
Reference Person ke; //only created the reference,not an object. It points to nothing now(null). ke new Person(); //create the object (allocate storage in memory),and ke is initialized. ke.name=“Ke Wang”; //access the object through the reference Can have multiple reference to one object No reference means the object is inaccessible forever goes to garbage collector
Reference Person ke; //only created the reference, not an object. It points to nothing now (null). ke = new Person(); //create the object (allocate storage in memory), and ke is initialized. ke.name=“Ke Wang”; //access the object through the reference Can have multiple reference to one object No reference means the object is inaccessible forever – goes to garbage collector
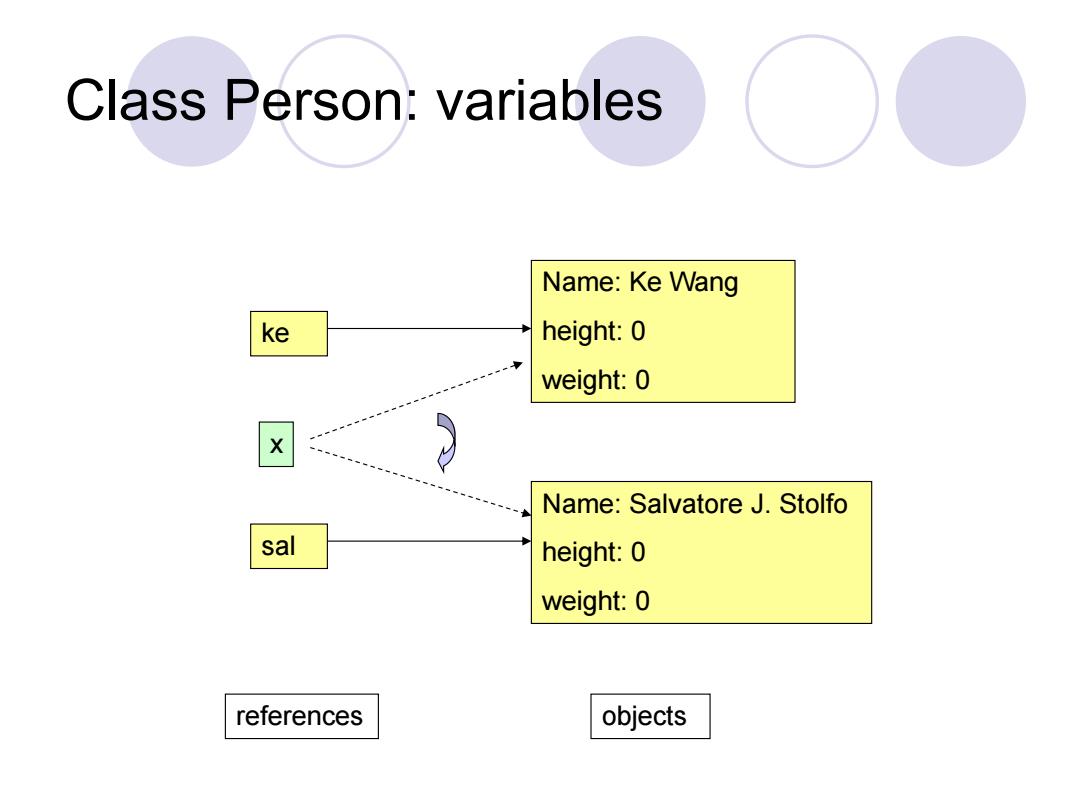
Class Person:variables Name:Ke Wang ke height:0 weight:0 Name:Salvatore J.Stolfo sal height:0 weight:0 references objects
Class Person: variables Name: Ke Wang height: 0 weight: 0 Name: Salvatore J. Stolfo height: 0 weight: 0 ke sal x references objects

Visibility of fields and methods Generally make fields private and provide public getField()and setField()accessor functions O-O term:encapsulation o Private fields and methods cannot be accessed from outside of the class
Visibility of fields and methods lGenerally make fields private and provide public getField() and setField() accessor functions lO-O term: encapsulation lPrivate fields and methods cannot be accessed from outside of the class

Static vs.non-static oStatic:class variable/method o Non-static:instance variable/method Static ones are associated with class,not object.Can be called using class name directly ●main()is static OEven though it's in a class definition,no instance of the class exist when main starts executing
Static vs. non-static lStatic: class variable/method lNon-static: instance variable/method lStatic ones are associated with class, not object. Can be called using class name directly lmain() is static ¡Even though it’s in a class definition, no instance of the class exist when main starts executing

Static vs.non-static (cont. o Instance fields define an object;the values of those fields make one object distinct from another o Instance method operates on an instance of a class (object)instead of operating on the class itself. o Class methods can only use class fields; while instance methods can use both instance fields and class fields
Static vs. non-static (cont.) lInstance fields define an object; the values of those fields make one object distinct from another lInstance method operates on an instance of a class (object) instead of operating on the class itself. lClass methods can only use class fields; while instance methods can use both instance fields and class fields