
Concurrency Control in Distributed Databases Database System Concepts-7th Edition 23.22 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 23.22 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Concurrency Control in Distributed Databases

Concurrency Control Modify concurrency control schemes for use in distributed environment. We assume that each site participates in the execution of a commit protocol to ensure global transaction atomicity. We assume all replicas of any item are updated Will see how to relax this in case of site failures later Database System Concepts-7th Edition 23.23 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 23.23 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Concurrency Control ▪ Modify concurrency control schemes for use in distributed environment. ▪ We assume that each site participates in the execution of a commit protocol to ensure global transaction atomicity. ▪ We assume all replicas of any item are updated • Will see how to relax this in case of site failures later

Single-Lock-Manager Approach In the single lock-manager approach,lock manager runs on a single chosen site,say S; All lock requests sent to central lock manager The transaction can read the data item from any one of the sites at which a replica of the data item resides. Writes must be performed on all replicas of a data item Advantages of scheme: Simple implementation Simple deadlock handling Disadvantages of scheme are: Bottleneck:lock manager site becomes a bottleneck Vulnerability:system is vulnerable to lock manager site failure. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 23.24 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 23.24 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Single-Lock-Manager Approach ▪ In the single lock-manager approach, lock manager runs on a single chosen site, say Si • All lock requests sent to central lock manager ▪ The transaction can read the data item from any one of the sites at which a replica of the data item resides. ▪ Writes must be performed on all replicas of a data item ▪ Advantages of scheme: • Simple implementation • Simple deadlock handling ▪ Disadvantages of scheme are: • Bottleneck: lock manager site becomes a bottleneck • Vulnerability: system is vulnerable to lock manager site failure

Distributed Lock Manager In the distributed lock-manager approach,functionality of locking is implemented by lock managers at each site Lock managers control access to local data items Locking is performed separately on each site accessed by transaction Every replica must be locked and updated But special protocols may be used for replicas (more on this later) Advantage:work is distributed and can be made robust to failures Disadvantage: Possibility of a global deadlock without local deadlock at any single site Lock managers must cooperate for deadlock detection Database System Concepts-7th Edition 23.25 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 23.25 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Distributed Lock Manager ▪ In the distributed lock-manager approach, functionality of locking is implemented by lock managers at each site • Lock managers control access to local data items • Locking is performed separately on each site accessed by transaction ▪ Every replica must be locked and updated ▪ But special protocols may be used for replicas (more on this later) ▪ Advantage: work is distributed and can be made robust to failures ▪ Disadvantage: • Possibility of a global deadlock without local deadlock at any single site • Lock managers must cooperate for deadlock detection
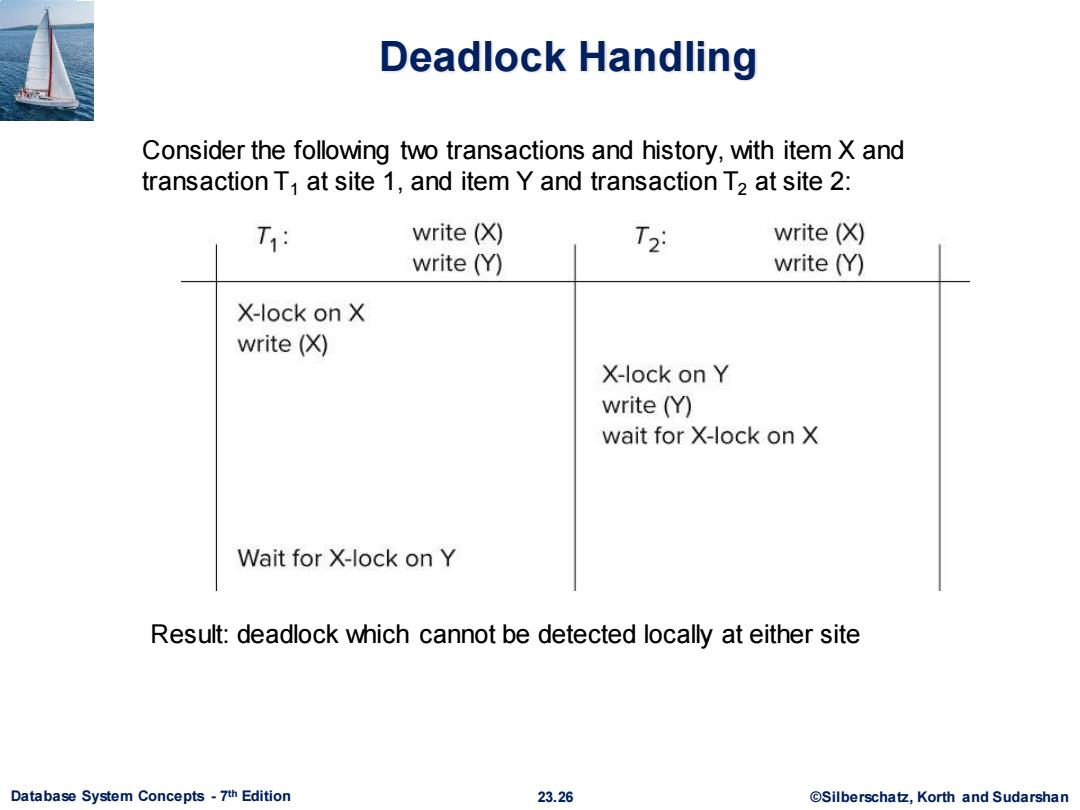
Deadlock Handling Consider the following two transactions and history,with item X and transaction T at site 1,and item Y and transaction T2 at site 2: T1 write (X) T2 write (X) write(Y) write (Y) X-lock on X write(X) X-lock on Y write (Y) wait for X-lock on X Wait for X-lock on Y Result:deadlock which cannot be detected locally at either site Database System Concepts-7th Edition 23.26 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 23.26 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Deadlock Handling Consider the following two transactions and history, with item X and transaction T1 at site 1, and item Y and transaction T2 at site 2: Result: deadlock which cannot be detected locally at either site