How to obtain 3D information? ●Cameras-2D ·Range sensors-3D 3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 6
3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 6 How to obtain 3D information? ⚫ Cameras-2D ⚫ Range sensors-3D

Challenges Obtain 3D information for tasks in a 3D world. .2D-to-3D reconstruction from a camera 3D directly-laser range sensor,kinect sensor ●Novel sensors Camera array/multiple camera One pixel camera light field camera 3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 7
3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 7 Challenges ⚫ Obtain 3D information for tasks in a 3D world. ⚫ 2D-to-3D reconstruction from a camera ⚫ 3D directly— laser range sensor, kinect sensor ⚫ Novel sensors ⚫ Camera array/ multiple camera ⚫ One pixel camera ⚫ light field camera
2D-to-3D reconstruction (feature based method) Camera (perspective projection) Features-extraction and correspondences Methods One-image method Two-image (Stereo)method Three-image method ●N-image method ·Bundle adjustment Kalman filter 3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 8
3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 8 2D-to-3D reconstruction (feature based method) ⚫ Camera (perspective projection) ⚫ Features-extraction and correspondences ⚫ Methods ⚫ One-image method ⚫ Two-image (Stereo) method ⚫ Three-image method ⚫ N-image method ⚫ Bundle adjustment ⚫ Kalman filter
