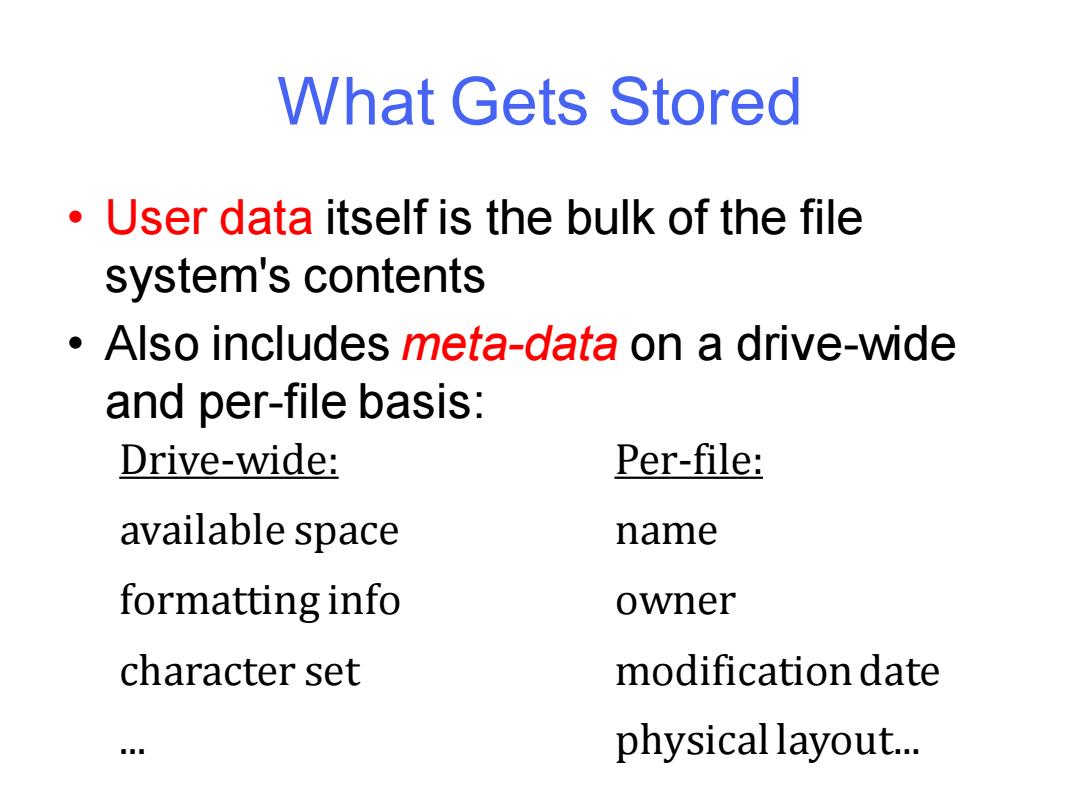
What Gets Stored User data itself is the bulk of the file system's contents Also includes meta-data on a drive-wide and per-file basis: Drive-wide: Per-file: available space name formatting info owner character set modification date physical layout
What Gets Stored • User data itself is the bulk of the file system's contents • Also includes meta-data on a drive-wide and per-file basis: Drive-wide: available space formatting info character set ... Per-file: name owner modification date physical layout

High-Level Organization ·Files are organized in a"tree”structure made of nested directories ·One directory acts as the“root'" ·links”(symlinks,shortcuts,etc)provide simple means of providing multiple access paths to one file ·Other file systems can be“mounted"and dropped in as sub-hierarchies (other drives, network shares)
High-Level Organization • Files are organized in a “tree” structure made of nested directories • One directory acts as the “root” • “links” (symlinks, shortcuts, etc) provide simple means of providing multiple access paths to one file • Other file systems can be “mounted” and dropped in as sub-hierarchies (other drives, network shares)

Low-Level Organization (1/2) File data and meta-data stored separately File descriptors meta-data stored in inodes Large tree or table at designated location on disk Tells how to look up file contents Meta-data may be replicated to increase system reliability
Low-Level Organization (1/2) • File data and meta-data stored separately • File descriptors + meta-data stored in inodes – Large tree or table at designated location on disk – Tells how to look up file contents • Meta-data may be replicated to increase system reliability

Low-Level Organization(2/2) ·“Standard"”read-write medium is a hard drive (other media:CDROM,tape,... Viewed as a sequential array of blocks Must address ~1 KB chunk at a time ·Tree structure is“flattened"into blocks Overlapping reads/writes/deletes can cause fragmentation:files are often not stored with a linear layout -inodes store all block ids related to file
Low-Level Organization (2/2) • “Standard” read-write medium is a hard drive (other media: CDROM, tape, ...) • Viewed as a sequential array of blocks • Must address ~1 KB chunk at a time • Tree structure is “flattened” into blocks • Overlapping reads/writes/deletes can cause fragmentation: files are often not stored with a linear layout – inodes store all block ids related to file

Fragmentation A B C (free space) A B C A (free space) A (free space) C A (free space) A D C A D (free)
Fragmentation A B C (free space) A B C A (free space) A (free space) C A (free space) A D C A D (free)