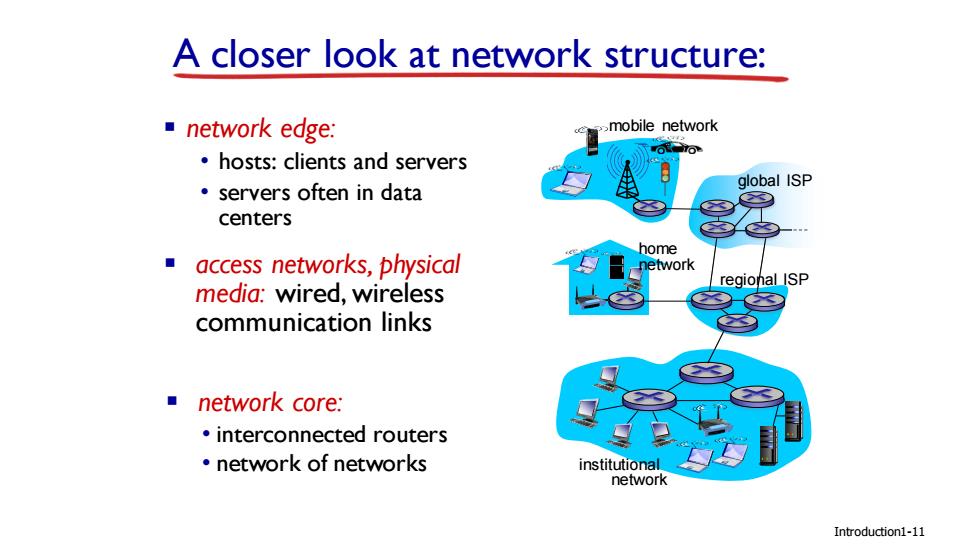
A closer look at network structure: ■network edge: .mobile network hosts:clients and servers global ISP ·servers often in data centers home access networks,physical etwork media:wired,wireless regional ISP communication links network core: interconnected routers ·network of networks institutional network Introduction1-11
Introduction A closer look at network structure: ▪ network edge: • hosts: clients and servers • servers often in data centers ▪ access networks, physical media: wired, wireless communication links ▪ network core: • interconnected routers • network of networks 1-11 mobile network global ISP regional ISP home network institutional network
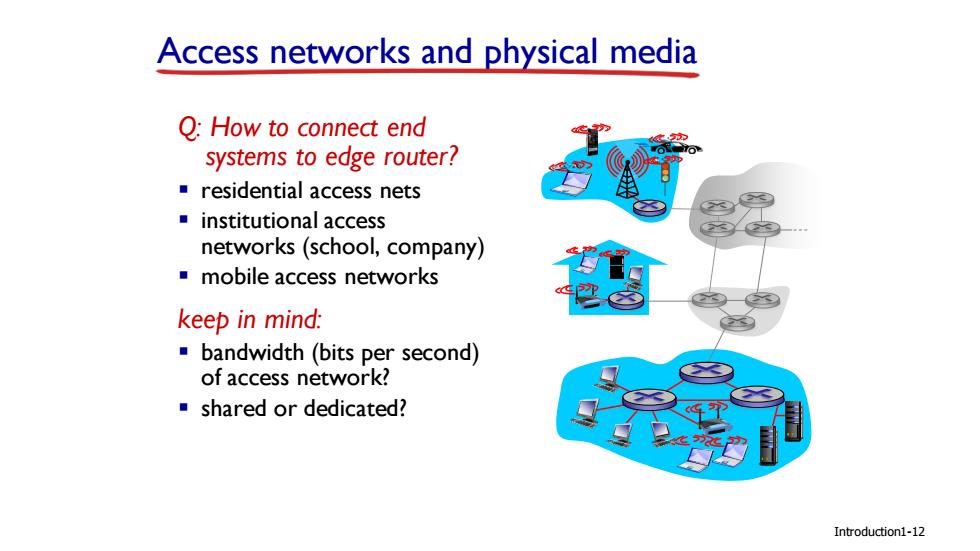
Access networks and physical media Q:How to connect end systems to edge router? residential access nets institutional access networks(school,company) mobile access networks keep in mind: bandwidth (bits per second) of access network? ■shared or dedicated? Introduction1-12
Introduction Access networks and physical media Q: How to connect end systems to edge router? ▪ residential access nets ▪ institutional access networks (school, company) ▪ mobile access networks keep in mind: ▪ bandwidth (bits per second) of access network? ▪ shared or dedicated? 1-12
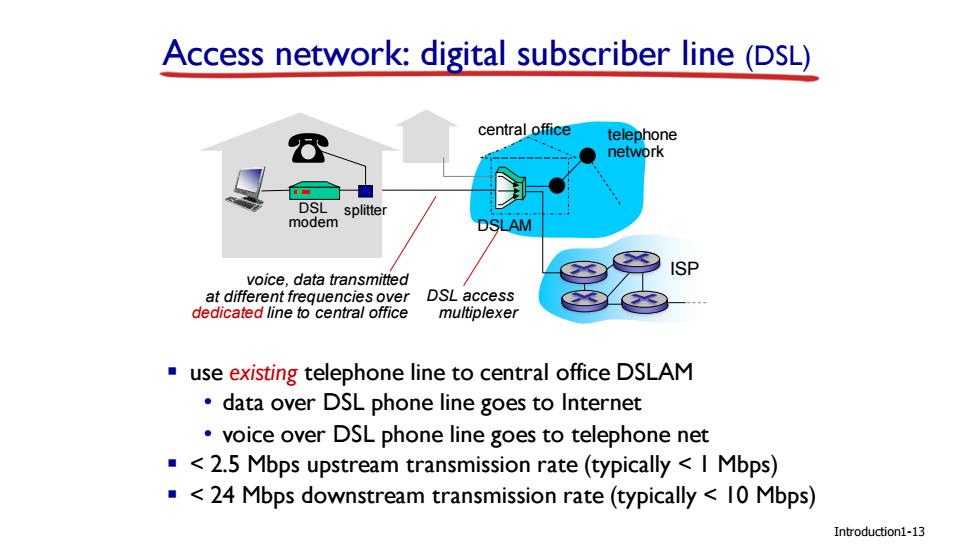