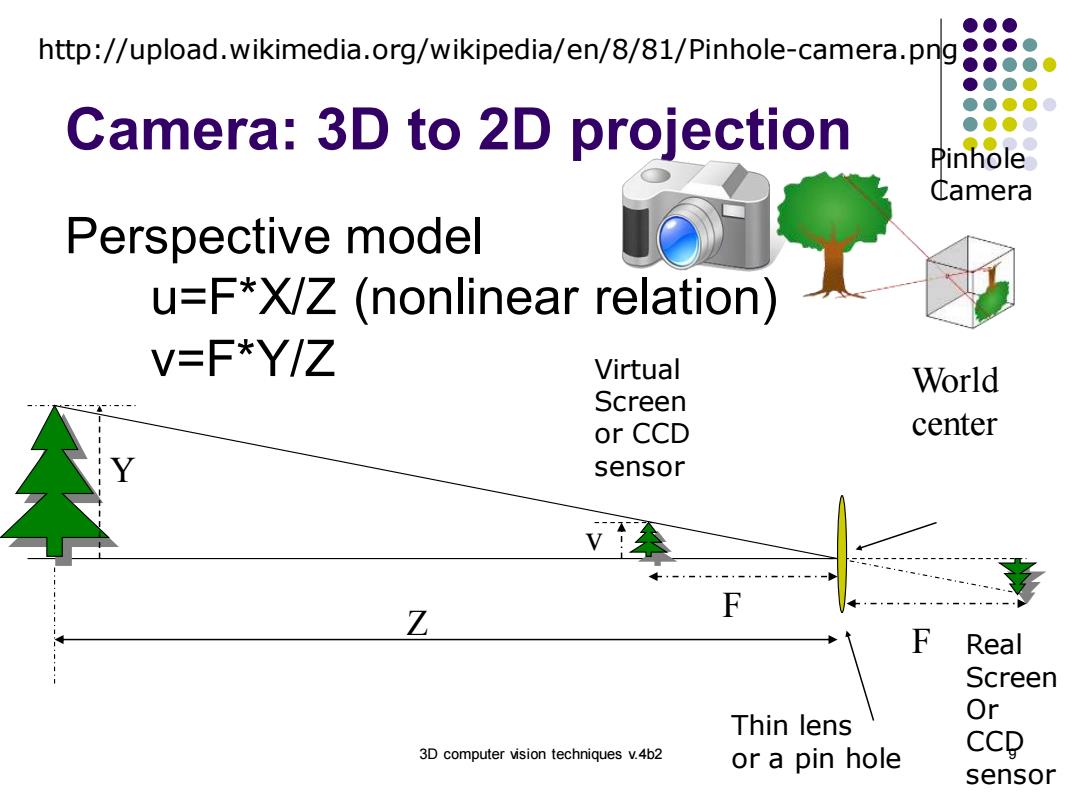
●●● http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/8/81/Pinhole-camera.png Camera:3D to 2D projection Pinhole ①amera Perspective model u=F*X/Z(nonlinear relation) V=F*Y/Z Virtual World Screen or CCD center sensor Z F F Real Screen Thin lens Or 3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 or a pin hole CCD sensor
3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 9 Camera: 3D to 2D projection Perspective model u=F*X/Z (nonlinear relation) v=F*Y/Z F Z Y v World center F Thin lens or a pin hole Virtual Screen or CCD sensor Real Screen Or CCD sensor Pinhole Camera http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/8/81/Pinhole-camera.png
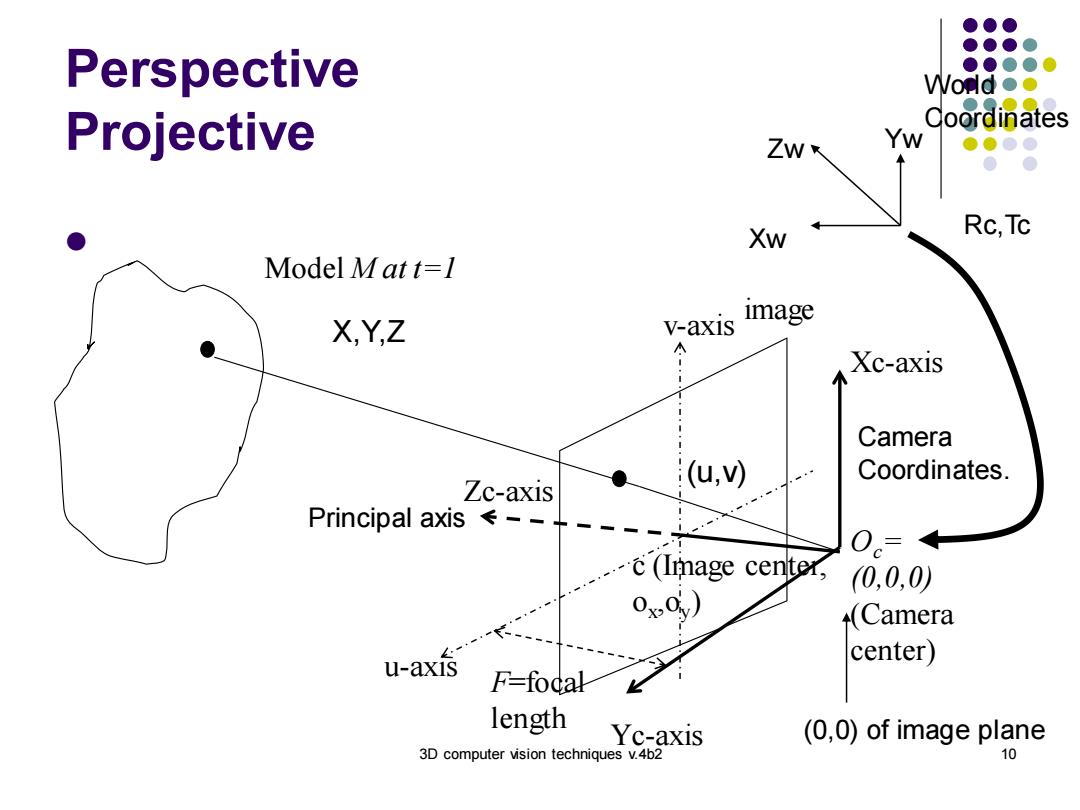
Perspective Womd●● Projective Coordinates Zw Yw Xw Rc,Tc Model Matt=l V-axIs image XYZ A Xc-axis Camera Coordinates. Zc-axis (u,V) Principal axis←---- 0= (Image center, 0,0,0) 0x0) (Camera “1 center) u-axis F-focal length Yc-axis (0,0)of image plane 3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 10
3D computer vision techniques v.4b2 10 Perspective Projective ⚫ Model M at t=1 c (Image center, ox ,oy ) F=focal length image Oc= (0,0,0) (Camera center) Xc-axis Zc-axis Yc-axis v-axis u-axis X,Y,Z (u,v) (0,0) of image plane Camera Coordinates. World Coordinates Zw Yw Xw Rc,Tc Principal axis