1.Optical principles of light microscopy Seeing is believing 100μm
1. Optical principles of light microscopy Seeing is believing
Optical/light microscopy The most widely used and the most fundamental measure to check the microstructure. ·Applications Quality control in materials processing Failure analysis of a component during service -Structure-property relationship establishment 2
Optical/light microscopy • The most widely used and the most fundamental measure to check the microstructure. • Applications – Quality control in materials processing – Failure analysis of a component during service – Structure-property relationship establishment 2

Optical principles Image formation and resolution ·Instrumentation Objective lens (numerical aperture, aberration) CCD/CMOS digital imaging system 3
Optical principles • Image formation and resolution • Instrumentation • Objective lens (numerical aperture, aberration) • CCD/CMOS digital imaging system 3

Refraction(折射) n=1 n>1 n=1 Refractive index(折 射率) Vacuum 1 。Air 1.0003 Water 1.333 Incident wave Reflected ● Cytoplasm 1.35-1.38? wave 9 ●Glycerol 1.475 (anhydrous) Refractive index n,=1 ●Immersion oil 1.515 Speed =c ●Fused silica 1.46 Optical glasses 1.5-1.9 Refractive index na Speed c/n Refracted wave 。Diamond 2.417 2/n Depends on wavelength and temperature →Snel'slaw: Mirror law: n Sin(0)=n2 Sin(02) 8.=6 4
Refraction (折射 ) • Refractive index ( 折 射率 ) 4
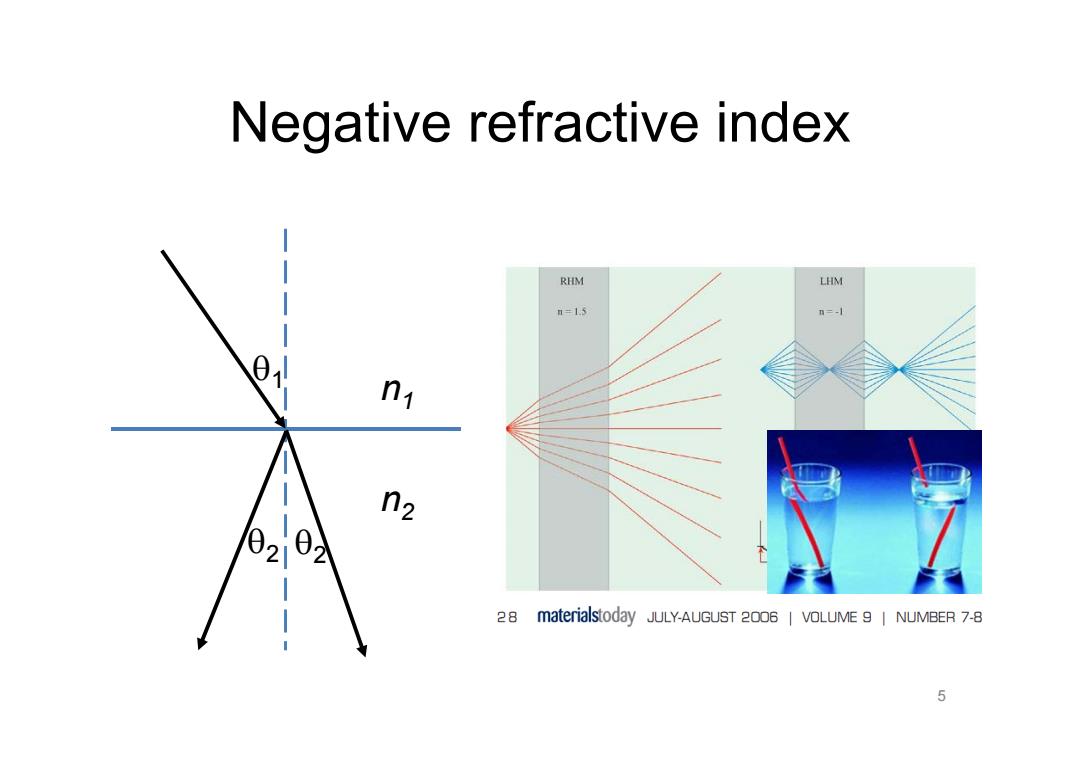
Negative refractive index RHM LHM =1.5 n=-1 n1 n2 28 materialstoday JULY-AUGUST 2006 VOLUME 9 NUMBER 7-8 5
Negative refractive index 5 2 1 2 n 1 n 2