
Air and Air Pollution Prof.JIANG Dahe de Nevers,N.1995:Air Pollution Control Engineering, McGraw-Hill Elsom,D.M.1992:Atmospheric Pollution-A Global Problem,2nd Ed.,Blackwell J.Glynn Henry and Gary W.Heinke 1989,Environmental Science and Engineering,Prentice-Hall
Air and Air Pollution Prof. JIANG Dahe de Nevers, N. 1995: Air Pollution Control Engineering, McGraw-Hill Elsom, D. M. 1992: Atmospheric Pollution - A Global Problem, 2nd Ed., Blackwell J. Glynn Henry and Gary W. Heinke 1989, Environmental Science and Engineering, Prentice-Hall
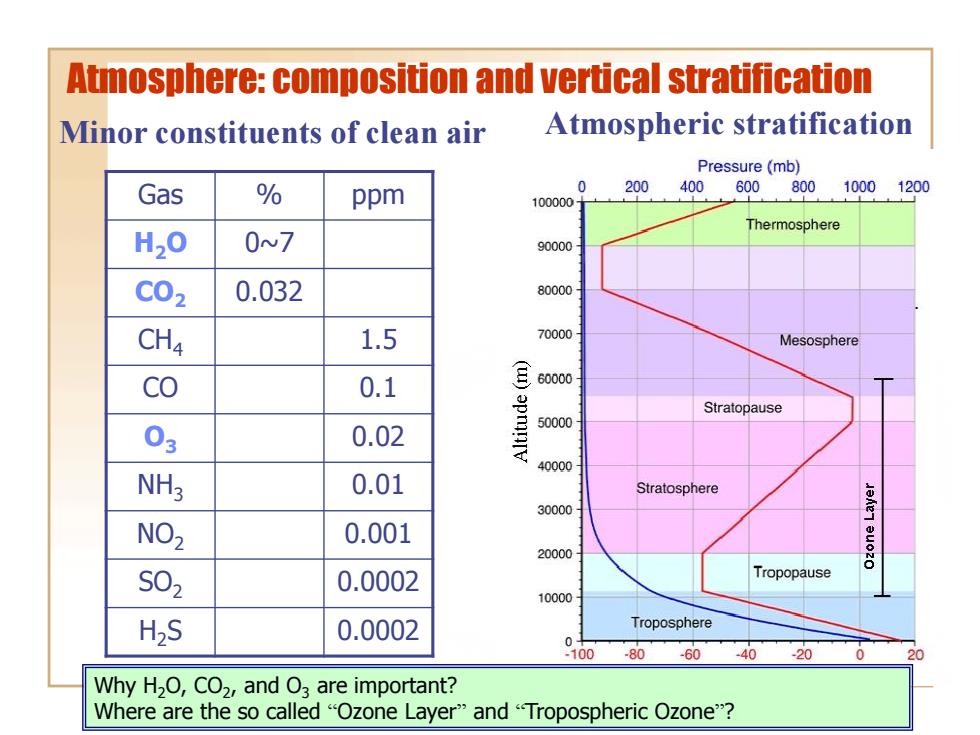
Atmosphere:composition and vertical stratification Minor constituents of clean air Atmospheric stratification Pressure(mb) Gas % ppm 0 200 400,600,80010001200 100000 Thermosphere H20 0N7 90000 C02 0.032 80000 CH4 1.5 70000 Mesosphere cO 0.1 E6000- 03 0.02 apmnIV Stratopause 50000 40000 NH3 0.01 Stratosphere 30000 NO 0.001 20000 S02 0.0002 Tropopause 10000 H>S 0.0002 Troposphere 0 100 -80 -60 -40 -20 20 Why H2O,CO2,and O are important? Where are the so called "Ozone Layer"and "Tropospheric Ozone"?
Atmosphere: composition and vertical stratification Gas % ppm H2O 0~7 CO2 0.032 CH4 1.5 CO 0.1 O3 0.02 NH3 0.01 NO2 0.001 SO2 0.0002 H2S 0.0002 Minor constituents of clean air Atmospheric stratification Why H2O, CO2 , and O3 are important? Where are the so called “Ozone Layer” and “Tropospheric Ozone”?

Air Pollutants ◆ Gaseous pollutants: SO2,combustion of coal,sulfur containing ores NOx(NO and NO,),combustion,high temperature or with HCs VOCs,petroleum,lubricants,solvents,paints,...(non-methane) CO,HCs (none-methane),... Particulates:(aerosols) TSP,total suspended particulate matter,diameter 100um PM1o,respirable particulate matter,diameter 10 um PM2.5,fine particulate matter,diameter 2.5 um falling dust,tons per month per km2 (not a concentration) ◆ Other air pollutants ■Toxic chemicals Lead (Pb)and mercury (Hg) Radioactive substances ■CFCs, ■Green house gases Natural effects:H2O,CO,CH4,N2O,O3... .By Kyoto protocol:CO2,N2O,CH4 SF6,HFC,PFC
Air Pollutants Gaseous pollutants: SO2 , combustion of coal, sulfur containing ores NOx (NO and NO2 ), combustion, high temperature or with HCs VOCs, petroleum, lubricants, solvents, paints, …(non-methane) CO, HCs (none-methane), … Particulates: (aerosols) TSP, total suspended particulate matter, diameter < 100μm PM10, respirable particulate matter, diameter < 10 μm PM2.5, fine particulate matter, diameter < 2.5 μm falling dust, tons per month per km2 (not a concentration) Other air pollutants Toxic chemicals Lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg) Radioactive substances CFCs, Green house gases Natural effects: H2O, CO2 , CH4 , N2O, O3… By Kyoto protocol: CO2 , N2O, CH4 , SF6 , HFC, PFC

Air Pollutants (continued) ◆ Regulated air pollutants China:before 2000,TSP,SO2,NOx;after 2001:PM1o,SO2,NO2 O3 and PM2.5 are also taken in some countries/regions Primary and secondary pollutants Directly emitted from sources or transformed in atmosphere,e.g. O in photochemical smog,fine particles (e.g.sulfates and nitrates), acid rain,... ◆Units ■Mass concentration inμg/m3ormg/m3 Volume concentration in %ppm and ppb by volume
Air Pollutants (continued) Regulated air pollutants China: before 2000, TSP, SO2 , NOx ; after 2001: PM10, SO2 , NO2 O3 and PM2.5 are also taken in some countries / regions Primary and secondary pollutants Directly emitted from sources or transformed in atmosphere, e.g., O3 in photochemical smog, fine particles (e.g. sulfates and nitrates), acid rain, … Units Mass concentration in μg/m3 or mg/m3 Volume concentration in %, ppm and ppb by volume

Air Quality Standards To establish ambient air quality standards Physical/chemical/biological analysis; ■Animal experiments, Short-term exposure of human volunteers(observe measurable,irreversible short-term or long-term effects); Epidemiology
Air Quality Standards To establish ambient air quality standards Physical/chemical/biological analysis; Animal experiments; Short-term exposure of human volunteers (observe measurable, irreversible short-term or long-term effects); Epidemiology