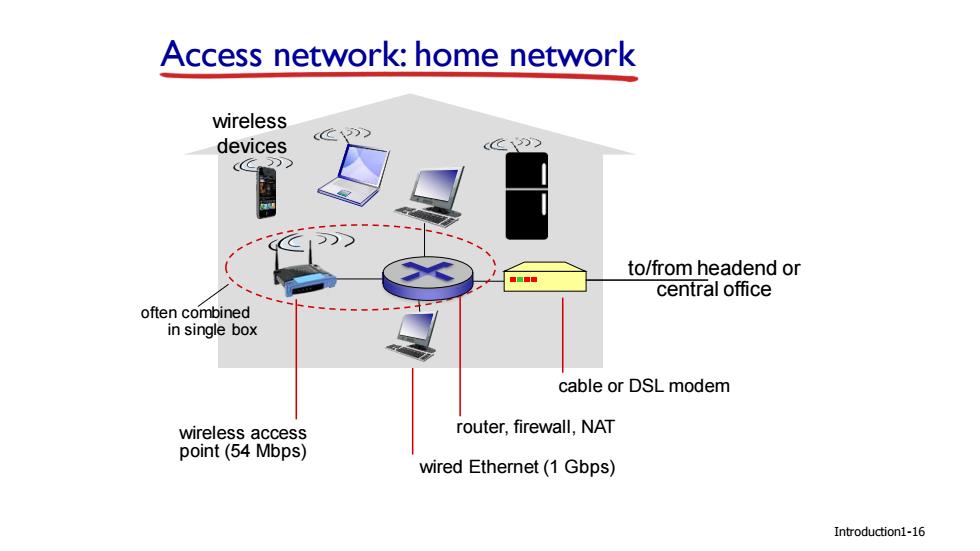
Access network:home network wireless C1)) devices C to/from headend or central office often combined in single box cable or DSL modem wireless access router,firewall,NAT point(54 Mbps) wired Ethernet(1 Gbps) Introduction1-16
Introduction Access network: home network to/from headend or central office cable or DSL modem router, firewall, NAT wired Ethernet (1 Gbps) wireless access point (54 Mbps) wireless devices often combined in single box 1-16
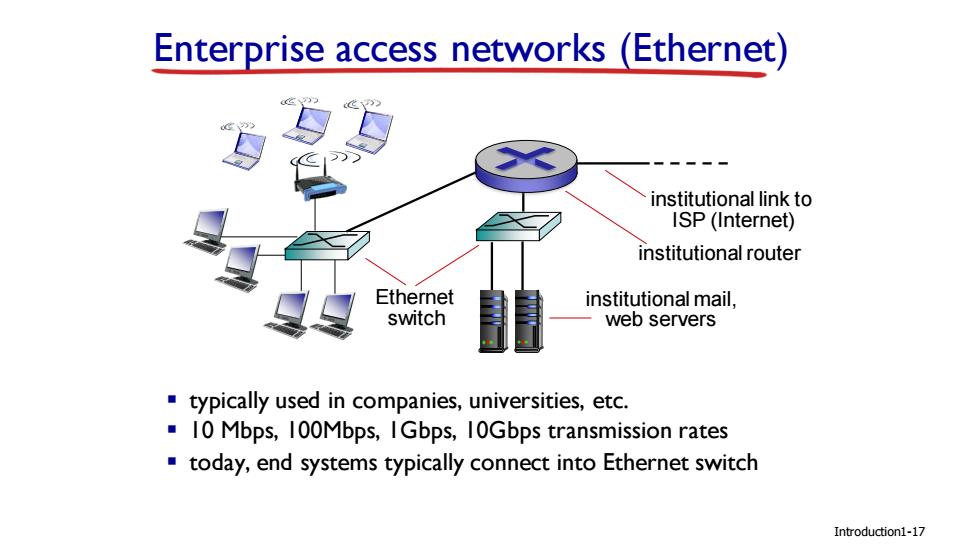
Enterprise access networks(Ethernet) institutional link to ISP(Internet) institutional router Ethernet institutional mail, switch web servers typically used in companies,universities,etc. 10 Mbps,100Mbps,IGbps,10Gbps transmission rates today,end systems typically connect into Ethernet switch Introduction1-17
Introduction Enterprise access networks (Ethernet) ▪ typically used in companies, universities, etc. ▪ 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps transmission rates ▪ today, end systems typically connect into Ethernet switch Ethernet switch institutional mail, web servers institutional router institutional link to ISP (Internet) 1-17
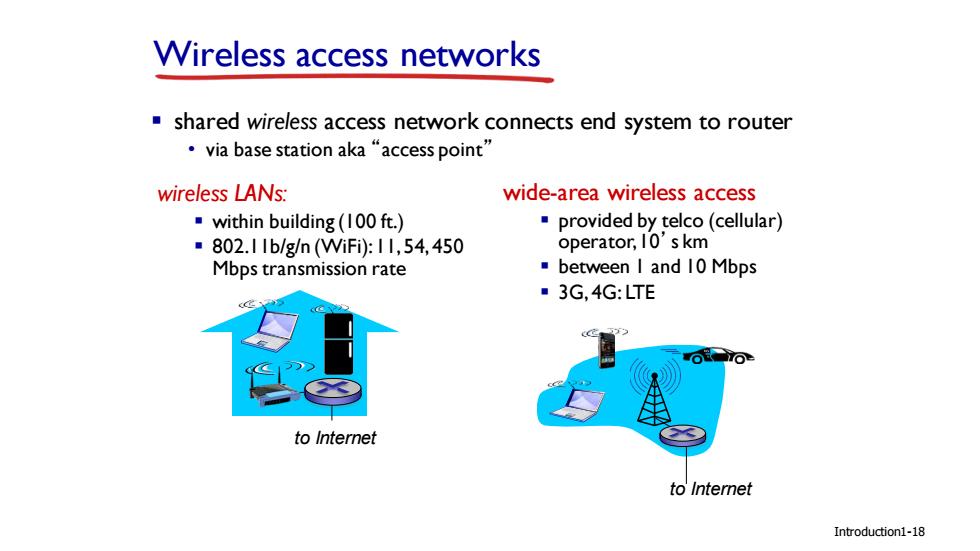
Wireless access networks shared wireless access network connects end system to router ·via base station aka“access point” wireless LANs: wide-area wireless access within building(100 ft.) provided by telco(cellular) ■802.1Ib/g/n(Wifi):11,54,450 operator,10's km Mbps transmission rate ·between I and I0Mbps ·3G,4G:LTE to Internet to Internet Introduction1-18
Introduction Wireless access networks ▪ shared wireless access network connects end system to router • via base station aka “access point” wireless LANs: ▪ within building (100 ft.) ▪ 802.11b/g/n (WiFi): 11, 54, 450 Mbps transmission rate wide-area wireless access ▪ provided by telco (cellular) operator, 10’s km ▪ between 1 and 10 Mbps ▪ 3G, 4G: LTE to Internet to Internet 1-18
