Introduction Parallel machines have become quite common and affordable prices of microprocessors,memory and disks have dropped sharply Data storage needs are growing increasingly large user data at web-scale 100's of millions of users,petabytes of data transaction data are collected and stored for analysis. multimedia objects like images/videos Parallel storage system requirements storing large volumes of data processing time-consuming decision-support queries providing high throughput for transaction processing Very high demands on scalability and availability Database System Concepts-7th Edition 21.2 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 21.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Introduction ▪ Parallel machines have become quite common and affordable • prices of microprocessors, memory and disks have dropped sharply ▪ Data storage needs are growing increasingly large • user data at web-scale ▪ 100’s of millions of users, petabytes of data • transaction data are collected and stored for analysis. • multimedia objects like images/videos ▪ Parallel storage system requirements • storing large volumes of data • processing time-consuming decision-support queries • providing high throughput for transaction processing • Very high demands on scalability and availability
Parallel/Distributed Data Storage History ■1980/1990s Distributed database systems with tens of nodes ■2000s: Distributed file systems with 1000s of nodes Millions of Large objects(100's of megabytes) Web logs,images,videos,... Typically create/append only Distributed data storage systems with 1000s of nodes Billions to trillions of smaller(kilobyte to megabyte)objects Social media posts,email,online purchases,.. Inserts,updates,deletes ·Key-value stores 2010s:Distributed database systems with 1000s of nodes Database System Concepts-7th Edition 21.3 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 21.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Parallel/Distributed Data Storage History ▪ 1980/1990s • Distributed database systems with tens of nodes ▪ 2000s: • Distributed file systems with 1000s of nodes ▪ Millions of Large objects (100’s of megabytes) ▪ Web logs, images, videos, … ▪ Typically create/append only • Distributed data storage systems with 1000s of nodes ▪ Billions to trillions of smaller (kilobyte to megabyte) objects ▪ Social media posts, email, online purchases, … ▪ Inserts, updates, deletes • Key-value stores ▪ 2010s: Distributed database systems with 1000s of nodes
I/O Parallelism Reduce the time required to retrieve relations from disk by partitioning the relations on multiple disks,on multiple nodes (computers) Our description focuses on parallelism across nodes Same techniques can be used across disks on a node Horizontal partitioning-tuples of a relation are divided among many nodes such that some subset of tuple resides on each node. Contrast with vertical partitioning,e.g.r(A,B,C,D)with primary key A into r1(A,B)and r2(A,C,D) By default,the word partitioning refers to horizontal partitioning Database System Concepts-7th Edition 21.4 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 21.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition I/O Parallelism ▪ Reduce the time required to retrieve relations from disk by partitioning the relations on multiple disks, on multiple nodes (computers) • Our description focuses on parallelism across nodes • Same techniques can be used across disks on a node ▪ Horizontal partitioning – tuples of a relation are divided among many nodes such that some subset of tuple resides on each node. • Contrast with vertical partitioning, e.g. r(A,B,C,D) with primary key A into r1(A,B) and r2(A,C,D) • By default, the word partitioning refers to horizontal partitioning
I/O Parallelism Partitioning techniques(number of nodes n): Round-robin: Send the ith tuple inserted in the relation to node i mod n. Hash partitioning: Choose one or more attributes as the partitioning attributes. Choose hash function h with range 0...n-1 Let i denote result of hash function h applied to the partitioning attribute value of a tuple.Send tuple to node i. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 21.5 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 21.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition I/O Parallelism ▪ Partitioning techniques (number of nodes = n): Round-robin: Send the i th tuple inserted in the relation to node i mod n. Hash partitioning: • Choose one or more attributes as the partitioning attributes. • Choose hash function h with range 0…n - 1 • Let i denote result of hash function h applied to the partitioning attribute value of a tuple. Send tuple to node i
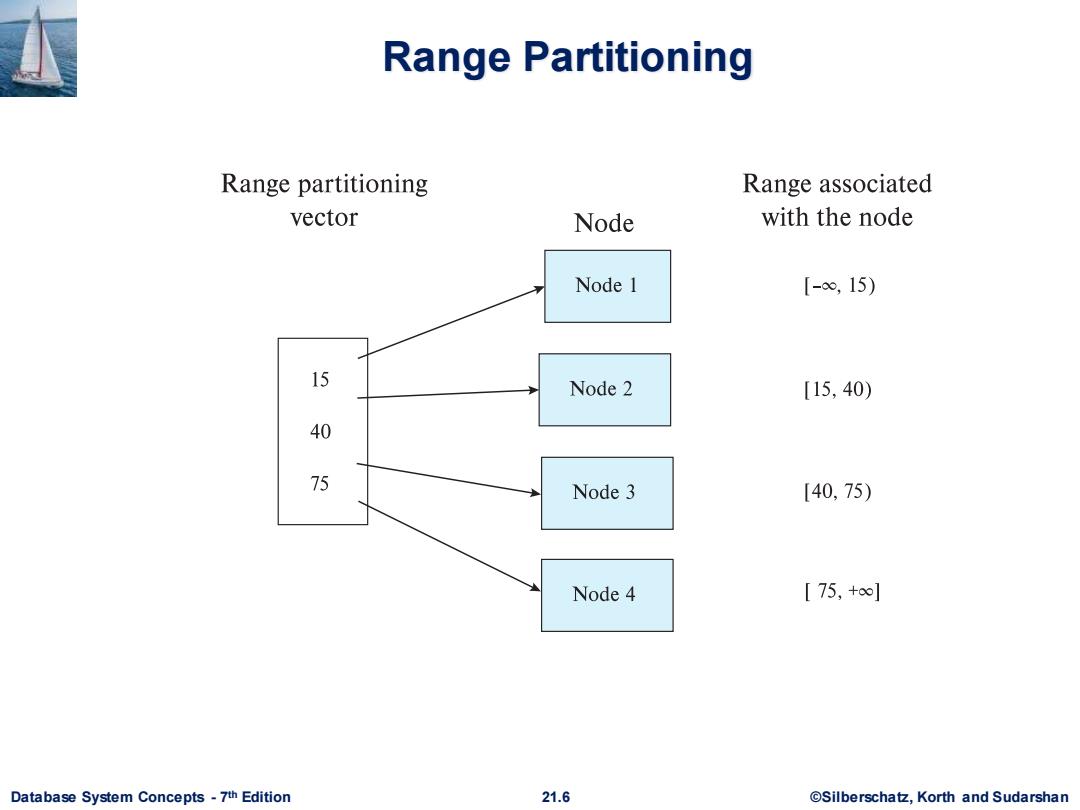
Range Partitioning Range partitioning Range associated vector Node with the node Node 1 [-o,15) 15 Node 2 [15,40) 40 75 Node 3 [40,75) Node 4 [75,+∞] Database System Concepts-7th Edition 21.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 21.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Range Partitioning