
OPERATING SYSTEM SERVICES o One set of operating-system services provides functions that are helpful to the user: User interface-Almost all operating systems have a user interface UI) o Varies between Command-Line (CLI),Graphics User Interface (GUI),Batch Program execution-The system must be able to load a program into memory and to run that program,end execution,either normally or abnormally (indicating error) 1/O operations-A running program may require I/O,which may involve a file or an I/O device. File-system manipulation-The file system is of particular interest. Obviously,programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them,search them,list file Information,permission management
OPERATING SYSTEM SERVICES One set of operating-system services provides functions that are helpful to the user: User interface - Almost all operating systems have a user interface (UI) Varies between Command-Line (CLI), Graphics User Interface (GUI), Batch Program execution - The system must be able to load a program into memory and to run that program, end execution, either normally or abnormally (indicating error) I/O operations - A running program may require I/O, which may involve a file or an I/O device. File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management
COMPUTER-SYSTEM OPERATION o I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently. o Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type. o Each device controller has a local buffer. o CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers o I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller. o Device controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt
COMPUTER-SYSTEM OPERATION I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently. Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type. Each device controller has a local buffer. CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller. Device controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt
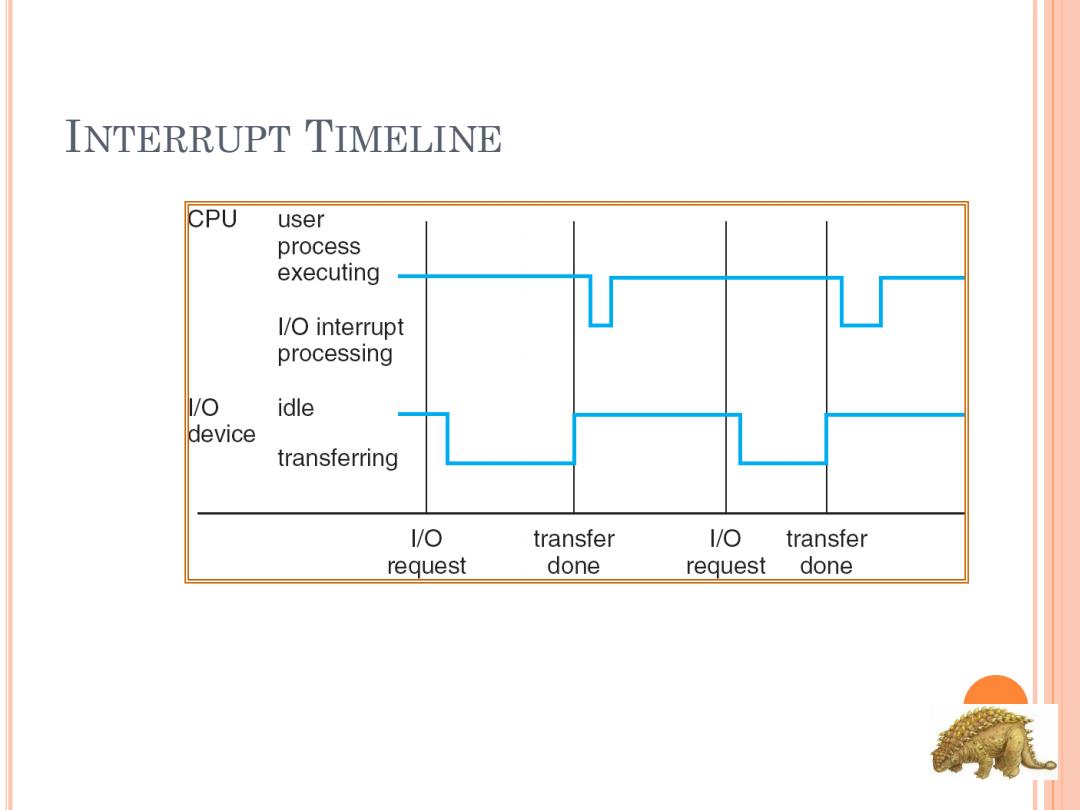
INTERRUPT TIMELINE CPU user process executing I/O interrupt processing l/o idle device transferring 1/o transfer 1/O transfer request done request done
INTERRUPT TIMELINE

COMMON FUNCTIONS OF INTERRUPTS o Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally,through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. o Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction. o Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. o A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request. o An operating system is interrupt driven
COMMON FUNCTIONS OF INTERRUPTS Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction. Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request. An operating system is interrupt driven

INTERRUPT HANDLING o The operating system preserves the state of the CPU by storing registers and the program counter. o Determines which type of interrupt has occurred: ·polling vectored interrupt system o Separate segments of code determine what action should be taken for each type of interrupt
INTERRUPT HANDLING The operating system preserves the state of the CPU by storing registers and the program counter. Determines which type of interrupt has occurred: polling vectored interrupt system Separate segments of code determine what action should be taken for each type of interrupt