
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Fields: Scalar field:A scalar quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t. p=p(x,y,z,)=P2(r,0,z,t)=P3(r,0,,) p=p1(x,y2,)=P2(r,0,z,t)=P3(c,0,,) T=T(x,y,2,t)=T(r,0,z,t)=T(,0,p,) Vector field:A vector quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t. V=Vi+Vj+Vk V.=V.(x,y,zt) V,=V,(x.y,z.t) V.=V.(x,y,zt)
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Fields: V V (x, y,z,t) V V (x, y,z,t) V V (x, y,z,t) V V i V j V k z z y y x x x y z ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 T T x y z t T r z t T r t x y z t r z t r t p p x y z t p r z t p r t Scalar field: A scalar quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t. Vector field: A vector quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t
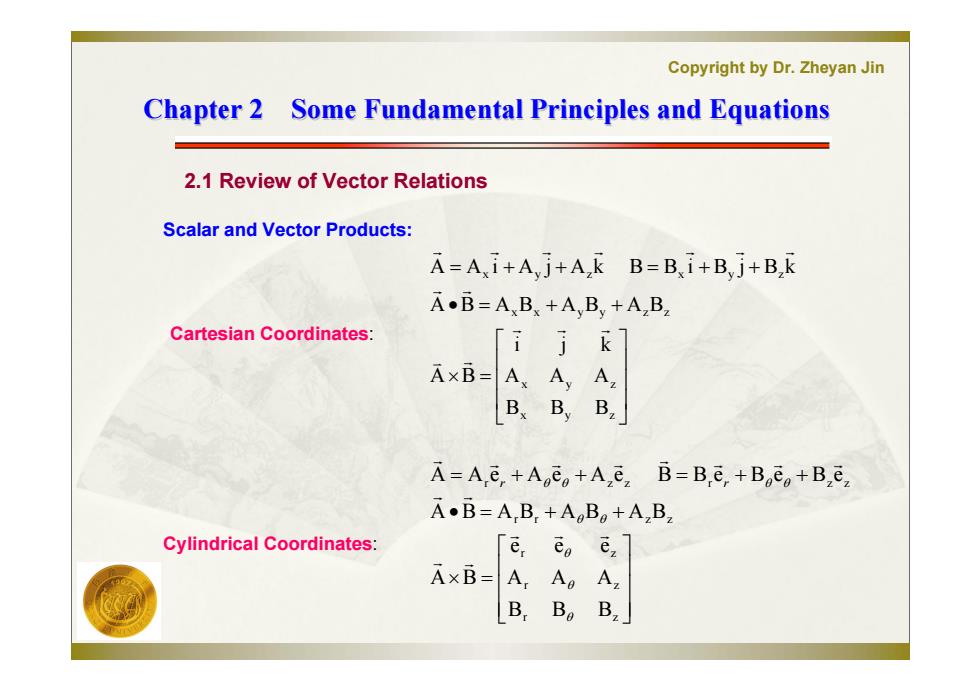
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Products: A=Ai+Ayj+A k B=Bi+Byj+B,k A.B=A,Bs +A,By +A,B Cartesian Coordinates: AxB= Bx BB. A=Ae+Ao+A e B=B.e,+Boeo+Bez A.B=A,B,+AoBo+A,B, Cylindrical Coordinates: e,eo A×B= A:Ao A B,B。 B
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Products: x y z x y z x x y y z z x y z x y z B B B A A A i j k A B A B A B A B A B A A i A j A k B B i B j B k Cartesian Coordinates: Cylindrical Coordinates: r z r z r z r r z z r z z r z z B B B A A A e e e A B A B A B A B A B A A e A e A e B B e B e B e r r
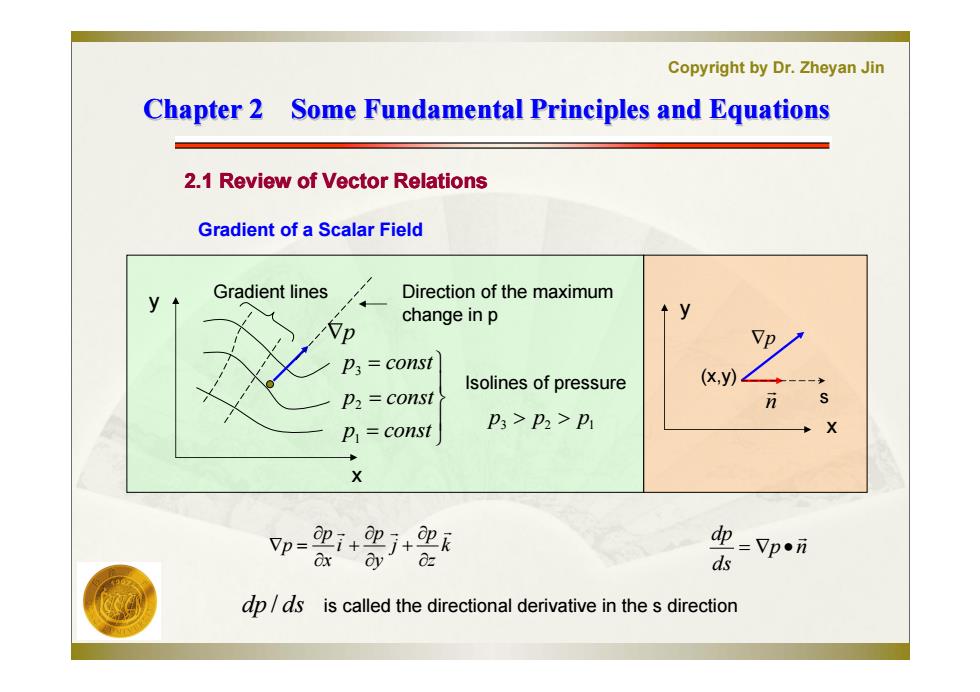
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Gradient of a Scalar Field Gradient lines Direction of the maximum p change in p ↑y p3 =const Isolines of pressure (xy) P2=const p=const P3>P2>P X X p=2i+2j+史x =Vpn ds p/ds is called the directional derivative in thes direction
