
Key points in X-ray properties and diffraction geometry Distinguish between continuous and characteristic radiation .of K&Ke radiation and ik Good aspects/uses of absorption:X-ray filters Bad aspects/uses of absorption:X-ray fluorescence ·Bragg'slaW ·Ewald sphere method 1
Key points in X-ray properties and diffraction geometry • Distinguish between continuous and characteristic radiation • of K & K radiation and K • Good aspects/uses of absorption: X-ray filters • Bad aspects/uses of absorption: X-ray fluorescence • Bragg’s law • Ewald sphere method 1

Intensity of diffraction Leyun Wang eyunwang@sjtu.edu.cn
Intensity of diffraction Leyun Wang leyunwang@sjtu.edu.cn 2
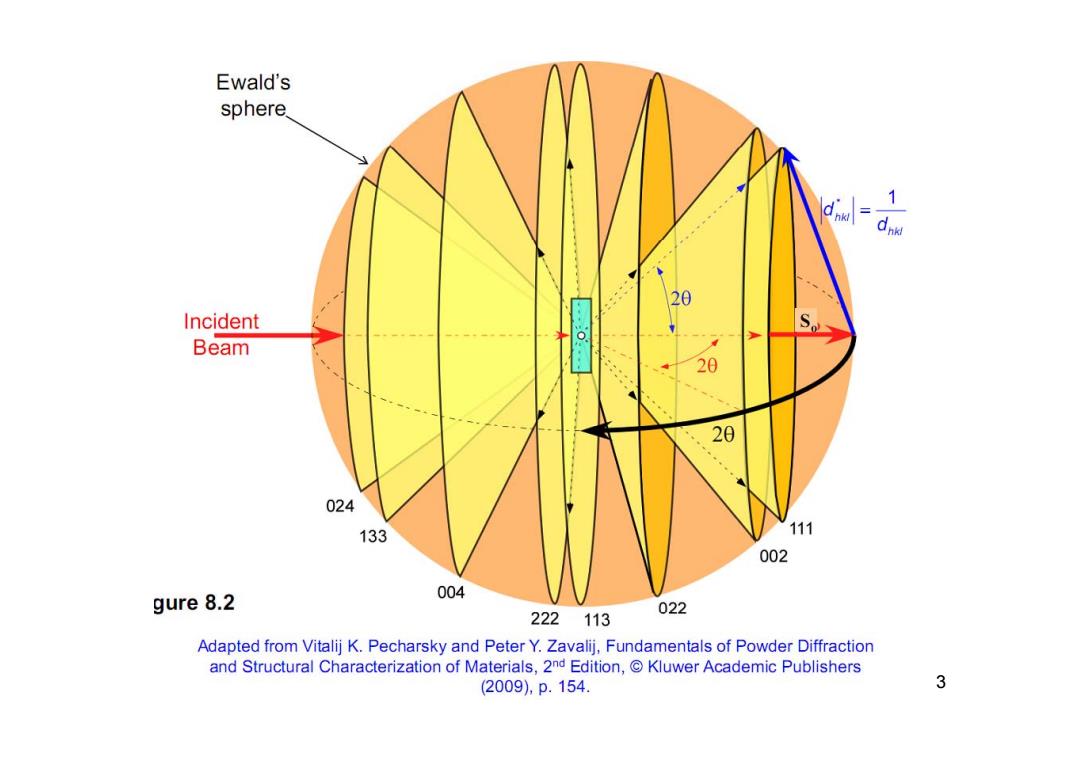
Ewald's sphere. 20 Incident Beam 20 20 024 133 111 002 gure 8.2 004 222113 022 Adapted from Vitalij K.Pecharsky and Peter Y.Zavalij,Fundamentals of Powder Diffraction and Structural Characterization of Materials,2nd Edition,Kluwer Academic Publishers (2009),p.154. 3
3

Types of diffraction X-ray:scattered by electron Electron:scattered by electrostatic potential Neutron:scattered by nuclei Diffraction pattern of X-ray Diffraction pattern of electron beam passing through Al foil beam passing through Al foil
Types of diffraction • X-ray: scattered by electron • Electron: scattered by electrostatic potential • Neutron: scattered by nuclei 4

Scattering of X-rays by atoms X-rays are scattered by electrons Electron positions are determined by atom positions 。Therefore: Size and shape of unit cell determine position of diffracted beam and Atom position determines the intensity of the diffracted beam 5
Scattering of X-rays by atoms • X-rays are scattered by electrons • Electron positions are determined by atom positions • Therefore: – Size and shape of unit cell determine position of diffracted beam and – Atom position determines the intensity of the diffracted beam 5