
CHAPTER 8:MAIN MEMORY
CHAPTER 8: MAIN MEMORY

CHAPTER 8:MEmory mAnagement o Background o Swapping o Contiguous Memory allocation o Paging o Structure of the Page Table o Segmentation o Example:The Intel Pentium
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure of the Page Table Segmentation Example: The Intel Pentium

REVIEW o Memory Management ·Partition o fixed o variable ·Paging o http://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77fldcccda38376ba flfae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94
REVIEW Memory Management Partition fixed variable Paging http://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77f1dcccda38376ba f1fae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94

PAGING 0 Logical address space of a process can be noncontiguous;process is allocated physical memory whenever the latter is available o Divide physical memory into fixed-sized blocks called frames(size is power of 2,between 512 bytes and 8,192 bytes) o Divide logical memory into blocks of same size called pages o Keep track of all free frames o To run a program of size n pages,need to find n free frames and load program o Set up a page table to translate logical to physical addresses o Internal fragmentation
PAGING Logical address space of a process can be noncontiguous; process is allocated physical memory whenever the latter is available Divide physical memory into fixed-sized blocks called frames (size is power of 2, between 512 bytes and 8,192 bytes) Divide logical memory into blocks of same size called pages Keep track of all free frames To run a program of size n pages, need to find n free frames and load program Set up a page table to translate logical to physical addresses Internal fragmentation
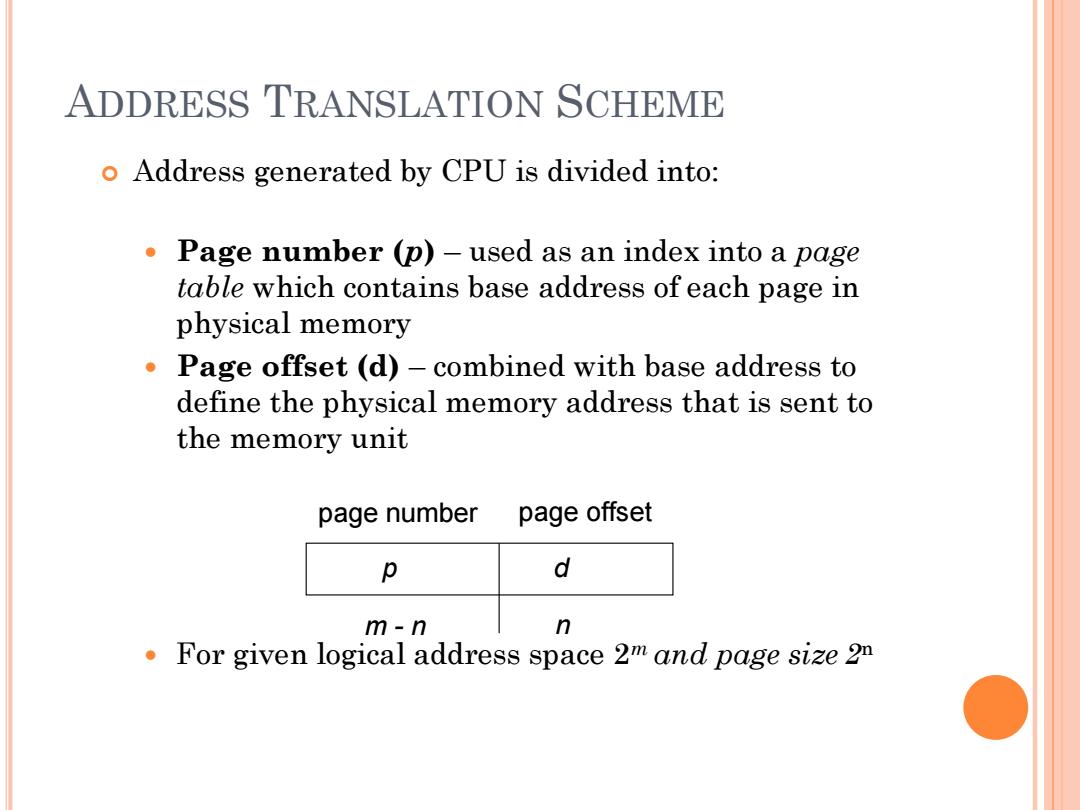
ADDRESS TRANSLATION SCHEME o Address generated by CPU is divided into: Page number (p)-used as an index into a page table which contains base address of each page in physical memory Page offset (d)-combined with base address to define the physical memory address that is sent to the memory unit page number page offset p d m-n n For given logical address space 2m and page size 2n
ADDRESS TRANSLATION SCHEME Address generated by CPU is divided into: Page number (p) – used as an index into a page table which contains base address of each page in physical memory Page offset (d) – combined with base address to define the physical memory address that is sent to the memory unit For given logical address space 2m and page size 2 n page number page offset p d m - n n