
Introduction Existing Methods Data-Dependent Methods Hash functions are learned from a given training dataset (learning to hash) Relatively short codes Seminal papers:(Salakhutdinov and Hinton,2007,2009;Torralba et al., 2008;Weiss et al.,2008) Two categories: 。Unimodal 。Supervised methods given the labels yi or triplet (xi,xj,x) Unsupervised methods Multimodal 。Supervised methods Unsupervised methods 日卡三4元,互Q0 Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lwj) Learning to Hash LAMDA,CS.NJU 11 /43
Introduction Existing Methods Data-Dependent Methods Hash functions are learned from a given training dataset (learning to hash). Relatively short codes Seminal papers: (Salakhutdinov and Hinton, 2007, 2009; Torralba et al., 2008; Weiss et al., 2008) Two categories: Unimodal Supervised methods given the labels yi or triplet (xi , xj , xk) Unsupervised methods Multimodal Supervised methods Unsupervised methods Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lwj) Learning to Hash LAMDA, CS, NJU 11 / 43
Introduction Existing Methods (Unimodal)Unsupervised Methods No labels to denote the categories of the training points. oPCAH:principal component analysis. o SH:eigenfunctions computed from the data similarity graph(Weiss etal.,2008). ITQ:orthogonal rotation matrix to refine the initial projection matrix learned by PCA(Gong and Lazebnik,2011). AGH:graph-based hashing (Liu et al.,2011). IsoHash:projected dimensions with isotropic variances(Kong and Li, 2012b). DGH:discrete graph hashing (Liu et al.,2014) o etc. 日卡三4元,互Q0 Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lvj) Learning to Hash LAMDA,CS.NJU 12/43
Introduction Existing Methods (Unimodal) Unsupervised Methods No labels to denote the categories of the training points. PCAH: principal component analysis. SH: eigenfunctions computed from the data similarity graph (Weiss et al., 2008) . ITQ: orthogonal rotation matrix to refine the initial projection matrix learned by PCA (Gong and Lazebnik, 2011) . AGH: graph-based hashing (Liu et al., 2011). IsoHash: projected dimensions with isotropic variances (Kong and Li, 2012b). DGH: discrete graph hashing (Liu et al., 2014) etc. Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lwj) Learning to Hash LAMDA, CS, NJU 12 / 43
Introduction Existing Methods (Unimodal)Supervised(semi-supervised)Methods Class labels or pairwise constraints: SSH:semi-supervised hashing(SSH)exploits both labeled data and unlabeled data for hash function learning(Wang et al.,2010a,b). MLH:minimal loss hashing(MLH)based on the latent structural SVM framework(Norouzi and Fleet,2011). KSH:kernel-based supervised hashing (Liu et al.,2012) LDAHash:linear discriminant analysis based hashing (Strecha et al., 2012) o LFH:supervised hashing with latent factor models(Zhang et al., 2014) o etc. Triplet-based methods: oHamming distance metric learning (HDML)(Norouzi et al.,2012) Column generation base hashing(CGHash)(Li et al.,2013) Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lvj) Learning to Hash LAMDA,CS.NJU 13/43
Introduction Existing Methods (Unimodal) Supervised (semi-supervised) Methods Class labels or pairwise constraints: SSH: semi-supervised hashing (SSH) exploits both labeled data and unlabeled data for hash function learning (Wang et al., 2010a,b). MLH: minimal loss hashing (MLH) based on the latent structural SVM framework (Norouzi and Fleet, 2011). KSH: kernel-based supervised hashing (Liu et al., 2012) LDAHash: linear discriminant analysis based hashing (Strecha et al., 2012) LFH: supervised hashing with latent factor models (Zhang et al., 2014) etc. Triplet-based methods: Hamming distance metric learning (HDML) (Norouzi et al., 2012) Column generation base hashing (CGHash) (Li et al., 2013) Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lwj) Learning to Hash LAMDA, CS, NJU 13 / 43
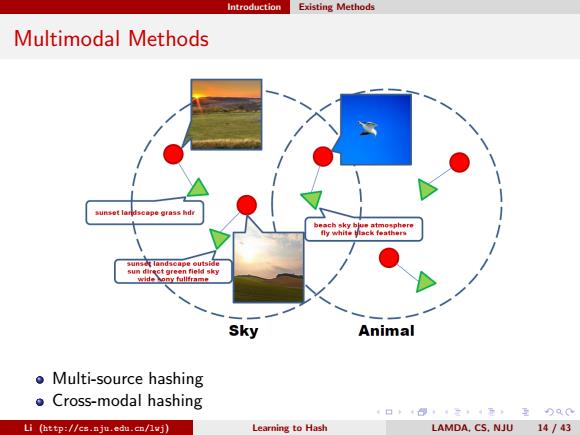
Introduction Existing Methods Multimodal Methods b带ch sky b带atmosph带rw fly white Back feathers sum4r气ct green角old sky sky Animal o Multi-source hashing ●Cross-modal hashing 口卡得三·4元互Q0 Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lvj) Learning to Hash LAMDA,CS.NJU 14 /43
Introduction Existing Methods Multimodal Methods Multi-source hashing Cross-modal hashing Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lwj) Learning to Hash LAMDA, CS, NJU 14 / 43