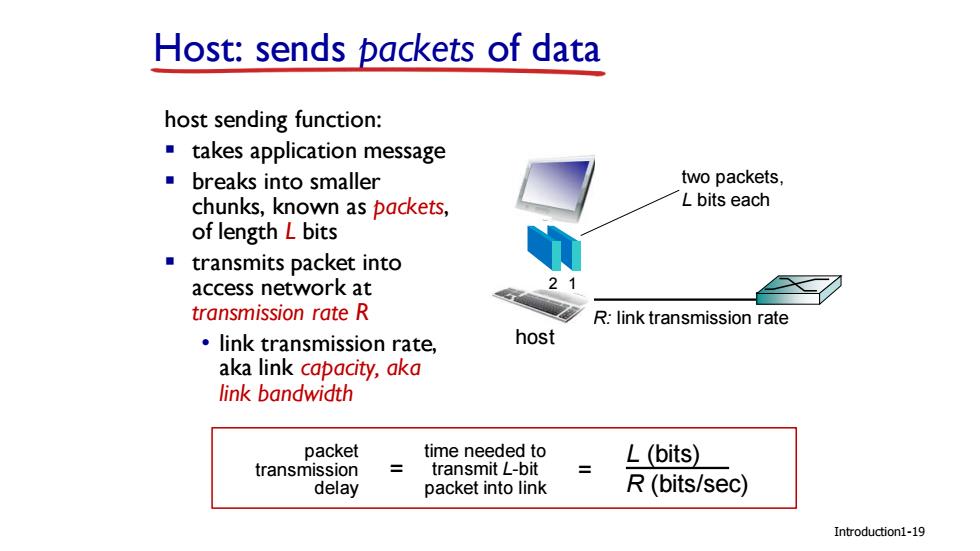
Host:sends packets of data host sending function: takes application message ■breaks into smaller two packets, chunks,known as packets, L bits each of length L bits transmits packet into access network at transmission rate R R:link transmission rate link transmission rate, host aka link capacity,aka link bandwidth packet time needed to L(bits) transmission transmit L-bit delay packet into link R(bits/sec) Introduction1-19
Host: sends packets of data host sending function: ▪ takes application message ▪ breaks into smaller chunks, known as packets, of length L bits ▪ transmits packet into access network at transmission rate R • link transmission rate, aka link capacity, aka link bandwidth R: link transmission rate host 2 1 two packets, L bits each packet transmission delay time needed to transmit L-bit packet into link L (bits) R (bits/sec) = = Introduction1-19

Physical media bit:propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs physical link:what lies twisted pair(TP) between transmitter ■two insulated copper receiver wires ■guided media: Category 5:100 Mbps,I Gbps Ethernet signals propagate in solid media:copper,fiber,coax Category 6:10Gbps unguided media: signals propagate freely, e.g.,radio Introduction1-20
Introduction Physical media ▪ bit: propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs ▪ physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver ▪ guided media: • signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax ▪ unguided media: • signals propagate freely, e.g., radio twisted pair (TP) ▪ two insulated copper wires • Category 5: 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps Ethernet • Category 6: 10Gbps 1-20