Access network:digital subscriber line (DSL) central office telephone network DSL splitter modem DSLAM ISP voice,data transmitted at different frequencies over DSL access dedicated line to central office multiplexer use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM data over DSL phone line goes to Internet voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net <2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate(typically I Mbps) <24 Mbps downstream transmission rate(typically 10 Mbps) Introduction1-13
ISP Introduction Access network: digital subscriber line (DSL) central office telephone network DSLAM voice, data transmitted at different frequencies over dedicated line to central office ▪ use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM • data over DSL phone line goes to Internet • voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net ▪ < 2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate (typically < 1 Mbps) ▪ < 24 Mbps downstream transmission rate (typically < 10 Mbps) DSL modem splitter DSL access multiplexer 1-13
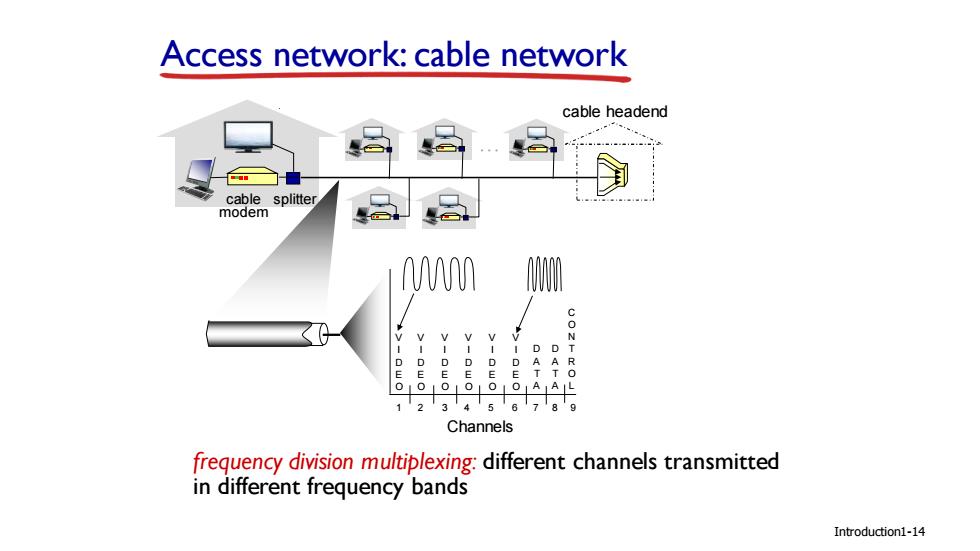
Access network:cable network cable headend cable splitter modem D D D D D E E 8 oioioioLoiOAAL 123456 Channels frequency division multiplexing:different channels transmitted in different frequency bands Introduction1-14
