mobility Increases the Connectivity of K-hop Clustered Wireless Networks