
上海交通大学通识核心课 教授李大伟电邮daweili(@sjtu.edu.cn 电话:34204744 助教陈昊 电话:34205436 基因与人 生命的基因中心法则 8.Genes And the Origin of Cooperation 基因与合作的起源
2022-3-11 1 1 上海交通大学通识核心课 教授 李大伟 电邮 daweili@sjtu.edu.cn 电话:34204744 助教 陈 昊 电话:34205436

Cooperation:Another Pillar of Human Evolution? SBACE SCIENCE MEDICINE ANTIFICIAL INTELL GENCE Mountain-Climbing Vaccine Clues fram Seeing the Future with MARS ROVER HIV SURVIVORS MACHINE LEARNING SCIENTIFIC The Evolution Cooperation Competition is not the only force that shaped life on earth SPECIAL REPORT Physles Revlews by Nobel Laureates

Cooperation or Defect:Prisoner's Dilemma 基因间的博弈:合作还是对抗? The Similarity and Differences Between Game Theory and Evolution BASICS 问:什么才是“好”? Natural Defection Agame theory paradox calledthe Prisoner's Dilemma illustrates why the existence of cooperation in nature is unexpected.Two 生命进化中的博弈 people face jail sentences for conspiring to commit a crime Their sentences depend onwhether they dlect tocooperate and remain silent or defect and oonfess to the crime [see payaff table below].Because neither knows what the other will do,the rational choice-the one that always offers the better payoff-is to defect. 总原则: INDIVIDUAL2 有利自身生存 COOPERATE DEFECT (remain silent) 的t的 TYnOIAIONI 2 years in jai 4years in jai 2 years in jail 1 year in jail 特点: 1.稳定性与多样性共存 2.可遗传性 ear in jail 4 years in jail 3 years in jai 3.可扩增性
基因间的博弈:合作还是对抗? Cooperation or Defect: Prisoner’s Dilemma The Similarity and Differences Between Game Theory and Evolution 问:什么才是“好”? 生命进化中的博弈 总原则: 有利自身生存 特点·: 1. 稳定性与多样性共存 2. 可遗传性 3. 可扩增性

基因与合作的起源 红利来源于特化与高效 合作范围的进化 1、基因→基因组: 不同基因间的合作使细胞在生存中胜出 2、单细胞→多细胞生物: 相同基因不同细胞间的合作使个体在繁衍中胜出 3、小范围合作→大范围合作: 相似基因不同个体的合作使物种在竞争中胜出 4、全球合作: 2022-3-11 同一物种更大范围的合作使社会在发展中胜出 4
2022-3-11 1 4 上海交通大学通识核心课 教授 李大伟 电邮 daweili@sjtu.edu.cn 电话:34204744 助教 朱 奇 电邮 zq0525@126.co 电话:34205436 1、基因基因组: 不同基因间的合作使细胞在生存中胜出 2、单细胞多细胞生物: 相同基因不同细胞间的合作使个体在繁衍中胜出 3、小范围合作大范围合作: 相似基因不同个体的合作使物种在竞争中胜出 4、全球合作: 同一物种更大范围的合作使社会在发展中胜出
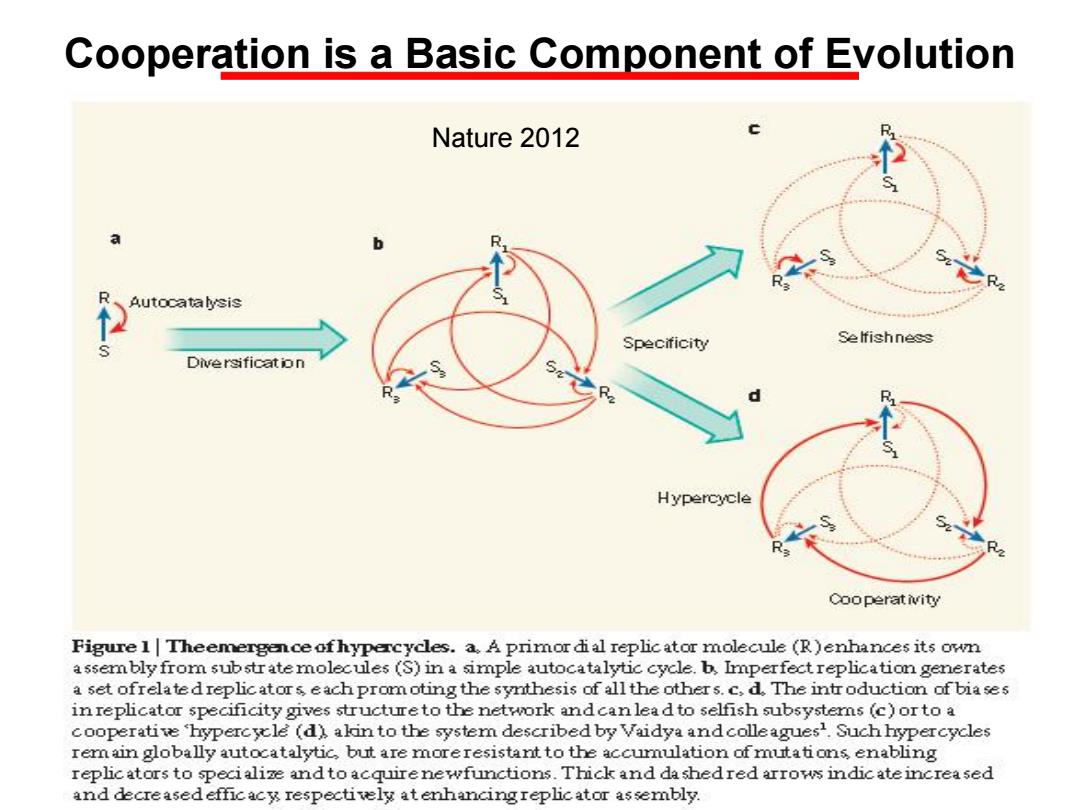
Cooperation is a Basic Component of Evolution Nature 2012 a b Autocatalysis Specificity Selfishness Dive rsification Hypercycle Cooperativity Figure I|Theemergenceofhypercycles.a.A primor dial replicator molecule (R)enhances its own assembly from substr atemolecules (S)in a simple autocatalytic cycle.b,Imperfect replication generates a set ofrelatedreplicators each promoting the synthesis of all the other s.c,d.The introduction of biases in replicator specificity gives structureto the network andcanlead to selfish subsystems(c)or to a cooperative hypercycle (d)akin to the system describedby Vaidya andcolleagues1.Such hypercycles remain globally autocatalytic,but are moreresistant to the accumulation of mutations,enabling replicators to specialize andto acquirenewfunctions.Thick and da shedred arrows indic ateincreased and decreased efficacy respectively atenhancingreplic ator assembly
2022-3-11 1 5 上海交通大学通识核心课 教授 李大伟 电邮 daweili@sjtu.edu.cn 电话:34204744 助教 朱 奇 电邮 zq0525@126.co 电话:34205436 Cooperation is a Basic Component of Evolution Nature 2012