Introduction Access network: cable network cable modem splitter … cable headend Channels V I D E O V I D E O V I D E O V I D E O V I D E O V I D E O D A T A D A T A C O N T R O L 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 frequency division multiplexing: different channels transmitted in different frequency bands 1-14
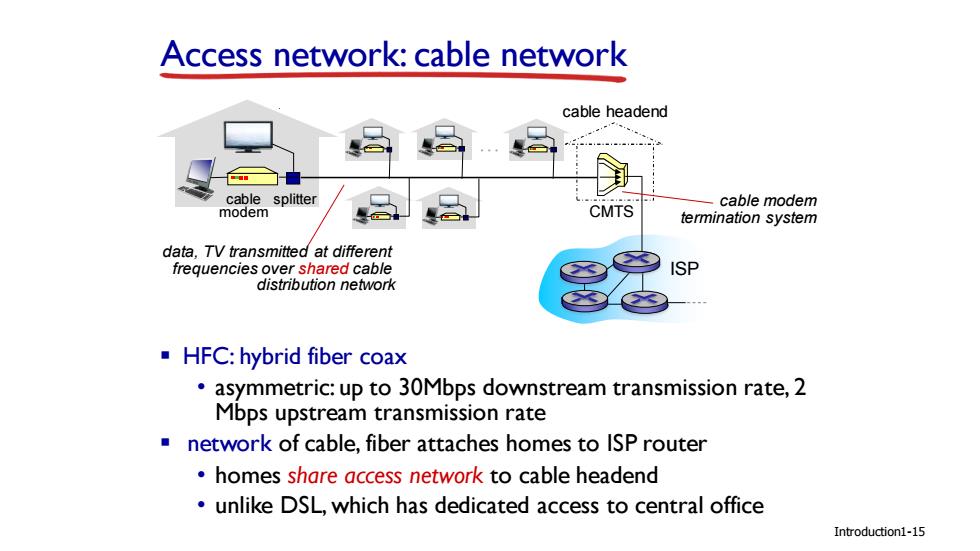
Access network:cable network cable headend cable splitter cable modem modem CMTS termination system data,TV transmitted at different frequencies over shared cable ISP distribution network HFC:hybrid fiber coax asymmetric:up to 30Mbps downstream transmission rate,2 Mbps upstream transmission rate network of cable,fiber attaches homes to ISP router homes share access network to cable headend unlike DSL,which has dedicated access to central office Introduction1-15
ISP Introduction data, TV transmitted at different frequencies over shared cable distribution network cable modem splitter … cable headend CMTS cable modem termination system ▪ HFC: hybrid fiber coax • asymmetric: up to 30Mbps downstream transmission rate, 2 Mbps upstream transmission rate ▪ network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISP router • homes share access network to cable headend • unlike DSL, which has dedicated access to central office Access network: cable network 1-15