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Gradient of a Scalar Field p k z p j y p i x p p p n ds dp n Gradient lines p p const p const p const 1 2 3 Isolines of pressure 3 2 1 p p p Direction of the maximum change in p x y (x,y) s x y dp / ds is called the directional derivative in the s direction 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Example 1: fΦ=1/r,findV f=xi+y+z求 V= i+0j+2 a x2+y2+z29 Vx2+y2+z2)3 Vx2+y2+z2)9 7中= xi+yi+z求 Vx2+y2+z2)
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Example 1: If Φ=1/r, find k ˆ j z ˆ i y ˆ r x 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 r r x y z ˆ x ˆ y ˆ z x y z ˆ z x y z y ˆ x y z x ˆ ˆ x y z 1 ˆ x y z 1 ˆ x y z 1 x y z 1 r 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) i j k i j k k z j y i x k z j y i x
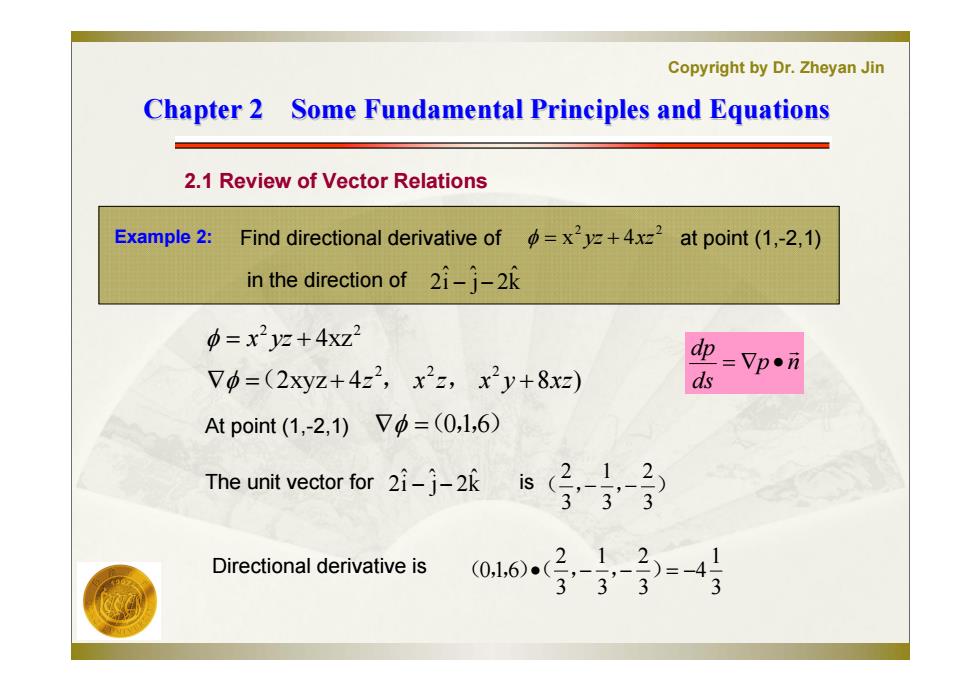
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Example 2:Find directional derivative of=x+4x2 at point(1,-2,1) in the direction of 2-j-2 =x2yz+4xz2 Vo=(2xyz+422,x2=,x2y+8xz) =Vpi d At point(1,-2,1)Vp=(0,l,6) The unit vector for 2-j-2k Directional derivative is
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations (0,1,6) k ˆ j 2 ˆ i ˆ 2 Example 2: 3 1 4 3 2 3 1 3 2 (0,1,6)( , , ) in the direction of ( , , ) 3 2 3 1 3 2 2xyz 4 8 ) 4xz 2 2 2 2 2 z x z x y xz x yz ( , , Find directional derivative of 2 2 x yz 4xz k ˆ j 2 ˆ i ˆ 2 at point (1,-2,1) The unit vector for At point (1,-2,1) p n ds dp Directional derivative is is