
Plasticity(可塑性)of jaw bone >Once formed,bone undergoes a process termed remodelling that involves break down(resorption)and build-up(synthesis) of bone;this occurs in micro scale throughout the skeleton. >Remodelling of jaw bone (especially alveolar bone)is most active among systematic skeleton
❖ Plasticity (可塑性) of jaw bone ➢Remodelling of jaw bone (especially alveolar bone) is most active among systematic skeleton. ➢Once formed, bone undergoes a process termed remodelling that involves break down (resorption) and build-up (synthesis) of bone; this occurs in micro scale throughout the skeleton
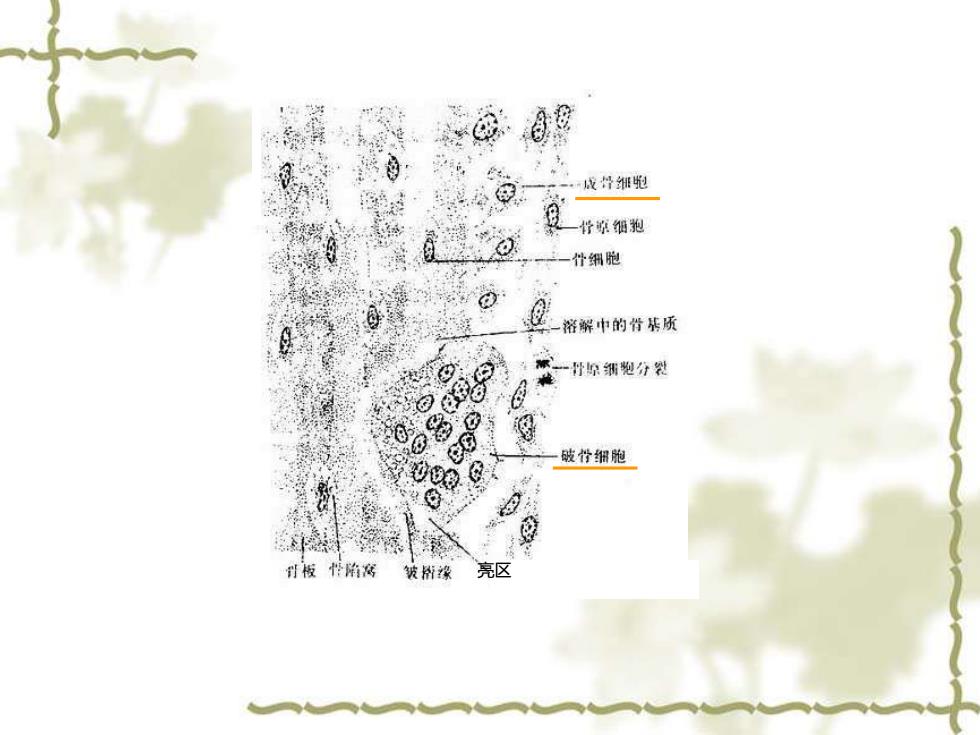
成骨细跑 竹鲸细抱 什细跑 溶解中的背基质 一野综细塑分裂 破柠细胞 背板性陷窝 皱州豫 亮区
亮区

Resistance of cementum to pressure >There is only deposition not resorption of cementum in physiological condition. >The root's outer layers,the cementoblasts,and the outer uncalcified cementum(precementum or cementoid)can protect cementum from resorption.These layers might contain noncollagenic materials,eg,the cells themselves, that possess potent anticollagenase properties
❖ Resistance of cementum to pressure ➢There is only deposition not resorption of cementum in physiological condition. ➢The root’s outer layers, the cementoblasts, and the outer uncalcified cementum (precementum or cementoid) can protect cementum from resorption. These layers might contain noncollagenic materials, eg, the cells themselves, that possess potent anticollagenase properties
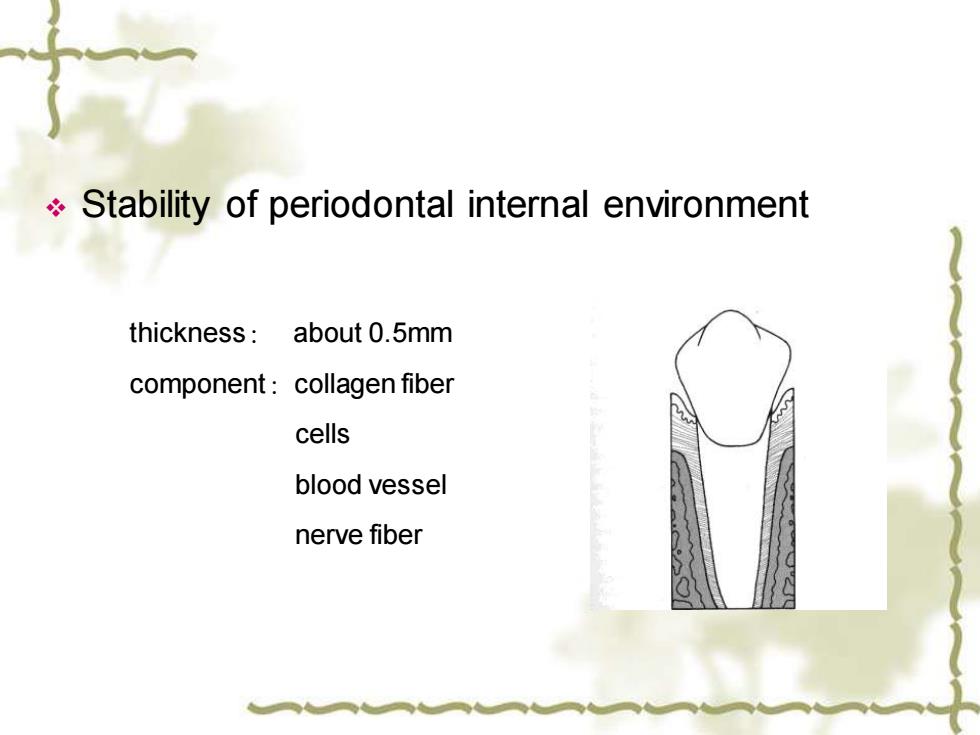
Stability of periodontal internal environment thickness:about 0.5mm component:collagen fiber cells blood vessel nerve fiber
❖ Stability of periodontal internal environment thickness: about 0.5mm component:collagen fiber cells blood vessel nerve fiber